The mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and the serum of recovered patients still have neutralizing activity against lambda variants
- Did Cloud Seeding Unleash a Deluge in Dubai?
- News draftScientists Identify Gut Bacteria and Metabolites that Lower Diabetes RiskNews draft
- OpenAI’s Model Matches Doctors in Assessing Eye Conditions
- UK: A Smoke-Free Generation by Banning Sales to Those Born After 2009
- Deadly Mutation: A New Monkeypox Variant Emerges in the DRC
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
The mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and the serum of recovered patients still have neutralizing activity against lambda variants
- Israel new drug for COVID-19: EXO-CD24 can reduce deaths by 50%
- COVID-19 vaccines for children under 12 will be available soon
- Breakthrough infection of Delta: No difference from regular COVID-19 cases
- French research: ADE occurred in Delta variant and many doubts on it
- The viral load of Delta variant is 1260 times the original COVID-19 strain
The mRNA COVID-19 vaccine and the serum of recovered patients still have neutralizing activity against lambda variants. The continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants with increased infectivity has raised concerns about the weakened protective efficacy of vaccines.
For example, the Lambda mutant strain that is popular in Peru has an increasing prevalence in Argentina, Ecuador, Chile and Brazil[1]. In June 2021, the World Health Organization listed it as a “variant strain of concern (VOI). )”[2].
The spike protein (S protein) of the lambda variant has new mutation sites, such as Δ246-252, G75V, T76I, L452Q, F490S, T859N, of which L452Q and F490S belong to RBD (S protein receptor binding domain) The new mutation of, represents that the virus may have a higher transmission power and may increase resistance to neutralizing antibodies. Therefore, the increasing prevalence of lambda variants has attracted people’s attention. Is the current vaccine still effective?
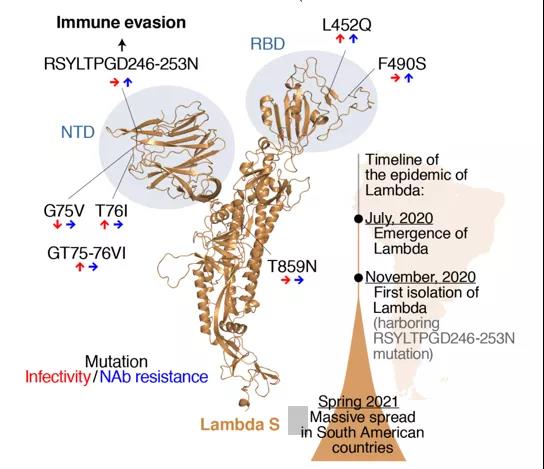
Schematic diagram of the mutation site of the lambda variant
Image source: screenshot of the paper
A study in the United States tested the sensitivity of the S protein mutation of the lambda variant strain to the neutralization effect of convalescent serum, vaccine-induced antibodies and therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. The results were published on the medRxiv platform on July 3 Form release [3].
Research Brief
The L452Q mutation doubles the infectivity of the Lambda mutant S protein pseudovirus
The infectivity of pseudovirus on ACE2.293T cells was analyzed, and it was found that the L452Q mutation on the S protein of the lambda mutant strain increased the infectivity by 2 times. Other mutations (G75V-T761, F490S, T859N and Δ246-252) There is no significant effect on infectivity.
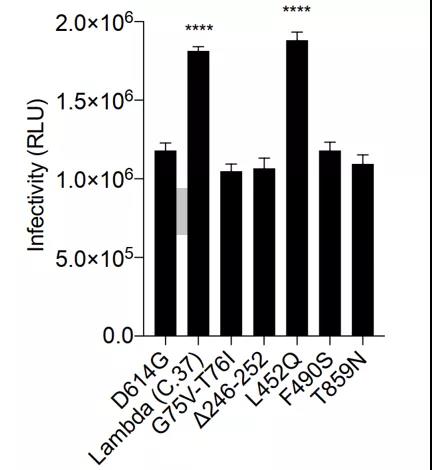
Infectivity of Lambda mutant S protein pseudovirus
Image source: screenshot of the paper
The neutralizing effect of serum and vaccine-induced antibodies during the convalescence period on the lambda variant strain is reduced by 2.3 to 3.3 times
Analysis of serum samples from patients who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 before the emergence of the lambda variant showed that compared with D614G, the resistance of the lambda variant S protein to serum neutralization activity during the convalescence period was 3.3 times , And the Beta variant (B.1.351) is 4.9 times.
Analysis of the serum samples inoculated with the BNT162b2 vaccine showed that the S protein of the lambda variant strain was about three times more resistant to the neutralizing activity of the BNT162b2 vaccine.
The analysis of serum samples inoculated with the mRNA-1273 vaccine showed that the S protein of the lambda variant strain was approximately 2.3 times resistant to the neutralizing activity of the mRNA-1273 vaccine.
The resistance of the aforementioned lambda variant strains are all related to the L452Q and F490S mutations of the S protein.
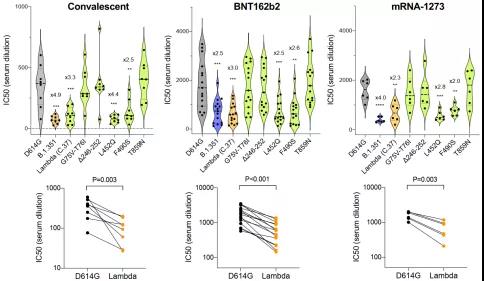
Neutralization of Lambda Variant Strains of Convalescent Serum and Vaccine Induced Antibodies
Image source: screenshot of the paper
L452Q increases the affinity of S protein and ACE2, or increases infectivity
Research data showed that the binding capacity of Lambda variant S protein and angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) increased by 3 times. This increase in binding force is caused by the L452Q mutation, and the F490S mutation has not been found to have an effect on ACE2 binding. The results of the study indicate that L452Q increases the affinity of the lambda variant strain for ACE2, which may contribute to the increase in infectivity.
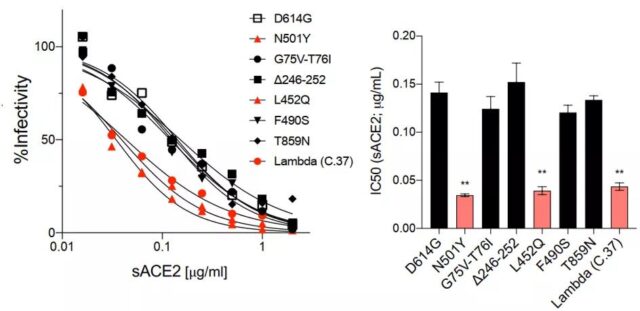
L452Q increases the affinity of S protein and ACE2
Image source: screenshot of the paper
The neutralizing effect of the REGN10933 and REGN10987 monoclonal antibodies on the lambda variant is weakened
Research data showed that the resistance of the Lambda variant S protein to the neutralizing activity of REGN10987 was about 3.6 times, and the resistance to the neutralizing activity of REGN10933 was not reduced. The resistance of the lambda variant strain is related to the mutation of S protein L452Q.
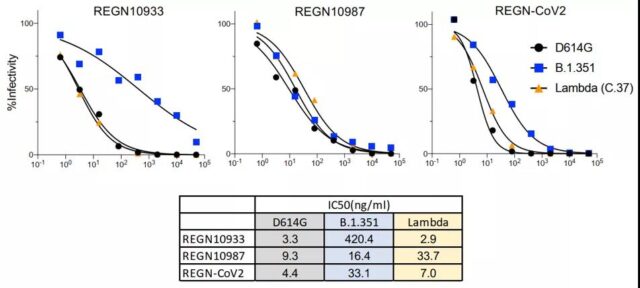
Neutralization of REGN10933 and REGN10987 Monoclonal Antibodies to Lambda Variant Strains
Image source: screenshot of the paper (invasion and deletion)
Similar to the S protein of the variant of concern (VOC), the S protein of the lambda variant is partially resistant to the neutralizing effect of the COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2 vaccine, mRNA-1273 vaccine) and serum during the recovery period. Research data shows that although the neutralizing titer of the COVID-19 vaccine against lambda variants has been reduced by about 3 times, the protection against infection has not been significantly reduced.
The average neutralization titer IC50 of the mutant strain is about 1:600 (this value is higher than the neutralization titer of the serum to D614G during the convalescence period). The serum antibody titers of a small number of vaccinators are lower than the average level. Whether this will reduce the protection of the vaccine against variant strains remains to be verified by epidemiological studies.
Another study explored the infectivity and immune escape ability of the lambda variant. It analyzed the serum of 75 medical staff who had received two doses of CoronaVac’s COVID-19 inactivated vaccine. The results showed that it was compared with the original strain. , Lambda mutant strains are more infectious, even higher than D614G, Alpha (Alpha) mutant strains or Gamma (Gamma) mutant strains; CoronaVac vaccine’s neutralizing effect on Lambda mutant strains is 3.05 times lower than that of the original strain , And the gamma mutant strain is 2.33 times lower than the original strain, and the alpha mutant strain is reduced by 2.03 times [4]. That is, certain mutations in the S protein of the lambda variant strain increased the infectivity of the strain, and immune escape also occurred to the neutralizing antibodies induced by the CoronaVac vaccine.
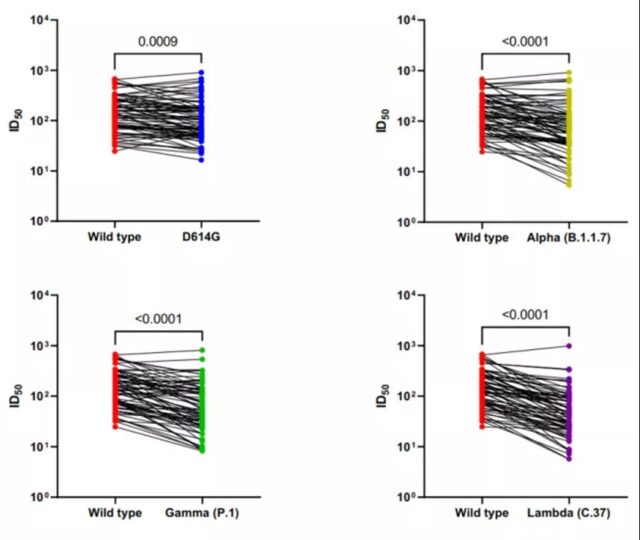
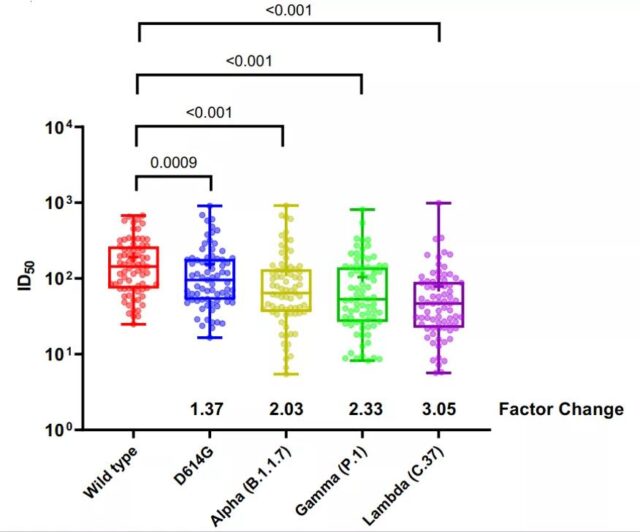
Neutralization test with serum samples of CoronaVac vaccine recipients
Image source: screenshot of the paper
Summary:
Based on the results of the above two studies, it can be seen that the lambda variant has increased infectivity and immune resistance, but we do not have enough reliable data to compare it with the VOC variant. The increased infectivity and immune resistance of lambda variants are related to the mutations of S protein L452Q and F490S.
This result is similar to the results of recent studies published by Japanese scholars, that is, the mutation of the S protein L452Q and T76I of the lambda variant strain can enhance the infectivity of the strain, which is one of the reasons for the higher infectivity of the lambda variant strain. ; The RSYLTPGD246-253N deletion, L452Q and F490S mutations in the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the S protein make the lambda variants have strong resistance to vaccine-induced neutralization, leading to immune escape of the virus [5].
Although the lambda variant strain is classified as VOI, compared with the pandemic VOC, it may be considered that the lambda variant strain does not pose a continuous threat to humans, but the lambda variant strain can neutralize vaccine-induced The role is resistant, and the risk of breakthrough infection still exists, that is, it is still possible to be infected with the COVID-19 virus after vaccination [5].
It is worth mentioning that the research data shows that although the current vaccine has reduced neutralizing activity to the lambda variant strain, it still maintains a certain protective effect.
At present, we still need to continuously monitor and in-depth study the prevalence of mutant strains, and be prepared to respond to the emergence of more resistant mutant strains at any time to prevent large-scale global infections. At the same time, it emphasizes the importance of widespread vaccination, which will protect individuals from disease, reduce the spread of the virus and slow the emergence of mutant strains.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.