Pseudovirus: A powerful tool to evaluate the protection of COVID-19 vaccines
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
- New Ocrevus Subcutaneous Injection Therapy Shows Promising Results in Multiple Sclerosis Treatmen
- Dutch Man Infected with COVID-19 for 613 Days Dies: Accumulating Over 50 Virus Mutations
- Engineered Soybeans with Pig Protein: A Promising Alternative or Pandora’s Dish?
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS): A Tick-Borne Threat with High Mortality
Pseudovirus: A powerful tool to evaluate the protection of COVID-19 vaccines
- Israel new drug for COVID-19: EXO-CD24 can reduce deaths by 50%
- COVID-19 vaccines for children under 12 will be available soon
- Breakthrough infection of Delta: No difference from regular COVID-19 cases
- French research: ADE occurred in Delta variant and many doubts on it
- The viral load of Delta variant is 1260 times the original COVID-19 strain
Pseudovirus: A powerful tool to evaluate the protection of COVID-19 vaccines. COVID -19 is an acute viral disease caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Since the outbreak of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, many variants have appeared.
At the end of December 2020, the COVID-19 mutant Alpha strain was discovered in the United Kingdom, and the epidemic in the United Kingdom suddenly began to get out of control. Soon after, Beta was discovered in South Africa, Delta was discovered in India, and Lambda appeared in Peru.
Various mutated new coronaviruses have sprung up from all over the world, and the epidemic has entered a more tense period. The epidemic mutants such as Alpha, Delta, and Lambda have stronger transmission ability, higher viral load, and increased immune escape ability than previous strains. Are the existing vaccines still protective? How to evaluate vaccine potency?
Facing the challenge of new coronavirus mutant strains, Moderna announced the results of its mRNA new coronavirus vaccine, the neutralizing ability of a variety of new coronavirus mutant strains including Delta.
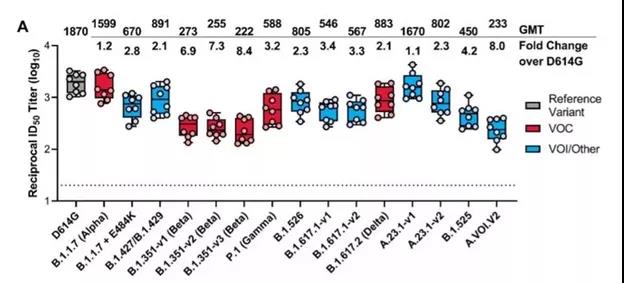
Neutralizing titer data of mRNA-1273 vaccine vaccinators against different new coronavirus mutant strains
Experimental results showed that for the Delta virus strain, the serum neutralization titer was reduced by 2.1 times, and for the Gamma virus strain, the serum neutralization titer was reduced by 3.5 times. Among the tested mutant strains, the Beta (B.1.351) virus strain and the A.VOI.V2 virus strain found in Angola caused the greatest decrease in serum neutralization ability.
Compared with the control virus strain, the neutralization titer decreased by up to 8.4 Times. Beta (B.1.351) virus strain causes a large reduction in serum neutralization ability. Therefore, Moderna developed mRNA-1273.351 as an enhanced vaccine against beta mutant strains, which significantly improved the neutralizing ability of beta mutant strains in clinical trials.
The Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology, the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, and many other units use the pseudovirus system to verify whether the neutralizing antibodies in the serum of vaccinators who have been vaccinated with BBIBP-CorV or CoronaVac can resist COVID-19. Mutant strain.
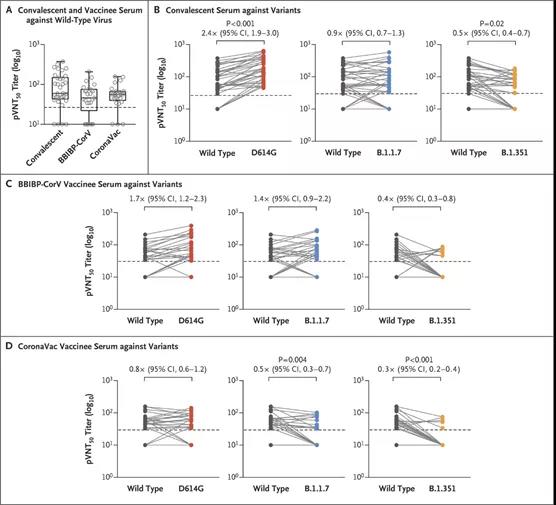
The neutralizing effect of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus in the recovery period and in the serum samples of vaccinators
The results showed that the Alpha mutant strain has almost no resistance to serum neutralization activity, while the Beta mutant strain is more resistant to serum neutralization activity (easier to escape the immune system).
The team of Shabir A. Madhi of Golden Mountain University in South Africa used a pseudovirus system to study the effectiveness of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Covid-19 vaccine against the B.1.351 variant.
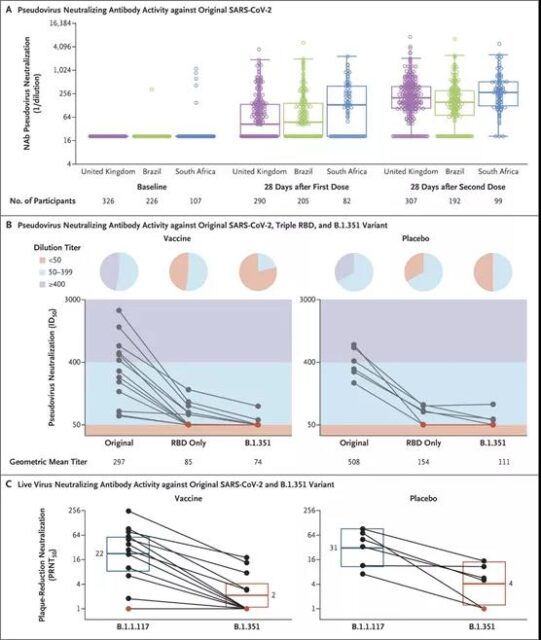
False virus and live virus neutralization test results
The results of the study showed that against the B.1.351 variant, the two-dose regimen of ChAdOx1-nCoV-19 vaccine has no protective effect on mild to moderate Covid-19.
Why do people use Pseudovirus to verify vaccine titers?
When developing a vaccine, to judge whether a certain vaccine has an immune effect, the most important indicator is whether it can produce enough neutralizing antibodies after immunizing the body. Many commercially available vaccines, including Moderna and BioNtech’s mRNA vaccines, have conducted neutralizing antibody experiments in clinical trials, and the neutralizing antibody titer is used as an important evaluation indicator.
As the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) is highly infectious and pathogenic, the research of SARS-CoV-2 live virus requires laboratory safety levels above P3. Currently, there are only more than 40 P3 laboratories in China, most of which belong to CDC. System, unconventional scientific research purpose. In addition, traditional methods such as plaque formation test are time-consuming and low in flux, which greatly restricts related research.
Therefore, in order to be able to conduct research on the new coronavirus in the secondary biosafety laboratory and to develop a high-throughput in vitro neutralization test is particularly important. In order to solve this problem, researchers have constructed a pseudovirus (Pseudovirus). It can simulate the process of virus invading cells, and can only infect cells once.
It has no autonomous replication ability, high safety and strong operability. It can realize high-throughput and rapid detection. It is widely used in the study of virus infection mechanism, monoclonal antibodies and anti- Viral drug screening and evaluation, serum neutralizing antibody detection, and vaccine potency evaluation.
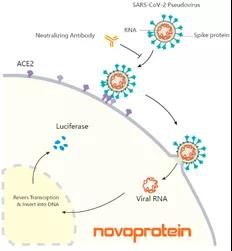
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic and a variety of COVID-19 mutant strains are currently rampant, how the vaccine protects against the COVID-19 mutant strains urgently needs to be verified. Nearshore proteins have developed a series of mutant strains including the epidemic strains Alpha, Delta and Lambda, pseudovirus and S protein. As well as ACE-2 overexpressing cell lines, it can be used for neutralizing antibody detection and vaccine titer evaluation.
Nearshore protein pseudovirus (Pseudovirus) is a SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus (Novoprotein Cat.XCV01-XCV11) packaged with HEK 293T based on a lentivirus packaging system. Spike protein is expressed on the surface of the virus, and the RNA core is green fluorescent protein ( GFP) or Luciferase. The virus can specifically infect cells expressing ACE2 (Novoprotein Cat. XCC14). After the virus infection is successful, the cells will emit green fluorescence or express Luciferase, and the infection efficiency can be judged by observing GFP under a microscope or detecting the Luciferase value with a microplate reader.
Features of Nearshore Protein New Coronavirus Pseudovirus:
Lentiviral system
SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus packaged with HEK 293T using a three-plasmid packaging system, and Spike protein is expressed on the surface of the virus;
Replication defective
It can only infect cells once, has no autonomous replication ability, and will not use host cells to produce new virus particles, which is highly safe;
Strong operability
No P3 laboratory is required, only the BSL-2 laboratory and Class Ⅱ biological safety cabinet conditions are required, and the detection can be carried out in real time;
GFP reporter gene
Microscope observation of GFP to determine the infection efficiency of pseudovirus is simple and convenient;
Luc reporter gene
The microplate reader detects the value of Luciferase to determine the infection efficiency of the false virus, and realizes the quantitative analysis;
Complete variety
A series of mutant pseudoviruses including Alpha, Delta and Lambda can be selected at will;
Data results:
Using the pseudovirus system, Nearshore Protein verified the GFP effect of SARS-CoV-2 (D614G) pseudovirus infecting cells and the Luc effect of the Delta mutant strain.
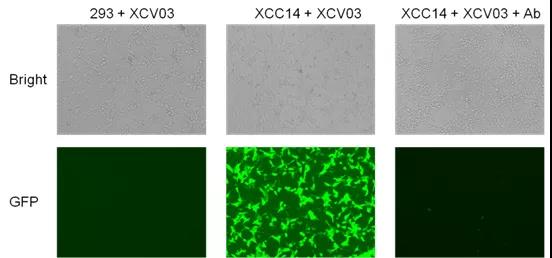
Neutralizing antibody inhibits pseudovirus infecting cells. Fluorescence photographs of cells after infection were taken with a fluorescent inverted microscope; 293 cells that do not express ACE-2 are not infected.
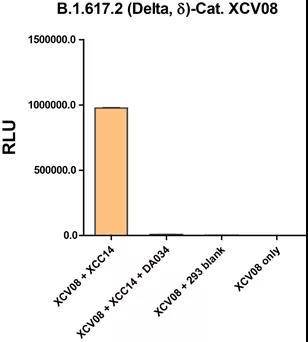
The Detla mutant strain has a strong ability to infect ACE-2 cell lines, and 293 cells that do not express ACE-2 will not be infected; neutralizing antibodies have a good inhibitory effect on the Delta mutant strain
Using the pseudovirus system, Nearshore Protein verified the blocking effect of a certain neutralizing antibody against 9 new coronavirus mutant strains. The data are as follows:
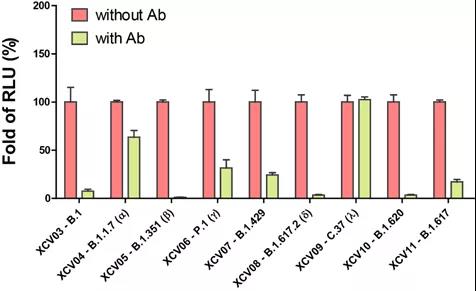
Neutralizing antibodies inhibit pseudoviruses from infecting cells
The results showed that this neutralizing antibody has a good blocking effect on B.1, B.1.351 (Beta), B.1.617.2 (Delta), and B.1.620 mutant strains, and has a good blocking effect on P.1 (Gamma), B.1.429 The blocking effect of B.1.617 (Kappa) mutant strain is average, and it has almost no blocking effect on B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and C.37 (Lambda) mutant strains. This data confirms the situation reported in the literature that the protective effects of vaccines or neutralizing antibodies in the serum of recovered patients are very different before different mutant strains.
Pseudovirus: A powerful tool to evaluate the protection of COVID-19 vaccines
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.