Why do women not get prostate cancer?
- A Persistent Crisis: The Looming Specter of Drug Shortages in United States
- Rabies: The fatality rate nearly 100% once symptoms appear
- Human Brain Continues to Grow: Study Shows Increase in Size and Complexity
- CRISPR Genome Editing: From Molecular Principles to Therapeutic Applications
- Metformin Helps Immune System Better Recognize Cancer Cells
- Highlights of Prostate Cancer Research at the 2024 EAU Congress
Why do women not get prostate cancer?
Why do women not get prostate cancer? The incidence of prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer? Women also have prostate, Why is it only in men?

The prostate is the largest accessory gonad in men, the teacher in the anatomy class had told you that although women also have prostates, but women’s prostates have degenerated and do not have any function, let alone pathological changes.
Early screening can get the best treatment time. Screening items include: digital rectal examination, serum PSA examination (prostate specific antigen).
There may be many people who think that cancer is caused by bad luck, and more people are also saying that once they get cancer, they can only wait to die, because not only can they not afford the expensive treatment costs, but also because the cancer itself is fatal. of.
But in fact, many cancers can be detected at an early stage and active treatment can not only prolong life, but also save a lot of costs in treatment.
In recent years, prostate diseases have endangered men’s health, and many men have missed the opportunity for treatment because it is difficult to tell.
According to 2020, there will be 10.07 million new cancer cases in men worldwide. In addition to the high incidence of lung cancer in men, prostate cancer is the second most common cancer case.
Prostate cancer is the second largest male tumor in the world. According to statistics, there will be 1.41 million new cases of prostate cancer worldwide and 380,000 deaths in 2020.
Due to lack of knowledge of the prostate and poor living habits, prostate diseases are getting younger and younger.
In men, the prostate is located between the base of the penis and the bladder and surrounds the posterior urethra. People do not know about it because of its secret location.
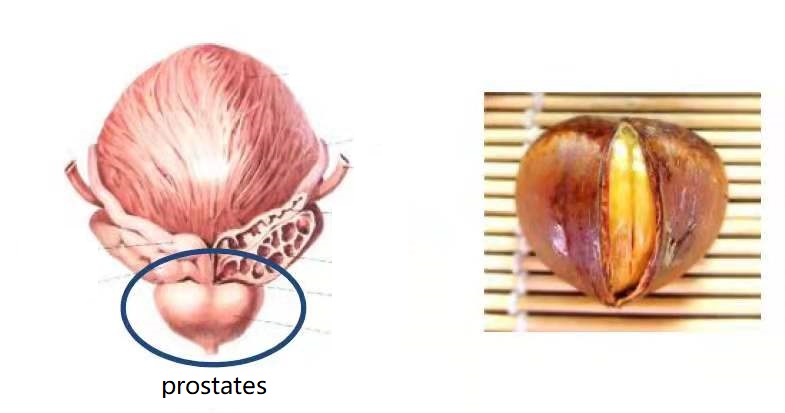
The role of the prostate:
- Secretion of prostate fluid is an important component of semen, why sperm activity and physiological functions play an important role in fertility.
- It is rich in 5α reductase, which can convert testosterone into more active dihydrotestosterone and maintain normal physiological functions of men.
- The prostate surrounds the male urethra and participates in the formation of the urethral sphincter, which can help men control normal urination and hold back urine.
- There are urethra and 2 ejaculatory ducts in the prostate parenchyma. When the muscles of the prostate and seminal vesicle glands contract, the substances in the vas deferens and seminal vesicle glands can enter the posterior urethra through the ejaculatory ducts to maintain the normal ejaculation function of men.
- There are clusters of nerves and blood vessels around the prostate, which can control the erection of the penis. However, if the nerves around the prostate are damaged due to diseases, it will cause erectile dysfunction in men.
In young men, acute and chronic prostatitis are prone to occur. According to statistics, about 50% of young men suffer from prostatitis.
For elderly men, although the incidence of prostatitis has decreased, 50% of prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer occur.
Cancer occurs because of the abnormal and disorderly growth of cells. When cancer cells lose the mutual restraint between normal cells, they no longer have the functions of normal cells.
Due to the abnormal metabolism of cancer cells, the cancer has spread, metastasized, and caused damage to other important organs of the human body. It will eventually cause the normal operation of the human body to be lost, and even lead to the death of the human body.
More than 90% of prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that occur in the glandular tissue of the prostate.
Sequence of development of prostate cancer
In the prostate → prostate capsule → invasion of seminal vesicle gland → metastasis to nearby lymph nodes → metastasis to bones and other organs
The other is small cell undifferentiated carcinoma, which is not in the prostate gland but in the neuroendocrine cells. It is a type of prostate cancer that has early metastasis and spread.
The incidence of prostate cancer is mostly in men over the age of 50, and the cause is mainly related to family heredity, sexual life and eating habits.
Although the obvious symptoms may not be seen in the early stage, as the tumor develops, there will be a sense of oppression and even metastasis.
Early warning signs of prostate cancer
Urination disorders:
As the tumor develops, the urethra is compressed, so dysuria occurs, such as thinning of the urine flow, crooked urine flow, bifurcation of the urine flow, frequent urination, urgency, painful urination, and incomplete urination.
In severe cases, urinary dripping or urinary retention may also occur.
However, these symptoms are easily confused with benign prostatic hyperplasia, and are prone to missed and misdiagnosed.
For prostate cancer, screening is currently the only effective way to detect prostate cancer early.
At present, nearly 90% of prostate cancer patients can be detected early through screening, and the 5-year survival rate can be as high as 90%.
Screening items include: digital rectal examination, serum PSA examination (prostate specific antigen)
If necessary, you can do a rectal and prostate B-ultrasound or prostate biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org