How to figure if mRNA or inactivated COVID-19 vaccine is more effective?
- Engineered Soybeans with Pig Protein: A Promising Alternative or Pandora’s Dish?
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS): A Tick-Borne Threat with High Mortality
- Why Isolating Bananas Extends Their Shelf Life?
- This common vitamin benefits the brain and prevents cognitive decline
- New report reveals Nestlé adding sugar to infant formula sold in poor countries
- Did Cloud Seeding Unleash a Deluge in Dubai?
How to figure if mRNA or inactivated COVID-19 vaccine is more effective?
- Israel new drug for COVID-19: EXO-CD24 can reduce deaths by 50%
- COVID-19 vaccines for children under 12 will be available soon
- Breakthrough infection of Delta: No difference from regular COVID-19 cases
- French research: ADE occurred in Delta variant and many doubts on it
- The viral load of Delta variant is 1260 times the original COVID-19 strain
How to figure if mRNA or inactivated COVID-19 vaccine is more effective? Which COVID-19 vaccine is better? how to choose? Science gives in-depth articles. In addition to neutralizing antibody titer, what other indicators are there?
With the continuous emergence of mutant strains of the new coronavirus, more and more public data show that the effect of vaccines on mutant strains is changing. In the case of phase 3 clinical studies that take a lot of time, how to keep up with the mutant strains faster, to judge the effectiveness of the vaccine, and to reveal the effectiveness of the enhanced needle has become a top priority.
Recently, Science published an in-depth analysis article on this issue. The main focus is to discuss whether the antibody titer level can be used as a criterion for judging the effectiveness of the vaccine.

Judging the effectiveness by neutralizing antibody titer, Highly recognized by the industry
The in-depth analysis of Science proposed at the beginning that the feasibility of measuring vaccine effectiveness by neutralizing antibody levels is recognized by many medical experts. At the end, the article again emphasizes the higher acceptance of this view.
Indeed, this inspection program is recognized by many medical experts. A Correspondence article published in The Lancet Microbe on July 15, local time, adopted a neutralizing antibody titer comparison scheme to evaluate which vaccine to choose.

(Original text by The Lancet Microbe)
This study from the University of Hong Kong reports the use of the mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 and the inactivated vaccine Coronavac among medical staff. This study is a cohort study, including 1442 medical workers from various public and private hospitals and clinics in Hong Kong.
The blood samples before the vaccination, the blood samples before the second injection, and the blood samples after the second injection were collected. 21-35 Day’s blood sample. Finally, the sample with all data collected completely was 93 people, of which 63 were vaccinated with mRNA vaccine and 30 were vaccinated with inactivated vaccine.
In terms of baseline data, 63 people received mRNA vaccines, of which 55.6% were males, with a median age of 37 years (range 26-60 years). Of the 30 people who received inactivated vaccines, 23.3% were males, with a median age of 47 years (range 31-65 years).
The researchers used the level of neutralizing antibodies produced by the vaccine as the main benchmark. In the neutralizing antibody level test, the researchers found that among the medical staff who received the mRNA vaccine, the neutralizing antibody increased significantly after the first and second doses. The original description of the study: “In contrast, the antibody concentration of the medical staff who received the inactivated vaccine was very low after the first dose, and the antibody level reached a moderate level after the second dose.”
At the same time, they further carried out antibody titre quantification analysis on 12 participants. The results showed that the antibody titre (geometric mean PRNT90 titre) of medical staff who received two doses of mRNA vaccine was 269, while that of inactivated vaccine was only 27.
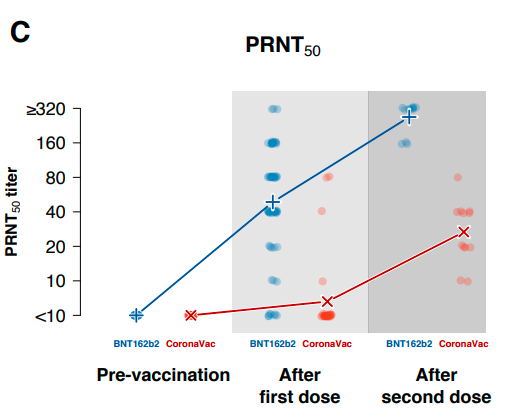
The author concludes in the last paragraph of the article that the level of neutralizing antibody titers is considered to be highly correlated with vaccine protective efficacy. The difference in neutralizing antibody titers in this study can be translated into differences in vaccine effectiveness.
However, the article also acknowledges that no information on T cell immunity and antibody-dependent cytotoxic immunity has been collected.
All in all, the latest research published by the University of Hong Kong is a corroboration that the level of neutralizing antibody titers has been recognized by industry experts.
Neutralizing antibody levels are related to the decline in effectiveness
The level of neutralizing antibody titer has received attention and investigation because it is also related to the effectiveness of the mutant strain and the attenuation of the vaccine’s protective efficacy.
Recently, more and more data have shown that the protective efficacy of vaccines against some variants with immune escape effects has decreased, and the corresponding neutralizing antibody titers have also decreased.
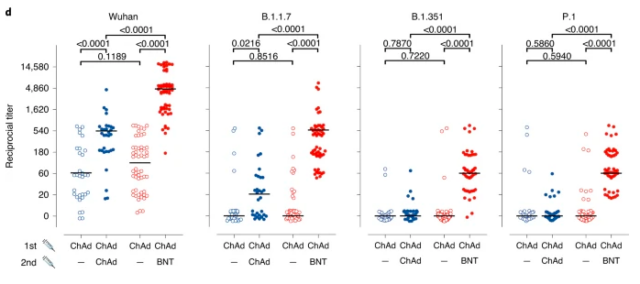
(Adenovirus vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 have different levels of neutralizing antibodies against mutant strains)
Nature Medicine has previously used neutralizing antibody titers and protective efficacy data to conduct model studies and found that the level of neutralizing antibody is proportional to the protective efficacy, and the lower the initial titer of neutralizing antibody, the lower the protective efficacy of the vaccine. The higher, the faster the speed.
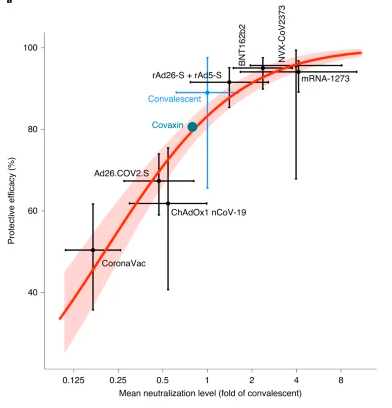
In the study published by Nature Medicine, this proportional relationship is shown in a graph. The 1 on the abscissa in the figure is the level of neutralizing antibodies in recovered patients. The protective efficacy data of all vaccines correspond to the original wild-type virus, not the mutation. Strain. The two vaccines used in the research of the University of Hong Kong mentioned above are also in this picture. The neutralizing antibody data of the two have a gap of about 10 times, which is basically consistent with the results of the University of Hong Kong.
From many studies, it can be seen that even if the level of neutralizing antibody titers cannot fully represent all the immune indicators of the vaccine, it is also a very important or even critical data to measure the effectiveness of the vaccine.
Other immune indicators are ambiguous
Science pointed out in its analysis article that although T cell immunity is an important indicator to measure the COVID-19 vaccine, because a large number of published studies have focused on the level of neutralizing antibodies, there are few literatures on T cell immunity, which is difficult. Form an effective comparison.
In addition, some researchers have proposed that the vaccine will produce a “binding antibody” (binding antibody). This antibody only binds to the virus and does not prevent the virus from entering the cell. There is speculation that this binding antibody may make it easier for macrophages to swallow the virus after binding to the virus, thereby causing an immune response. But this speculation has not been confirmed. There is no evidence of what effect the conjugated antibody plays.
Because the binding antibody is produced together with the neutralizing antibody, some researchers have called for consideration of its role-especially for vaccines with poor neutralizing antibody levels, the effect of the binding antibody can be investigated.
However, since there are few studies on binding antibodies, T cell immunity, and antibody-dependent cytotoxic immunity mentioned in the University of Hong Kong research, and even the mechanism of binding antibodies is not clear, the current measurement value of these indicators is very vague. More research is needed.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



