Nature: SARS-CoV-2 uses a multi-pronged strategy to hinder host protein synthesis
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
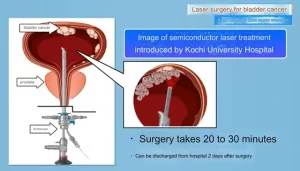
- Kochi University pioneers outpatient bladder cancer treatment using semiconductor lasers
- ASPEN 2024: Nutritional Therapy Strategies for Cancer and Critically Ill Patients
- Which lung cancer patients can benefit from neoadjuvant immunotherapy?
- Heme Iron Absorption: Why Meat Matters for Women’s Iron Needs
- “Miracle Weight-loss Drug” Semaglutide Is Not Always Effective
Nature: SARS-CoV-2 uses a multi-pronged strategy to hinder host protein synthesis
Nature: SARS-CoV-2 uses a multi-pronged strategy to hinder host protein synthesis. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the cause of the ongoing novel coronavirus pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 is a coronavirus that can cause respiratory diseases called COVID-19.
Coronavirus has developed a variety of mechanisms to inhibit the translation of host mRNA to allow the translation of viral mRNA and at the same time prevent the cell’s innate immune response. Although different SARS-CoV-2 proteins are related to host expression shutdown, there is still a lack of comprehensive understanding of the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on cell gene expression.
Researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel used techniques such as RNA sequencing, ribosome analysis, and metabolic labeling of newly synthesized RNA to study the mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 shuts down cell protein synthesis. Related papers are published on Nature.
Researchers found that viral infection caused an overall reduction in translation, but viral transcripts were not preferentially translated. On the contrary, the researchers found that viral infection leads to accelerated degradation of cytoplasmic cell mRNA, thereby facilitating the virus to take over the mRNA pool in the infected cell. In addition, the researchers revealed that the translation of transcripts (including innate immune genes) induced in response to infection by the virus is impaired. Studies have found that this damage may be achieved by inhibiting nuclear mRNA output and preventing newly transcribed cellular mRNA from entering the ribosome.
In conclusion, the results of this study reveal that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses a multi-tube combination strategy to control protein translation and inhibit the host’s defenses.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org