Clear the beta plaque: Brain cholesterol can regulate Alzheimer’s plaque
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
- New Ocrevus Subcutaneous Injection Therapy Shows Promising Results in Multiple Sclerosis Treatmen
- Dutch Man Infected with COVID-19 for 613 Days Dies: Accumulating Over 50 Virus Mutations
PNAS: Clear the beta plaque! Brain cholesterol can regulate Alzheimer’s plaque
Clear the beta plaque: Brain cholesterol can regulate Alzheimer’s plaque. The production of the toxic protein β amyloid associated with Alzheimer’s disease in the brain is strictly regulated by cell membrane cholesterol. By observing this phenomenon in living mice, the researchers even found that they can interfere with the production of cholesterol, making the plaque almost disappear.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), commonly known as “Alzheimer’s disease”, has about 50 million cases of dementia worldwide, with about 10 million new cases every year. In China, there are tens of millions of patients, ranking first in the world. Although the scientific community has invested a lot of energy in Alzheimer’s disease, there is still no very effective treatment plan to prevent or cure it.
Recently, researchers from the Scripps Research in the United States published a research paper entitled “Regulation of beta-amyloid production in neurons by astrocyte-derived cholesterol” in the top issue of “PNAS”.
The study used advanced imaging to show that the production of Alzheimer’s disease-related toxic protein beta amyloid in the brain is strictly regulated by cell membrane cholesterol. By observing this phenomenon in living mice, the researchers even found that they can interfere with the production of cholesterol, making the plaque almost disappear.

The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is not yet known, but one of the main hypotheses is that the abnormal accumulation of toxic plaques (amyloid beta and tau) in the brain caused the disease. The accumulation of these protein clusters and tangles in and around brain cells affects cognitive function, so much research on Alzheimer’s disease has focused on how these proteins are formed and how to avoid them.
In this study, the researchers used super-resolution microscopy imaging to study brain cells in living mice and tracked how cholesterol regulates the production of amyloid beta.
Researchers focused on cholesterol produced by astrocytes in the brain and found that it is carried to the outer membrane of neurons by apolipoprotein E (apoE). On the outer membrane, they promote the accumulation of cholesterol and other molecules called lipid rafts. Lipid rafts are regarded as the hub where other cells gather and control key cell functions.
A protein called APP is also found in neuronal membranes, which produces amyloid β. When apoE and its astrocytes enter the area together, APP will come into contact with lipid rafts, which are the place and time when amyloid β is produced. Therefore, this point of contact is the key to the whole process.
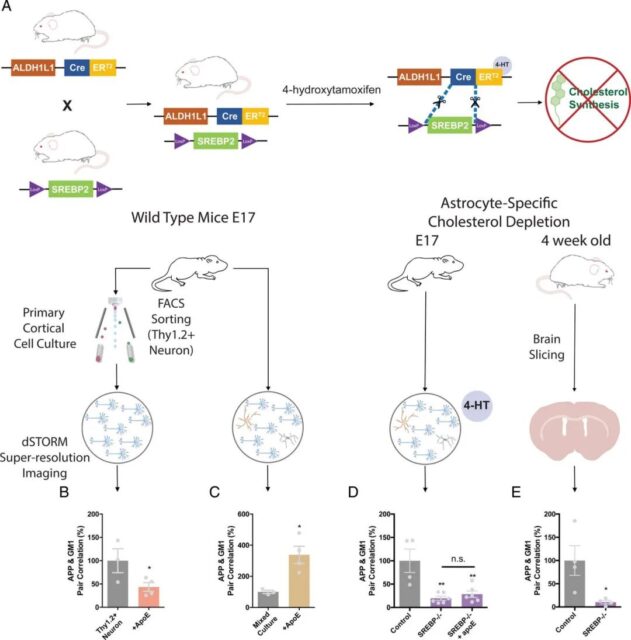
Astrocyte cholesterol regulates APP processing in neurons
In addition, the researchers found that blocking the flow of cholesterol causes APP to disengage from the lipid rafts, thereby effectively preventing the production of amyloid beta.
The researchers conducted a series of experiments in elderly “3xTg-AD” mice that were genetically engineered to overproduce amyloid beta, form plaques, and extensively mimic Alzheimer’s disease.
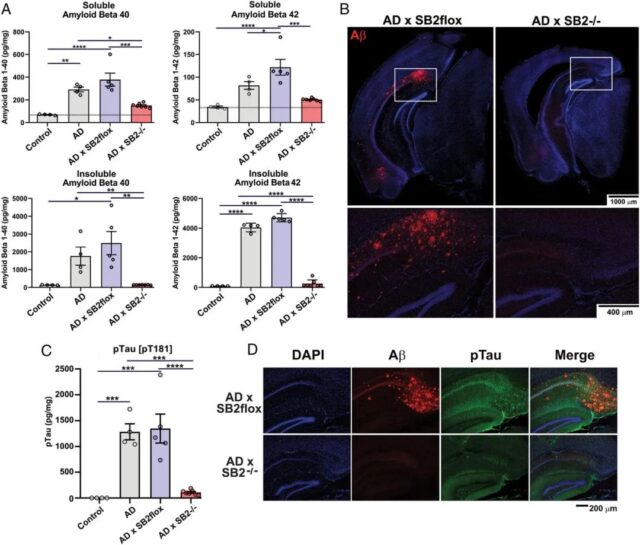
Shut down the cholesterol production of astrocytes in mice, and the plaque disappeared
The researchers found that when the cholesterol production of astrocytes in the mice was turned off, the production of amyloid beta plummeted to normal levels and the plaques almost disappeared.
Researchers say that cholesterol is essential for the normal functioning of the brain. It cannot just eliminate cholesterol in neurons. It needs cholesterol to set an appropriate threshold for amyloid beta production and normal cognition.
In short, the research promoted people’s understanding of the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and emphasized the role of brain cholesterol, which has been underestimated for a long time. By confirming and elucidating the role of cholesterol produced by astrocytes in the production of amyloid β, this study shows that this process is worth exploring the potential to prevent the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



