Triple-modality therapy maximizes anti-tumor immune response
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
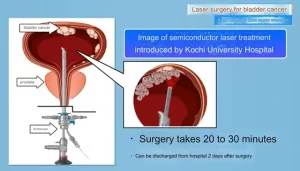
- Kochi University pioneers outpatient bladder cancer treatment using semiconductor lasers
- ASPEN 2024: Nutritional Therapy Strategies for Cancer and Critically Ill Patients
- Which lung cancer patients can benefit from neoadjuvant immunotherapy?
- Heme Iron Absorption: Why Meat Matters for Women’s Iron Needs
- “Miracle Weight-loss Drug” Semaglutide Is Not Always Effective
Triple-modality therapy maximizes anti-tumor immune response
Triple-modality therapy maximizes anti-tumor immune response. Science Sub-Journal: Three-pronged approach shows miraculous effects, immunotherapy + radiotherapy + surgery, to maximize anti-tumor immune response.
IL-15SA combined with agonist anti-GITR therapy showed local and systemic anti-tumor effects after sub-debridement radiotherapy in a mouse model of mesothelioma.
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a rare tumor that originates from pleural mesothelioma. It has a relatively high degree of malignancy, with an incidence of 0.02% to 0.4% of all tumors, and about 80% of primary pleural tumors. %.
Most patients will have advanced or metastatic disease, usually with a poor prognosis, with a median survival of 12 to 18 months.
It is generally believed that combination therapy can bring better therapeutic effects. Preclinical studies have shown that immunotherapy combined with conventional therapy has a better effect on MPM.
Preclinical studies have shown that sub-debridement radiotherapy (RT) makes the tumor microenvironment more immunogenic, releases tumor-specific antigens, and triggers an anti-tumor immune response. However, sub-debridement radiotherapy leads to upregulation of regulatory T (Treg) cells in the tumor microenvironment, which limits the systemic anti-tumor immune response.
Recently, the research team of MPM research experts and Professor Marc de Perrot from Toronto General Hospital in Canada published a research paper titled “Triple-modality therapy maximizes antitumor immune responses in a mouse model of mesothelioma” in Science Translational Medicine journal.
Based on the limitation of Treg cells in the tumor microenvironment, in the mouse mesothelioma model, the selective removal of Treg cells in the tumor can enhance the immunogenic effect of sub-debridement radiotherapy. At the same time, it is proved that sub-debridement radiotherapy combined with dual immunotherapy IL-15SA and DTA-1 (a glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor related protein (GITR) agonist) can maximize the efficacy of radiotherapy, which is a malignant pleura The clinical treatment of mesothelioma (MPM) provides new ideas.

In this study, the researchers used interleukin-15 (IL-15) that does not stimulate Treg cells in combination with sub-debridement radiotherapy, and proved that this combination therapy can induce memory cell toxicity mediated by CD8+ T cells Anti-tumor immune response.
During the research, the researchers found that compared with IL-15, the IL-15 superagonist IL-15SA can produce greater memory CD8+ T cell expansion and NK cell expansion. And IL-15SA also does not affect the proliferation of tumor cells and Treg cells. Then use DTA-1 to optimize the combination of IL-15SA and sub-debridement RT to maximize the efficacy.
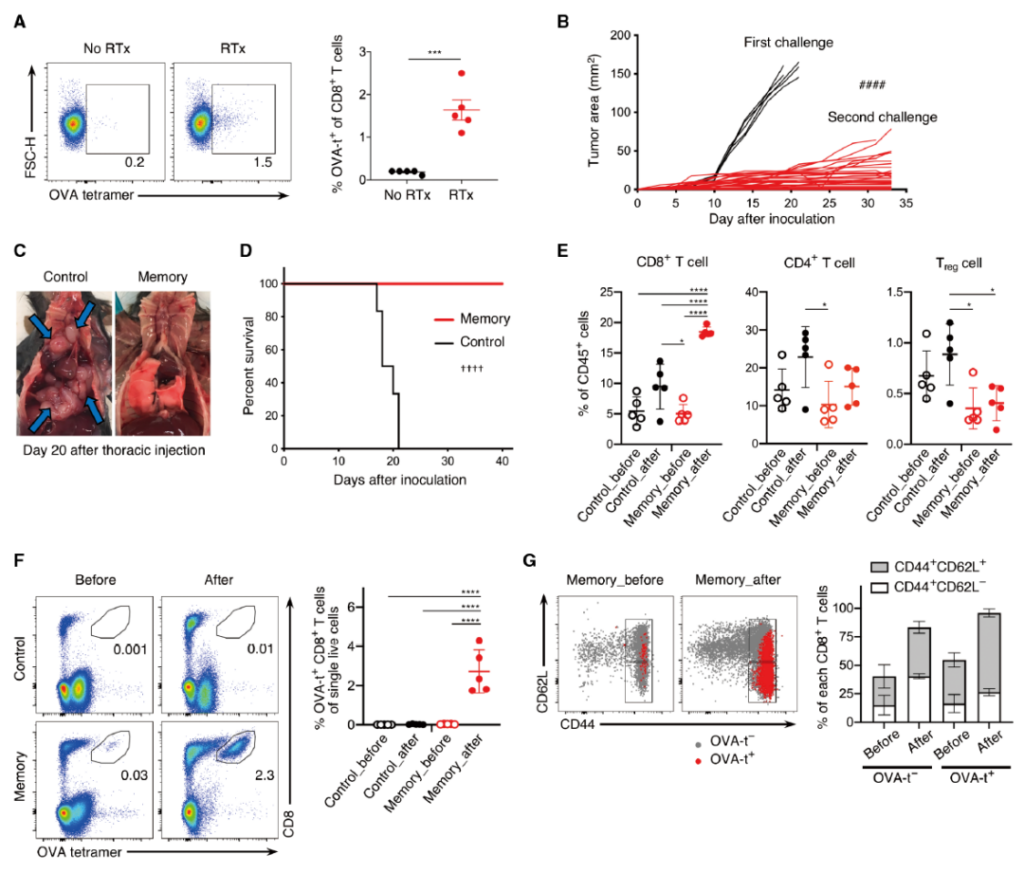
Distribution of tumor antigen-specific and memory CD8+ T cells after local radiotherapy for subcutaneous mesothelioma
Since Treg cells have a major anti-inflammatory effect in the tumor microenvironment after radiotherapy, the researchers explored the ability of Treg cells to inhibit the proliferation of CD8+ T cells after IL-15SA administration. Using an in vitro Treg cell inhibition test, it was observed that even with IL-15SA, Treg cells inhibited the proliferation of CD8+ T cells. On this basis, it is speculated that the loss of Treg cells will enable IL-15SA to play the greatest role in anti-tumor immunity.
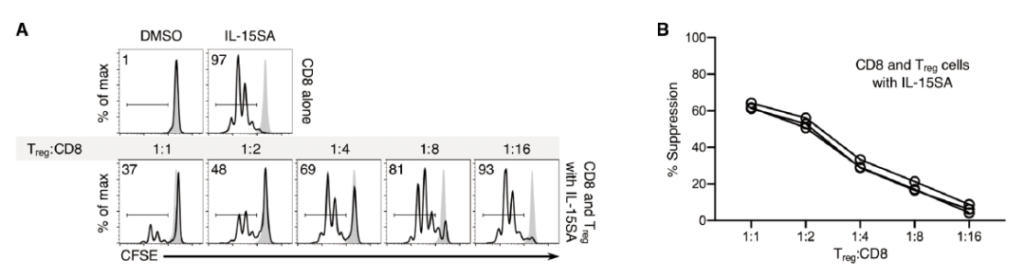
Treg cells inhibit CD8+ T cell proliferation
At the same time, research data showed that in mice treated with the combination, tumor regression was related to the largest CD8+ T cell infiltration and very low Treg cell infiltration.
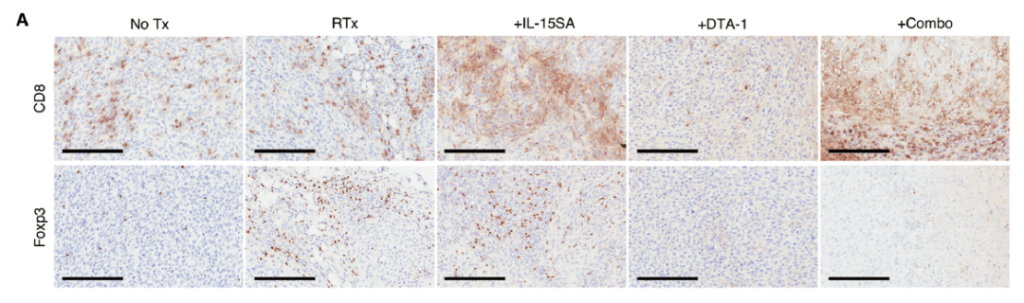
The combined application of IL-15SA and DTA-1 can promote CD8+ T cell infiltration and reduce T cell infiltration
In addition, the researchers found that CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells and NK cells play a particularly important role in the anti-tumor process, because when any of these cell types are depleted, RT and IL-15SA The curative effect of /DTA-1 combination therapy will be partially eliminated, and CD8+T cells play the greatest role.
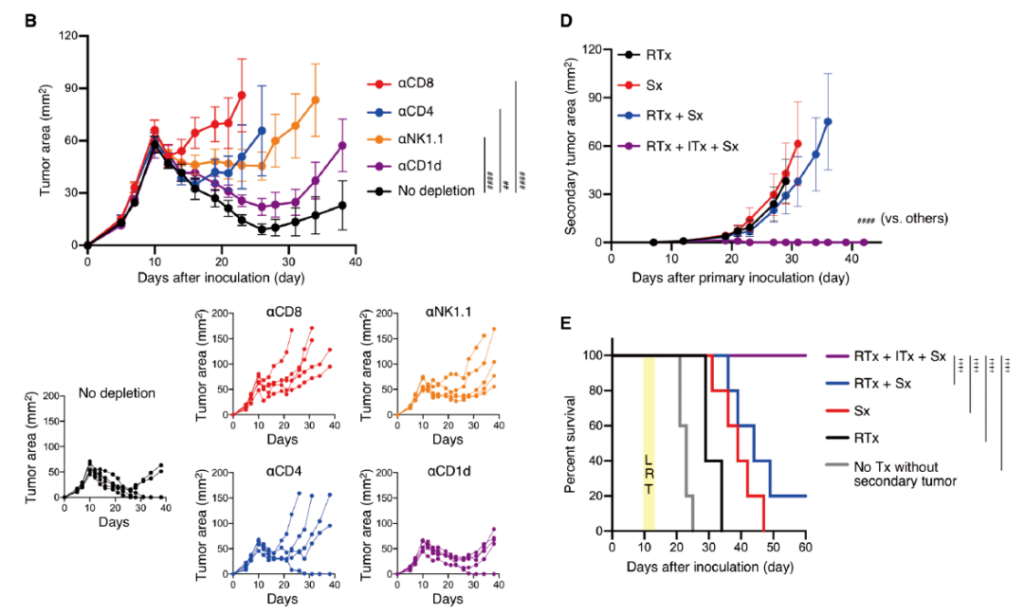
Tumor size after radiotherapy combined with IL-15SA/DTA-1
Therefore, researchers use DTA-1 to remove Treg cells, and use IL-15SA to promote the expansion of CD8+ T cells in the periphery and tumors, reduce the infiltration of Treg cells into radiotherapy mesothelioma, and maximize the efficacy of radiotherapy. It can be seen that surgical resection of radiotherapy tumors combined with IL-15SA and DTA-1 achieved the best long-term efficacy in the accompanying tumor model, which enhanced the importance of surgery after sub-debridement and radiotherapy, and gave full play to the advantages of immunotherapy.
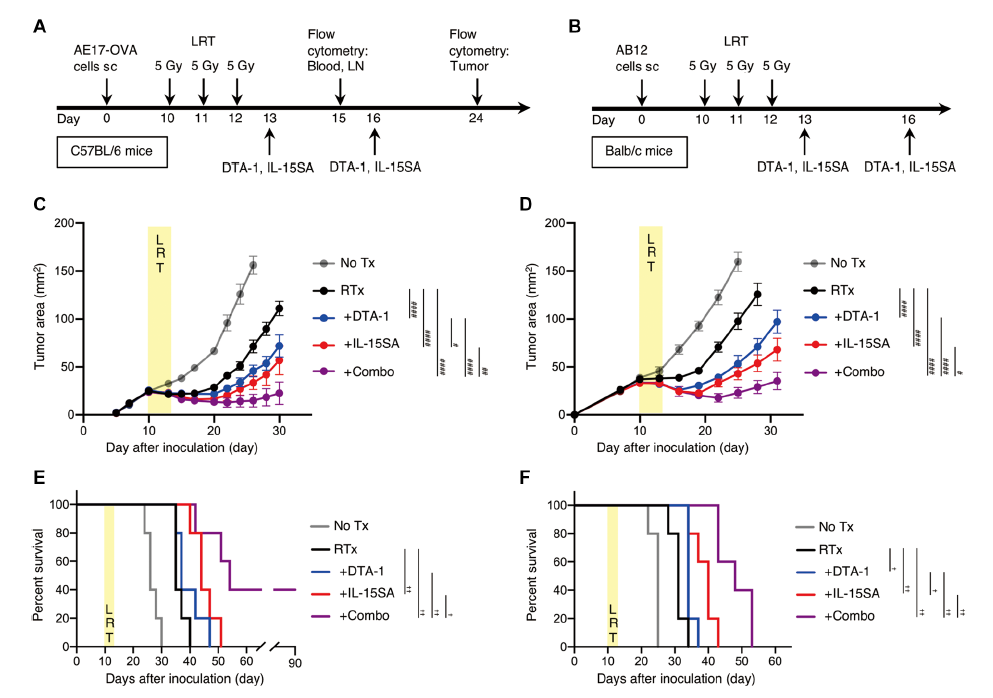
Anti-tumor effect of IL-15SA and DTA-1 local radiotherapy on mesothelioma model
In summary, IL-15SA combined with agonist anti-GITR treatment showed local and systemic anti-tumor effects after sub-debridement radiotherapy in a mouse model of mesothelioma.
These data support the development of clinical trials for MPM and other advanced malignancies with poor prognosis. In addition, sub-debridement radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy and surgical treatment may be a radical treatment option for patients with locally advanced or metastatic cancer.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org