mRNA vaccine: Only one dose can resist HPV-related tumors
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
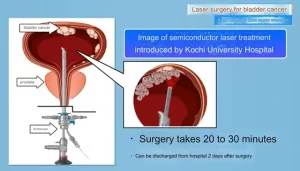
- Kochi University pioneers outpatient bladder cancer treatment using semiconductor lasers
- ASPEN 2024: Nutritional Therapy Strategies for Cancer and Critically Ill Patients
- Which lung cancer patients can benefit from neoadjuvant immunotherapy?
- Heme Iron Absorption: Why Meat Matters for Women’s Iron Needs
- “Miracle Weight-loss Drug” Semaglutide Is Not Always Effective
mRNA vaccine: Only one dose can resist HPV-related tumors
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
mRNA vaccine: Only one dose can resist HPV-related tumors, and the effect is better than DNA or recombinant protein vaccines.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common gynecological malignancies.
Clinical studies have shown that human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, especially the persistent infection of high-risk HPV, is an important cause of cervical precancerous lesions and cervical cancer.
The development and vaccination of HPV vaccine is very important to reduce the incidence of cervical cancer.
Real-world data also show that HPV vaccination significantly reduces cervical cancer incidence.
For example, the free HPV vaccination program in the UK has almost completely eliminated cervical cancer in women born after 1 September 1995.
In addition, HPV infection can not only cause cervical cancer in women , but also genital warts , anal cancer and other diseases that can affect both men and women.
HPV6 and HPV11 cause about 90% of genital warts, and HPV16 and HPV18 cause about 70% of genital warts.
Cervical and anal cancer. Therefore, many countries vaccinate both males and females against HPV at the same time.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, mRNA vaccines have been brilliant and have achieved unprecedented development.
The enormous potential of this new form of vaccine is also driving scientists to develop potent mRNA vaccines against other infectious diseases, as well as cancer.
Recently, researchers from the University of Sao Paulo, the University of Pennsylvania, Acuitas, and BioNTech jointly published a paper entitled: Single immunizations of self-amplifying or non-replicating mRNA-LNP vaccines control HPV-associated tumors in mice in the journal Science Translation Medicine Research Papers.
The study tested the immunogenicity and therapeutic efficacy of three different HPV mRNA vaccines in an HPV-induced mouse tumor model.
The results show that a single dose of HPV mRNA vaccine can induce a strong CD8+ T cell response and exert a strong anti-tumor effect, which is better than HPV recombinant protein vaccine and HPV DNA vaccine.

mRNA vaccines can be divided into non-replicating mRNA (nr-mRNA) vaccines and self-replicating mRNA (sa-mRNA) vaccines.
Expression levels of nr-mRNA vaccine-encoded antigens decrease over time. In contrast, sa-mRNA adds a replicase sequence from an alphavirus, which can replicate itself after entering the cell, thereby prolonging the time for expressing the antigen and reducing the dosage.
In addition, nr-mRNA vaccines can be divided into two types. One is composed of unmodified mRNA and is highly pro-inflammatory.
These strong inflammatory responses may favor the activation of CD8+ T cells, which play a key role in the anti-tumor response, but strong inflammatory responses may also lead to adverse events.
The other is composed of modified mRNA, which can reduce the inflammatory response and enhance the efficiency of mRNA translation.

Comparison of translation efficiencies of three mRNA vaccines (sa-mRNA, unmodified nr-mRNA, and modified nr-mRNA)
These three mRNA vaccine platforms (sa-mRNA, unmodified nr-mRNA, and modified nr-mRNA) have been extensively tested in animal models and found to induce potent immune responses against various pathogens and tumor types.
It is worth mentioning that mRNA vaccines have successfully treated HPV-related tumors in preclinical studies. In addition, an ongoing phase 1/2 clinical trial for HPV-16 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is also treated with mRNA-encoded anti-CD40 (NCT03418480) .
In this latest study, the research team used these three mRNA vaccine platforms to generate a chimeric vaccine encoding a fusion of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) glycoprotein D (gD) and HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein (E7). Protein-based mRNA vaccines are also delivered using lipid nanoparticles (LNP) .
Next, on the basis of experimental HPV-related tumor models that have been widely studied, the research team conducted a detailed comparative analysis of the induced immune responses and therapeutic effects of three mRNA vaccines encoding the same target antigen.
 Three mRNA vaccines all have potent antitumor effects
Three mRNA vaccines all have potent antitumor effects
The findings showed that any of the three gDE7 mRNA vaccines, following a single, low-dose vaccination, induced activation of E7-specific CD8+ T cells, generated memory T cell responses capable of preventing tumor recurrence, and eradicated different Subcutaneous tumors in the growth phase, and even late in growth can control tumor progression.
 A single immunization with gDE7 mRNA-LNP induces robust e7-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses
A single immunization with gDE7 mRNA-LNP induces robust e7-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses
More importantly, a single dose of gDE7 mRNA-LNP vaccine induced effective tumor protection in two different orthotopic mouse tumor models.
Finally, comparative studies showed that the three gDE7 mRNA-LNP vaccines were superior to gDE7 DNA vaccine and gDE7 recombinant protein vaccine in terms of immunogenicity and anti-tumor effect, and significantly improved the survival rate of tumor mouse models.
 Comparison of immunogenicity and antitumor efficacy of gDE7 mRNA-LNP vaccine, gDE7 DNA vaccine and gDE7 recombinant protein vaccine
Comparison of immunogenicity and antitumor efficacy of gDE7 mRNA-LNP vaccine, gDE7 DNA vaccine and gDE7 recombinant protein vaccine
In conclusion, this study demonstrated the immunogenicity and therapeutic efficacy of three different mRNA vaccines in an extensive comparative experiment, outperforming conventional DNA- and protein-based gDE7 vaccines.
These data support further evaluation of these mRNA vaccines in clinical trials, opening up exciting prospects for the clinical application of anti-tumor mRNA vaccines.
References :
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abn3464
mRNA vaccine: Only one dose can resist HPV-related tumors
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.