AMG757 may become the first targeted drug for small cell lung cancer
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
AMG757 may become the first targeted drug for small cell lung cancer
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
AMG757 may become the first targeted drug for small cell lung cancer, relapsed, refractory, and PD1 resistance won in one fell swoop.
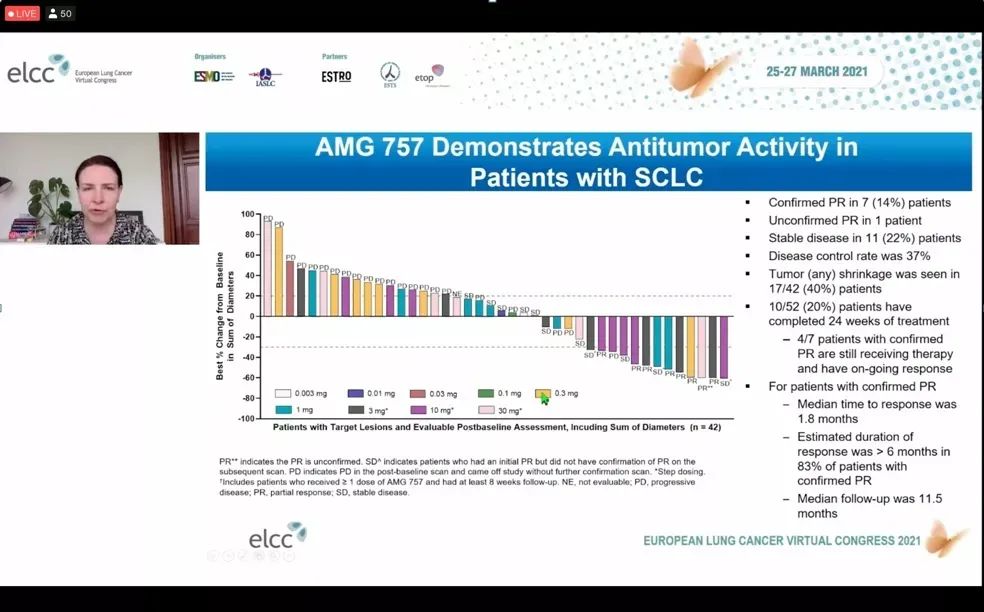
In terms of efficacy, the confirmed objective response rate (ORR) is 14%, and the disease control rate (DCR) is 37%.
SCLC is a refractory and poor prognosis subtype of lung cancer, accounting for about 15% of lung cancers. It is characterized by rapid growth and early spread. The vast majority of patients are already in stage IV or extensive stage (ES) at the time of diagnosis. .
The first-line standard chemotherapy regimen for ES-SCLC has limited efficacy, and the first-line immunization combination has shown good efficacy on SCLC.
However, with the successive withdrawal of O drugs and K drugs in SCLC indications, immunotherapy can be described as mixed. In terms of targeting, there are no approved drugs yet.
At the just-concluded European Lung Cancer Conference 2021 (ELCC Virtual 2021), AMG 757 demonstrated good efficacy and safety.
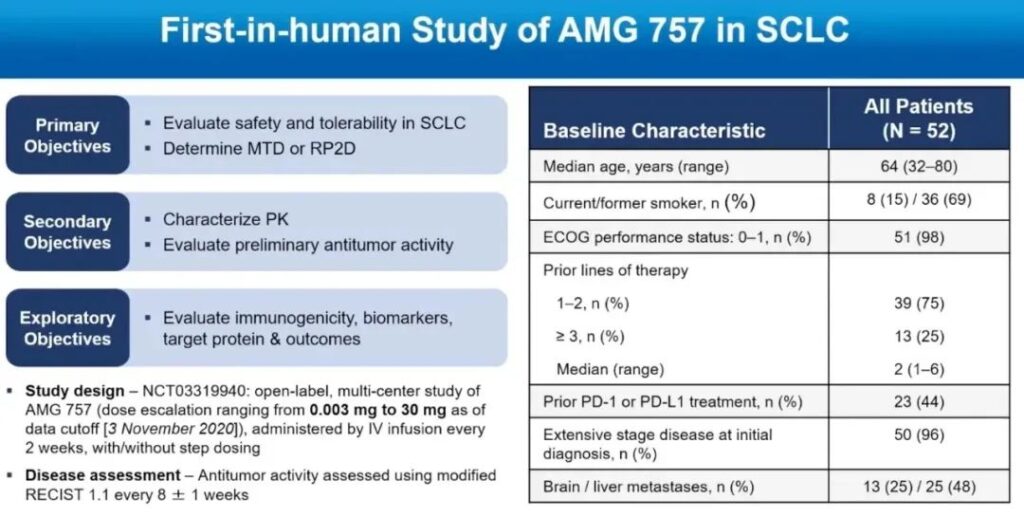
This multicenter, phase I study included 52 SCLC patients, all of whom had relapsed/refractory SCLC patients who received at least 1 line of platinum chemotherapy.
The median number of treatment lines was 2, and 98% of patients had an ECOG PS score of 0 or 1. 44% of patients had previously received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor treatment, 96% of patients had ES-SCLC at the initial diagnosis, 25% had brain metastases, and 48% had liver metastases.
The study used dose escalation (0.003-30 mg q2w nine dose groups). The primary endpoint is safety and the recommended dose for phase II.
The results show that:
In terms of efficacy, the confirmed objective response rate (ORR) is 14%, and the disease control rate (DCR) is 37%. Among the 7 patients with confirmed partial remission (PR), the median time to disease remission was 1.8 months. Among patients with a median follow-up of 11.5 months, 83% of patients had a duration of remission (DoR) greater than 6 month.

Further analysis showed that DLL3 high expression ORR was higher, reaching 38%.

The researcher of the study said: Although the study has set up 9 dose cohorts, the maximum tolerated dose of AMG 757 has not yet been reached, and the study is still going on to determine the phase II recommended dose.
In terms of safety, the incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAE) of grade ≥3 was 23%, the incidence of common TRAE cytokine release syndrome (CRS) was 44%, and the incidence of grade ≥3 CRS was 2%.
The incidence of grade 4 AEs was 8%, including pneumonia (n=1) and lymphopenia (n=3); 1 patient died of pneumonia. CRS has nothing to do with discontinuation or death of the patient.
About SCLC
The origin cells of SCLC are pulmonary neuroendocrine cells (PNEC). These PNECs have potential stem cells and damage repair under normal physiological conditions. The maintenance of this damage repair ability depends on a variety of signal pathways, including the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway And Notch pathway.
The Notch signaling pathway is mostly in an uncontrolled state in tumors, and affects tumor growth, tumor blood vessels and tumor immunity. Notch has four receptor expressions (Notch 1-4) and five ligand expressions (DLL1, DLL3, DLL4 and Jagged1, Jagged2).
Among them, the high expression of DLL3 in SCLC and neuroendocrine cells is an ideal target for SCLC. Amgen’s DLL3 target layout, in addition to AMG757, the CAR-T therapy AMG119 targeting DLL3 is also in Phase I clinical.


About AMG 757
AMG757 is a bispecific antibody targeting DLL3 and CD3. DLL3 is the ligand of Notch, and CD3 antigen is an important marker on the surface of T cells.
T lymphocyte activation is the basis of immune response and one of the hot targets. CD3 is one of the bispecific antibody targets in tumor targeted therapy.
This type of bispecific antibody is also called T cell-directed bispecific antibody.
The CD3 target binds to the CD3 indicated by the T cell and activates the T cell, DLL3 The target is bound to tumor cells, and AMG757 binds to SCLC and T respectively, so that T cells can accurately bind to tumor cells, enhance immune response, and promote tumor cell lysis.

Amgen’s blinatumomab double antibody is a BiTE form of bispecific antibody drug. It was approved by the US FDA in December 2014 for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and it also targets the CD19 antigen on the surface of tumor cells and the CD3 antigen on the surface of T cells.
BiTE has a small molecular weight and is easy to penetrate tumor tissues. It is low-dose, but it has a short half-life without Fc fragments. AMG757 uses Amgen’s new generation of bi-antibody platform HLE BiTE. Compared with the previous generation of BiTE platform, HLE BiTE molecule contains Fc with increased half-life.
In short, AMG 757 has shown a very good initial clinical effect. As the dose escalation study is further carried out, the optimal dose will be determined, and the Phase II clinical data is expected. As the most difficult to treat small cell lung cancer, it is also expected to usher in the first targeted drug.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org