What is the difference between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
- New Ocrevus Subcutaneous Injection Therapy Shows Promising Results in Multiple Sclerosis Treatmen
- Dutch Man Infected with COVID-19 for 613 Days Dies: Accumulating Over 50 Virus Mutations
What is the difference between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis?
- Israel new drug for COVID-19: EXO-CD24 can reduce deaths by 50%
- COVID-19 vaccines for children under 12 will be available soon
- Breakthrough infection of Delta: No difference from regular COVID-19 cases
- French research: ADE occurred in Delta variant and many doubts on it
- The viral load of Delta variant is 1260 times the original COVID-19 strain
What is the difference between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis? Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are two similar-sounding words that are easy to confuse. Old age, smoking, obesity, and family history are all risk factors for the two. So what are the differences between the two?
1. Vascular structure
First of all, we first understand the structure of the inferior artery wall.
From the lumen to the outside, the vessel wall is generally intimal, media and adventitia.
1) Intima
It is the innermost layer of the tube wall, composed of the endothelium and the subendothelial layer, and is the thinnest of the three layers.
The endothelium is a single layer of flat epithelium lining the blood vessel lumen. As the lining of blood vessels, endothelial cells form a smooth surface to facilitate blood flow. The endothelial cells and the substrate constitute a permeability barrier through which liquid, gas and macromolecular substances can selectively penetrate.
Outside the endothelium is a thin layer of loose connective tissue, which together form the inner membrane.
2) Media
Outside the intima is the muscular media.
The large arteries are dominated by elastic membranes with a little smooth muscle in between; the middle arteries are mainly composed of smooth muscles. The elastic fibers of the media have the function of retracting the expanded blood vessels, and the collagen fibers have the function of maintaining tension and supporting functions.
3) Outer membrane
The outside of the media, the outermost layer of the artery wall, is called the adventitia. The adventitia is composed of loose connective tissue. The connective tissue cells of the blood vessel wall are mainly fibroblasts. When the blood vessel is damaged, the fibroblasts have the ability to repair the adventitia.
2. Arteriosclerosis vs. Atherosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis (that is, the increase in arterial stiffness) refers to the process of aging of the arterial vessel wall. With age, the smooth muscle of the arterial media can move into the intima to proliferate and produce fibrous connective tissue, which thickens the intima and makes the arterial tube The stiffness of the wall will slowly and gradually increase, the vascular resistance will increase, and the elasticity will decrease. The main consequence is an increase in blood pressure.
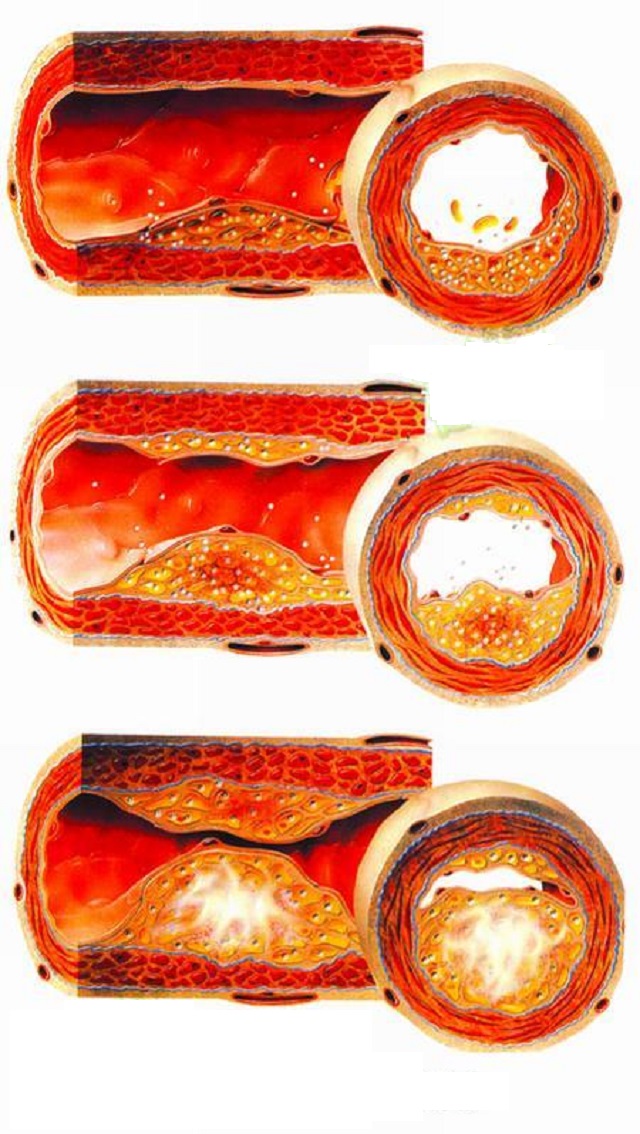
Atherosclerosis (AS) is caused by vascular endothelial damage, subsequent lipid deposition, macrophage phagocytosis and foam cell formation, as well as the formation of a lipid core under the action of pro-inflammatory factors, accompanied by fibrous cap formation. Sclerosing lesions are called atherosclerosis because the lipids accumulated in the arterial intima are yellowish atherosclerosis. At the same time, the chemicals released by inflammatory cells promote the proliferation of smooth muscle cells and interstitial cells, resulting in thickening of the inner and media.
The above-mentioned changes in the arterial wall can cause significant stenosis of the vascular lumen. When the plaque ruptures, thrombosis will occur, which can lead to acute vascular occlusion. This is the pathophysiological process of stroke, myocardial infarction and peripheral artery disease.
3. What is the difference between the two?
The difference between arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis:
1) Different mechanisms
Arteriosclerosis is a change of vascular aging, involving intimal fibrosis, often without obvious stenosis of the lumen, and does not involve plaque rupture and thrombosis;
Atherosclerosis is a pathological change, which often starts with vascular endothelial damage under the action of risk factors such as smoking and hypertension, which often leads to luminal stenosis, involves plaque rupture and can lead to thrombosis.
2) Different endings
Arteriosclerosis often leads to increased vascular resistance, leading to the formation of high blood pressure; and the outcome of atherosclerosis often leads to coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke and so on.
3) Different treatment
There is no special medication for arteriosclerosis;
Atherosclerosis can be delayed by lipid-lowering drugs and antiplatelet drugs.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



