How to “rescue” yourself when encountering Hypothermia?
- Did Cloud Seeding Unleash a Deluge in Dubai?
- Scientists Identify Gut Bacteria and Metabolites that Lower Diabetes Risk
- OpenAI’s Model Matches Doctors in Assessing Eye Conditions
- UK: A Smoke-Free Generation by Banning Sales to Those Born After 2009
- Deadly Mutation: A New Monkeypox Variant Emerges in the DRC
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
21 players died in China Marathon due to Hypothermia!! How to “rescue” yourself when encountering Hypothermia?
How to “rescue” yourself when encountering Hypothermia? On May 22, the 100-kilometer marathon cross-country race held in Jingtai County, Baiyin City, Gansu Province, China encountered extreme weather. Participants became unwell and were threatened with extreme temperature loss. As of 10:15 on the 23rd, 21 people have been killed, including the leader of the Super Marathon in China Liang Jing and the Paralympic marathon champion Huang Guanjun.
According to the contestants’ subsequent review, the weather was still fine on the morning of the race, but before the start of the race, the sky suddenly turned cloudy and windy. During the race, many contestants had symptoms of hypothermia, twitching, foaming at the mouth, and wearing shorts and short sleeves Next to the track line at an altitude of more than 2000 meters.
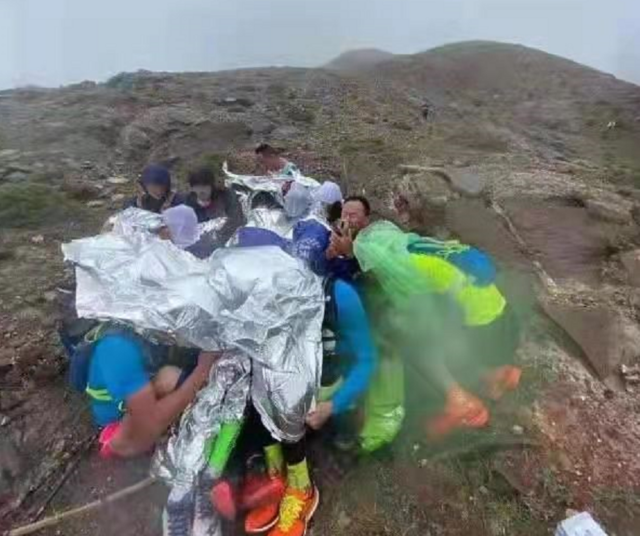

Many people are trapped on the top of the mountain
What is hypothermia?
According to Encyclopedia, hypothermia means that the body’s heat loss is greater than the heat supply, which causes the temperature of the core area of the human body to drop, and produces a series of symptoms such as chills, confusion, cardiopulmonary failure, and even death.
Hypothermia can be divided into the following four stages:
1. Mild hypothermia:
core temperature is 37~35.55°C, tremor, increased heart rhythm, increased urination, increased breathing frequency, muscle incoordination, staggering, abnormal behavior.
2. Moderate hypothermia:
The core temperature is 35~33.88°C. Due to insufficient peripheral blood flow, people will experience trance, reduced or disappeared tremor, weakness, numb thinking, decreased IQ, slurred speech, memory impairment, visual impairment, heart rhythm Symptoms such as irregularities and dilated pupils.
3. Severe hypothermia:
33.88~30°C, the exposed skin is blue-purple and swollen, unable to walk, coma, loss of nerve reflexes (no response to pain), extremely low respiratory rate and heart rate, hypotension, and ventricular fibrosis may appear Tremor, the patient cannot adjust the body temperature autonomously.
4. Fatal stage:
Below 30°C, the muscles are stiff, the heartbeat or breathing is rarely noticed, and ventricular fibrillation is prone to occur and then truly die.
Causes of hypothermia
In outdoor activities, there are two main reasons for temperature loss: too low ambient temperature and too little wearing, which makes the human body lose too much heat through conduction on the surface of the body; insufficient body energy, especially in the later stages of exercise, because the body The consumption of energy materials does not have enough energy to produce heat to maintain body temperature.
In this Gansu Marathon, many participants wear shorts and short sleeves. As the exercise intensifies, the human body sweats and the humidity increases, and the wind increases. It is very easy to lose heat quickly, causing Hypothermia, and severe extreme weather. It further increases the risk of participants losing temperature.
How to rescue yourself if encountering hypothermia?
The first step: safe transfer
In many cases of Hypothermia, the victims were exposed to harsh environments to cause Hypothermia.
- Wrong approach: continue to expose-when teammates have symptoms of hypothermia, rescue them directly in exposed areas such as the pass and the top of the mountain. Patients in the wind and snow environment will increase the loss of temperature.
- The correct approach: transfer or camp-immediately stop outdoor activities, move the patient to a shelter from the wind, and hide behind rocks and other obstructions. Set up tents for rescue if necessary.
Step 2: Isolate the cold surface
After the patient is safely transferred to a sheltered place, the cold ground will continue to eat away precious heat. At this time, the second step of the rescue team is to isolate the human body from the ground.
- Wrong approach: touch the ground-if you let the patient lie directly on the ground, or there is no sleeping mat in the tent, the ground will pull away the only heat left by the patient a little bit.
- The correct approach: Isolate the ground-when transferring the patient, the rescuer should quickly isolate the patient from the ground using a sleeping pad to prevent the patient’s core body temperature from continuing to lose. Because heat will be conducted from high-temperature objects to low-temperature objects, the function of the sleeping pad is to block the ground and slow down the heat conduction process.
Step 3: Drying
When the patient has symptoms of hypothermia, he may have been walking for a long time in the wind and snow, and the inner layer of clothing has been wet; the outer rain and snow will also wet the clothing. The rescuer should help the patient change clothes as soon as possible, keep the patient’s body dry, and reduce the heat loss caused by the wet clothes.
- Wrong way: wear wet clothes-if you let the clothes wet by rain and snow stick to the patient, the body will always be in a small damp environment. The moisture in the clothes becomes a heat transfer conductor, and the evaporation of moisture will also take away more heat.
- The correct method: change the dry clothes and enter the sleeping bag-no matter how many layers of clothes the patient wears, as long as the clothes are soaked, all the wet clothes should be taken off quickly, dry the patient’s body with fabric, put on dry clothes, and use a sleeping bag Or thick clothing wraps the patient’s body.
Step 4: Heating the core area
When the patient loses temperature severely, they will be confused and the muscles will no longer tremble. This also shows that the patient’s body has lost the ability to heat the body. At this time, it will not help to put it in a thick warmth. It can only target the core. It is wrong to heat the parts externally and heat the limbs.
- Wrong approach: rubbing hands and feet-a common mistake is rubbing the palms of the hands and feet. First of all, friction will cause secondary injuries when the patient has frostbite; secondly, the increase in temperature of the limbs will cause cold blood to return to the heart.
- Correct method: heating the core area-the core area can be heated by hot water bottles, fever patches, and the patient’s neck, armpits, groin and other core areas are heated.
Step 5: Energy injection
The reason why people lose temperature is that the body’s heat production is no match for loss. The source of body heat is energy. Patients with severe hypothermia have exhausted their energy, so they need to be supplemented by eating to restore the body’s heating capacity as soon as possible.
- Wrong approach: Drinking alcohol-it is a common mistake to let patients with hypothermia drink alcohol. Drinking alcohol does have an illusion of “warmness”, but then it will accelerate the loss of calories. Alcohol itself does not provide much heat to the human body, and it will cause the expansion of blood vessels and accelerate blood circulation, thereby accelerating the loss of body heat, and the expanded blood vessels will also accelerate the return of cold blood to the core area.
- Correct way: supplementing liquid hot foods-the rescue of hypothermia is the body’s recovery of heat production, so feed the patient some liquid high-calorie foods at room temperature, such as concentrated sugar water, hot chocolate, etc., so that the hypothermic patients can get what they need for thermogenesis energy.
How to prevent Hypothermia?
Pay attention to the choice of underwear. Most people who travel outdoors focus on protection from rain and snow, and only care about keeping warm, while ignoring the risk of Hypothermia caused by a lot of sweating. To choose underwear that dries quickly and wicks away sweat, avoid cotton underwear. Cotton fabrics are very sweat-absorbent and are not easy to export and cause Hypothermia.
Pay attention to the increase or decrease of clothing. Put warm clothes in your carry-on bag before starting on a hike in the alpine region, and wear a thin quick-drying T-shirt or a well-ventilated jacket when you start. Whenever you get to a rest point, immediately take out warm clothes and put on them to avoid catching cold and losing temperature.
Pay attention to thermal protection. If you travel in cold weather, you should take appropriate wind protection measures to avoid exposure to the cold wind. Warm hats, gloves, snoods, windbreakers, thick socks, windshields, etc. are all essential items for traveling in windy and cold weather.
Replenish physical fitness in time. Don’t let yourself be overdrawn, prevent dehydration, and avoid excessive sweating and fatigue. Prepare food and hot drinks to replenish body heat at any time.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org