Targeting mitochondrial DNA to cut off the energy supply of cancer cells
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
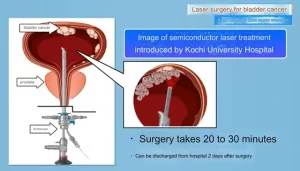
- Kochi University pioneers outpatient bladder cancer treatment using semiconductor lasers
- ASPEN 2024: Nutritional Therapy Strategies for Cancer and Critically Ill Patients
- Which lung cancer patients can benefit from neoadjuvant immunotherapy?
- Heme Iron Absorption: Why Meat Matters for Women’s Iron Needs
- “Miracle Weight-loss Drug” Semaglutide Is Not Always Effective
Nature: Targeting mitochondrial DNA to cut off the energy supply of cancer cells
Nature: Targeting mitochondrial DNA to cut off the energy supply of cancer cells. Nature: A new method of cancer treatment that targets mitochondrial DNA and cuts off the energy supply of cancer cells.
Mitochondria (mitochondrion) is the “energy factory” of the cell, which is equivalent to the “power plant” in the cell. There is a set of genetic material independent of the nucleus in the mitochondria-mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The length of human mitochondrial DNA is 16569bp. 37 genes, encoding 13 kinds of proteins, these proteins are involved in cell energy metabolism.
In human aging and a series of diseases (such as congenital metabolic diseases, neurodegeneration, and cancer, etc.), the expression changes of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) are involved, and the mutations of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) will directly cause dozens of types. Serious genetic disease.

In December 2020, a research team from Max Planck Institute in Germany and the University of Gothenburg in Sweden published a research paper entitled: Small-molecule inhibitors of human mitochondrial DNA transcription in Nature.
The research team designed an oral inhibitor that specifically targets mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Experiments in mice have shown that the inhibitor has a strong anti-tumor effect and slows tumor growth without affecting healthy cells. Experimental data shows that this inhibitor has great research value as a First in Class innovative anti-cancer drug.

Cancer cells not only need mitochondria to obtain energy, but also mitochondria to support the various structures required for their brutal division and reproduction.
Previous cancer treatment attempts that targeted mitochondria often resulted in serious side effects because mitochondria also played a key role in maintaining normal cell function.
Because cancer cells are splitting uncontrollably, they must continue to replicate to create new mitochondria.
Previous studies have found that rapidly dividing cells (such as cancer cells) rely heavily on mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) to form new functional mitochondria. Therefore, the research team no longer directly targets the existing mitochondria in the cell, but chooses to target mitochondria. DNA transcription, this transcription process is essential for the formation of new mitochondria and the production of energy.
The research team used a high-throughput recombinant in vitro transcription assay system to identify compounds that inhibit mitochondrial transcription, and discovered and improved a small molecule inhibitor called IMT1B (LDC203974), which can specifically target human mitochondrial RNA polymerase (POLRMT). ), thereby inhibiting mitochondrial transcription (IMT).
The research team conducted tests in various cancer cell lines and found that the inhibitor can cause about a third of the cell viability to drop significantly, and the small molecule inhibitor is not toxic to human peripheral blood mononuclear cells or human liver cells .

Molecular structure of IMT1B (LDC203974)

The research team further analyzed and revealed the mechanism of the inhibitor causing a cell energy crisis, and found that after the inhibitor targets mitochondrial DNA transcription, it significantly reduces the production of ATP in the mitochondria, which is the direct energy source of the cell.
The effect of in vitro experiments is remarkable. In order to further verify the effect of the inhibitor, the research team conducted experiments in mouse models of ovarian cancer and rectal cancer.

The experimental results showed that the tumor volume of the treated mouse model was significantly reduced. In addition, once a day of oral drug treatment, after four weeks of continuous treatment, there were no signs of liver or kidney toxicity, anemia or other serious side effects.

In general, this study shows that targeting mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a feasible cancer treatment strategy, proving that this novel cancer treatment method can play a significant role in animal models, and the research team said that it will further develop inhibitors For the treatment of human cancer.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org