First discovery of interleukin IL-17D receptor
- Engineered Soybeans with Pig Protein: A Promising Alternative or Pandora’s Dish?
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS): A Tick-Borne Threat with High Mortality
- Why Isolating Bananas Extends Their Shelf Life?
- This common vitamin benefits the brain and prevents cognitive decline
- New report reveals Nestlé adding sugar to infant formula sold in poor countries
- Did Cloud Seeding Unleash a Deluge in Dubai?
First discovery of interleukin IL-17D receptor
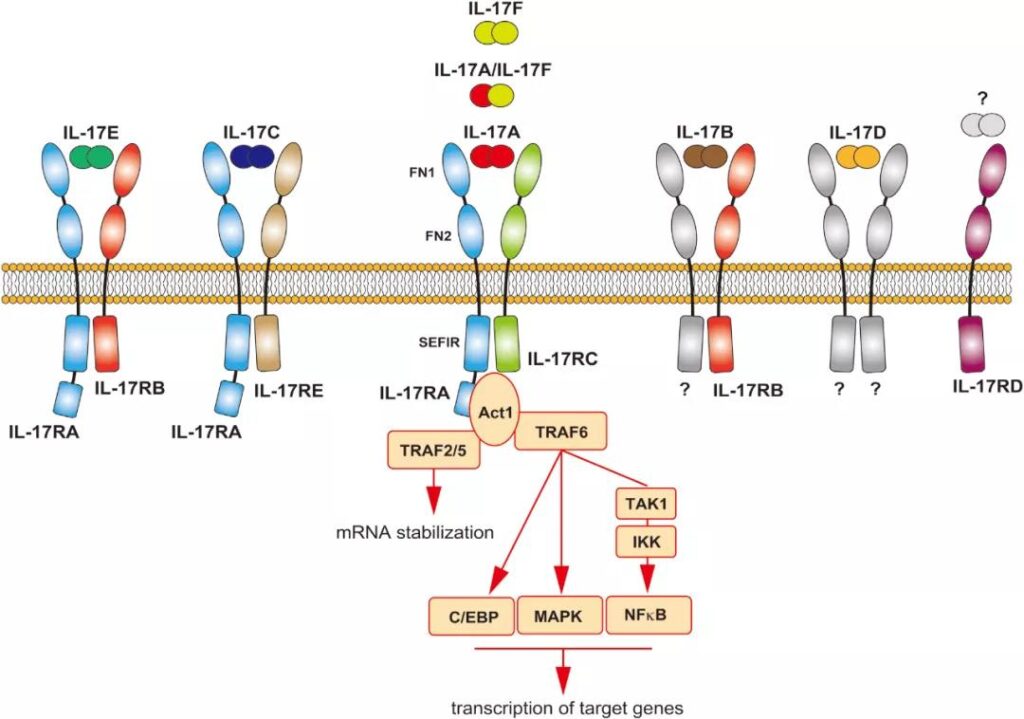
First discovery of interleukin IL-17D receptor. The IL-17 family consists of six members (including IL-17A, B, C, D, E, and F). IL-17D is the least understood member of the IL-17 family, and its receptor is not yet clear.
On April 13, 2021, the team of Academician Dong Chen from the School of Medicine of Tsinghua University published an online study titled Interleukin-17D regulates group 3 innate lymphoid cell function through its receptor CD93 (2) on Immunity. The study found that IL-17D derived from intestinal epithelial cells can play a key role in regulating the function of type III intrinsic lymphoid cells (ILC3s) and maintaining intestinal homeostasis by binding to its receptor CD93.
What are the physiological functions of IL-17D?
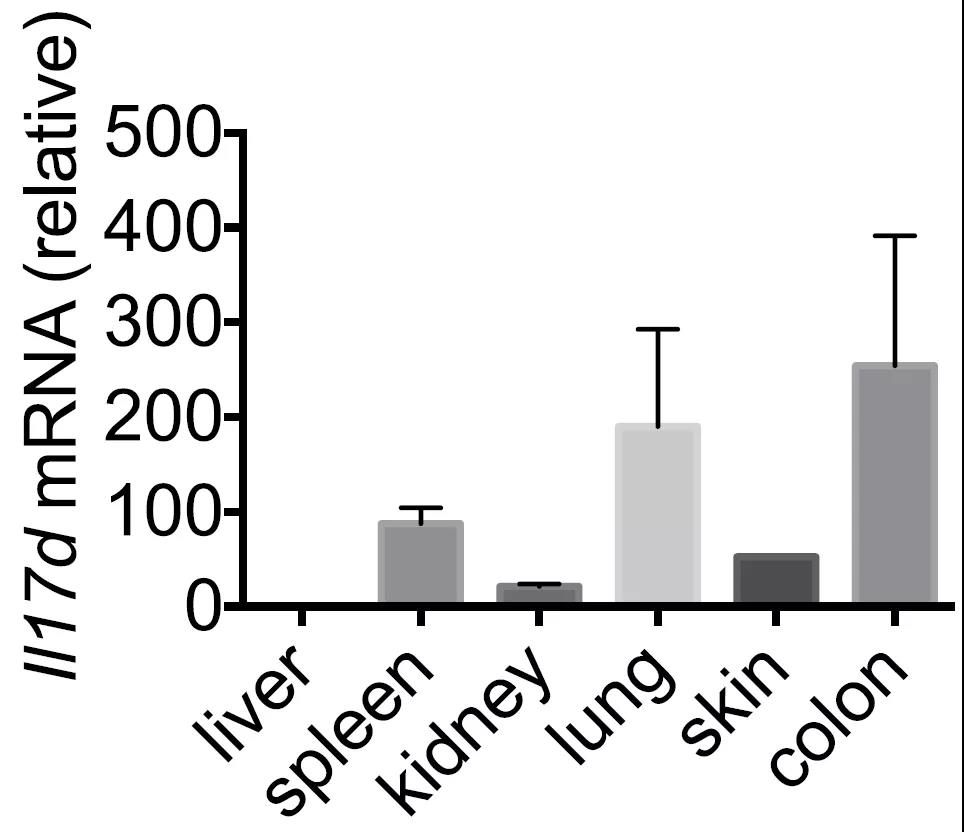
The researchers first detected the expression of IL-17D in mouse tissues, and found that IL17D is highly expressed in the colon and lungs of mice, suggesting that IL-17D may play important functions in these two organs.
The authors further studied the role of IL-17D in DSS-induced colitis, and found that IL-17D-deficient mice showed more severe enteritis, and administration of exogenous IL-17D to mice could reduce IL-17D-deficient mice The severity of colitis suggests that IL-17D has an important protective effect in colitis.
What cell is IL-17D secreted by?
The source of IL-17D cells was explored by isolating CD45 + and CD45-cells from mouse colon tissue, and it was found that CD45-cells (mainly colonic epithelial cells) highly expressed Il17d mRNA, suggesting that colonic epithelial cells may be IL-17D Main source.

What cell does IL-17D function on?
The results showed that in the colitis model, IL-17D-deficient mice had significantly reduced expression of IL-22, Reg3b and Reg3g, suggesting that IL-17D is a key factor in the production of IL-22 in the intestine.
By constructing the IL-17D-hIg fusion protein, it was found that IL-17D-hIg can specifically bind to ILC3 in the lamina propria lymphocytes of the small intestine, but not T cells, dendritic cells or macrophages. In addition, in IL-17D-deficient mice, the IL-22 expression of ILC3s was significantly reduced. These results indicate that IL-17D plays an important role in maintaining the normal function of intestinal ILC3 cells.
Through RNA-seq analysis, it was found that in IL-17D-deficient ILC3 cells, the expression of some characteristic genes related to ILC1 cells and ILC2 cells was up-regulated, while the expression of characteristic genes in ILC3 cells decreased, suggesting that IL-17D may maintain ILC3-related genes. Expression to regulate the plasticity and stability of ILC3.
In addition, given that IL-22-secreting ILC3s is essential for maintaining intestinal microbial homeostasis, the authors also performed 16S rRNA sequencing analysis on the feces of wild-type and IL17D-deficient mice, and found that IL17D-deficiency led to intestinal microbiota imbalance. And may therefore aggravate the development of colitis.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org