Can bariatric surgery really successfully reverse type 2 diabetes?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
- New Ocrevus Subcutaneous Injection Therapy Shows Promising Results in Multiple Sclerosis Treatmen
- Dutch Man Infected with COVID-19 for 613 Days Dies: Accumulating Over 50 Virus Mutations
Can bariatric surgery really successfully reverse type 2 diabetes?
Can bariatric surgery really successfully reverse type 2 diabetes? Compared with conventional drugs, surgery can also improve the patient’s overall metabolic level, reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, improve kidney function, and improve the quality of life.
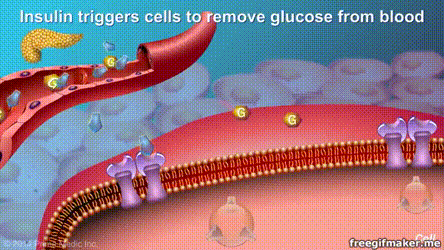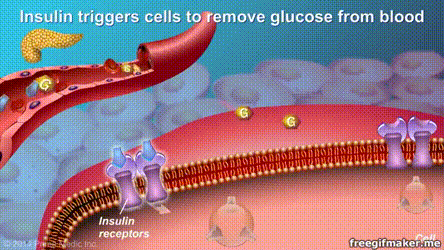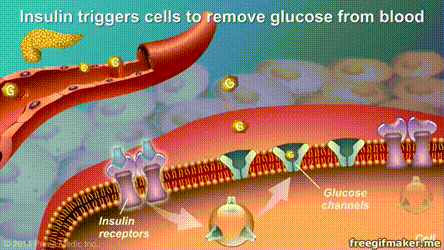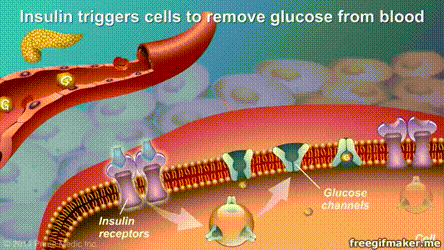
The results of randomized clinical trials with the longest follow-up time so far indicate that surgery may be more effective than medication and lifestyle interventions in the long-term control of severe type 2 diabetes.
Recently, “The Lancet” published an important paper on the progress of diabetes treatment online. A study with a follow-up of up to 10 years showed that for patients with severe type 2 diabetes, metabolic surgery can be more effective and long-term control of the disease than drugs and lifestyle interventions. , And more than 1/3 of surgical patients achieved long-term relief. This means that the “cure” of type 2 diabetes can be achieved.
Metabolic surgery Cure type 2 diabetes
- Question one: The origin of surgical treatment of diabetes?
- Question two: Why is the surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes effective?
- Question three: Compared with conventional drugs, what are the advantages of surgery?
- Question four: What conditions need to be met for surgery to “cure” diabetes?
The origin of surgical treatment of diabetes?
Surgical treatment of diabetes began in the 1980s. A doctor in the United States accidentally discovered that after bariatric surgery, the blood sugar level of obese patients with type 2 diabetes dropped significantly, and eventually stopped all blood sugar lowering drugs.
With in-depth research, more and more examples have proved that bariatric surgery can significantly reduce hyperglycemia in diabetic patients, and the treatment effect is better than traditional drug treatment.
Thirty years later, surgical treatment of diabetes has finally gained recognition and is widely promoted worldwide.
24791612598471488
Why is the surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes effective?
Surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes is effective mainly because: 1. K cells distributed in the gastrointestinal tract are stimulated by food to secrete insulin resistance factors, which makes the body produce insulin resistance; 2. Pancreatic islet cells are damaged and apoptosis under the action of insulin resistance factors.
The uniqueness of gastric bypass surgery is that it changes the physiological flow of food to complete it, and volume reduction also plays a role. After the operation, the insulin resistance of the patient’s body is eliminated, and the flow of food after the operation can promote the secretion of insulin in the patient’s body, reduce the apoptosis and proliferation of islet cells, restore the function of the islets, and cure the diabetes.
After the patient’s blood sugar became normal, a series of complications were well recovered. For example, retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic dermatitis, diabetic sexual dysfunction, high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia, etc. have gradually recovered. The occurrence of serious complications is eliminated, and the occurrence of disability and death is avoided.
18921612598471680
Compared with conventional drugs, what are the advantages of surgery?
Researchers from King’s College London and Agostino Gemelli IRCCS of Fondazione Policlinico University in Rome, Italy reported the 10-year results of the trial, which compared surgical interventions that interfere with metabolism with traditional medicine and lifestyle.
The study involved 60 patients with advanced type 2 diabetes who were treated in a major academic hospital in Rome, Italy. The patients were randomized to receive medication plus lifestyle intervention or metabolic intervention surgery (gastric bypass or biliary-pancreatic transfer). At the beginning of the study, all patients had serious illnesses, had poorly controlled blood sugar levels, and had a history of diabetes for more than 5 years.
The results of the study showed that during the 10-year study period, 37.5% of patients undergoing surgical treatment could maintain non-diabetic blood glucose levels without deliberately controlling glucose. In 2009, the American Diabetes Association defined the “cure” of diabetes as a state of remission that lasted more than five years.
Professor Francesco Rubino, the senior author of the report, chairman of weight loss and metabolic surgery at King’s College London, and consultant surgeon at King’s College Hospital in London, said: “The findings of this study provide the most mature and best There is strong scientific evidence. Type 2 diabetes is a curable disease, not inevitably progressive and irreversible. In addition to traditional diabetes treatment, metabolic intervention surgery may be our best solution to the disease.”
Compared with conventional drugs, surgery can also improve the patient’s overall metabolic level, reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, improve kidney function, and improve the quality of life. It is worth noting that the incidence of diabetes-related complications (including adverse events of the heart, kidneys and nervous system) in patients undergoing surgery has been significantly reduced. Metabolic surgery also reduces the use of drugs, including drugs for diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
The study investigated the early and long-term safety of different intervention strategies. Compared with patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, patients receiving conventional drug treatment have a significantly higher chance of serious adverse events.
The report’s lead author, Professor Gertrude Mingrona, Professor of Medicine at the Roman Catholic University and Professor of Diabetes and Nutrition at King’s College London, said: “These data confirm the following view: Surgery can be a form of treatment for diabetes. Patients with cost-effective treatment types. There is now ample evidence that metabolic surgery should be regarded as the main treatment option for patients with severe type 2 diabetes and obesity.”
Previous studies have shown that weight loss or bariatric surgery can help very severely obese patients with long-term relief of their diabetes problems. However, most patients undergoing traditional bariatric surgery usually have mild or recent onset diabetes. This trial shows the potential efficacy of metabolic surgery for critically ill patients.
Diabetes is one of the main causes of mortality and morbidity in Western society, and it significantly increases the risk of severe COVID-19 infection and the mortality rate of the virus. Although there is evidence that surgery can quickly and significantly improve diabetes, in most countries, less than 1% of surgical candidates can undergo metabolic intervention surgery. In addition, during the current COVID-19 pandemic, metabolic intervention surgery in many hospitals has been suspended, and the waiting time is often longer than other more important surgical operations.
Professor Rubino added: “Metabolic intervention surgery is arguably the most effective treatment for type 2 diabetes, and it can save lives for many patients. It should be given priority during and after the pandemic.”
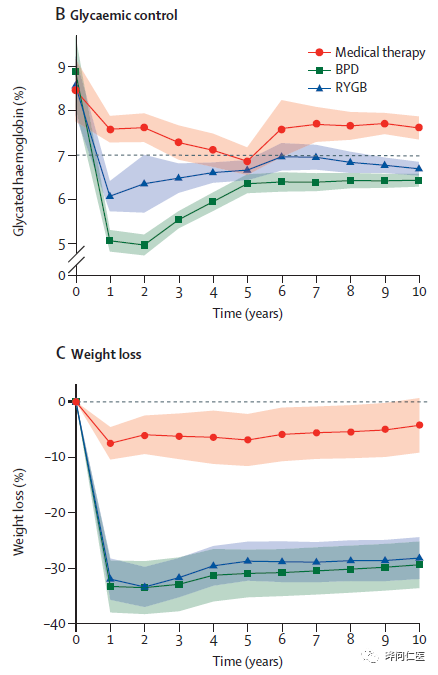
▲Over time, blood glucose levels (Figure B) and weight changes (Figure C) of patients in the drug treatment (red line), gastric bypass surgery (RYGB, blue line) and biliary-pancreatic bypass (BPD, green line) group (Figure B) Picture source: reference [1])
What are the conditions for surgical treatment?
1. The course of type 2 diabetes is ≤15 years, and the pancreatic islets still have a certain function of insulin secretion.
2. The recommended age for surgery is 16 to 65 years old.
3. Meet the following indicators:
● BMI≥32.5, active surgery is recommended;
● 27.5≤BMI<32.5, surgery is recommended;
● 25≤BMI<27.5, it is difficult to control blood sugar after changing lifestyle and drug treatment, and it meets at least two metabolic syndrome components, or there are comorbidities, surgery should be carried out carefully.
BMI calculation method: body mass index (BMI) = weight (kg) ÷ height square (m²).
For example: a person’s height is 1.75 meters and weight is 68 kg, his BMI=68÷(1.75×1.75)=22.2 (kg/m²).
4. For patients with 25≤BMI<27.5, waist circumference ≥90 cm for men, waist circumference ≥85 cm for women, and reference imaging examinations, it indicates central obesity, which is what we commonly call “general belly” and “lifebuoy.
References:
Geltrude Mingrone, Simona Panunzi, Andrea De Gaetano, Caterina Guidone, Amerigo Iaconelli, Esmeralda Capristo, Ghassan Chamseddine, Stefan R Bornstein, Francesco Rubino. Metabolic surgery versus conventional medical therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: 10-year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 2021; 397 (10271): 293 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32649
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



