Is it reliable to achieve “COVID-19 herd immunity” from natural infections?
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
- New Ocrevus Subcutaneous Injection Therapy Shows Promising Results in Multiple Sclerosis Treatmen
- Dutch Man Infected with COVID-19 for 613 Days Dies: Accumulating Over 50 Virus Mutations
- Engineered Soybeans with Pig Protein: A Promising Alternative or Pandora’s Dish?
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS): A Tick-Borne Threat with High Mortality
Is it reliable to achieve “COVID-19 herd immunity” from natural infections?
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Is it reliable to achieve “COVID-19 herd immunity” from natural infections? Three top journals released shocking results
On March 23, the New England Journal of Medicine published an article by an Austrian scholar showing that people who were only infected with the Omicron variant but not vaccinated may not be adequately protected against infection with other variants.

Coincidentally, two studies published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases and Cell on March 17 and March 18, respectively, came to similar conclusions.
The latter researchers found that the rise in antibody titers from a breakthrough infection in Omicron was only one-third that of receiving a booster shot.
This may reveal that the breakthrough infection of Omicron is less immunogenic, reducing protection against reinfection or against future mutant infection.
Unvaccinated infected person: Neutralizing antibodies are barely detectable
Let’s start with an article published by an Austrian scholar in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Four groups were studied (Figure 1) :
- A: Vaccines who have not been infected with the new coronavirus before (15 people) ;
- B: have not been infected with the new coronavirus before and have not been vaccinated (18 people) ;
- C: Patients who have been vaccinated and have been infected with the new coronavirus (11 people) ;
- D: Unvaccinated patients (15 people) who have been infected with the new coronavirus .
After group B was infected with Omicron, the serum only had antibodies against Omicron, and only a small amount against other mutants. Two of them had no neutralizing antibodies at all against other mutants, indicating that infection with Omicron alone cannot provide adequate protection against other mutants.
At the same time, after infection with Omicron, the serum neutralizing antibody titers of subjects in group A were significantly higher than those in group D, suggesting that vaccination may be more “effective” than previous infection.
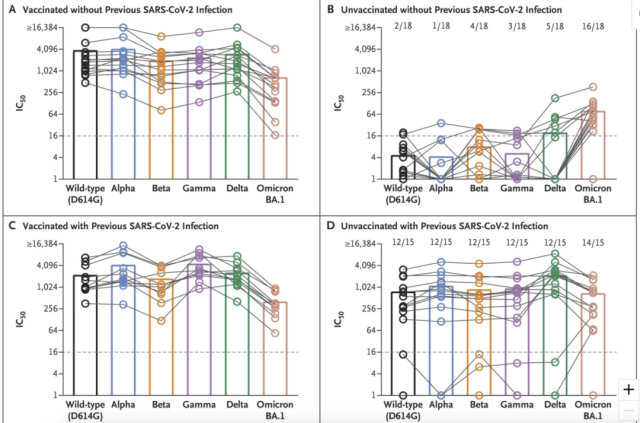
Figure 1 Study groups and results
In The Lancet Infectious Diseases, Swedish researchers came to a similar conclusion.
The researchers collected serum samples from 26 medical staff who were diagnosed with new coronavirus infection in April or May 2020. Of these, 9 medical staff had serum samples taken two months later (before vaccination) , and another 17 were vaccinated thereafter.
In the sera of 9 infected but unvaccinated medical staff, the neutralizing activity against wild-type SARS-CoV-2 remained to some extent, but the neutralizing activity against Omicron was almost undetectable.
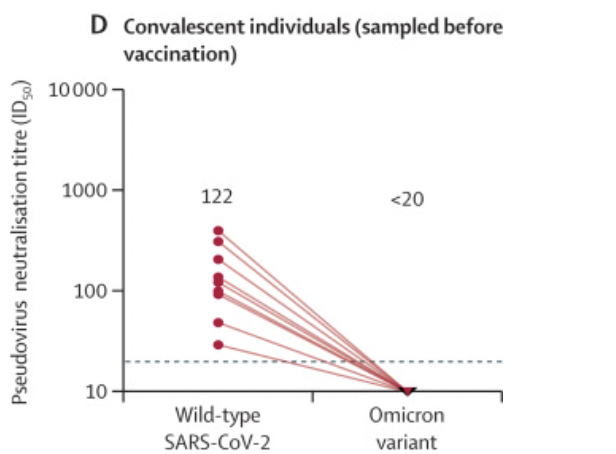
Figure 2 Neutralizing antibodies in 9 infected but unvaccinated individuals
Health care workers who were vaccinated fared much better. Both the wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and the Omicron variant showed high neutralizing antibody activity.
The average ID50 titers of these 17 medical staff were 495 for wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and 105 for Omicron strain, and 2 of them showed no difference in neutralizing antibody activity against the two strains (Figure 3). .
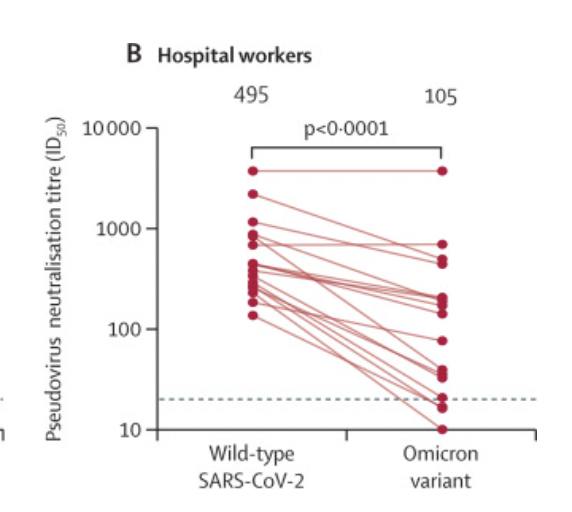 Figure 3 Neutralizing antibodies of 17 vaccinated people
Figure 3 Neutralizing antibodies of 17 vaccinated people
“Although other components of the immune system also help prevent severe disease, the significantly reduced susceptibility to neutralization may translate into reduced vaccine-mediated protection against infection,” the Swedish researchers said.
At the same time, the researchers believe that re-vaccination after infection can significantly increase the activity of neutralizing antibodies against mutant strains, again suggesting that simple acquired immunity after infection has limited effects, and the effect of vaccination is irreplaceable.
The antibody titer after infection is only 1/3 of the booster needle
Compared with the research of Swedish scholars, the research published by American scholars in “Cell” is much more complicated. It analyzed the breakthrough infection of Delta and the breakthrough infection of Omicron respectively, and included the control of booster injection separately. Group.
These people were all vaccinated, either mRNA vaccine or adenovirus vaccine, in 4 groups:
- a: 48 people who received two doses of the vaccine but were not infected;
- b: 15 people who received booster shots but were not infected;
- c: 39 patients who were vaccinated (no distinction was made between booster shots) and were breakthroughly infected by Delta;
- d: 14 patients who were vaccinated (no distinction was made between booster shots) and were breakthrough infected by Omicron.
In the pseudovirus experiment, the comparison between the two groups a and b showed that after two doses of vaccine, the neutralizing antibody activity against Omicron decreased to a very low level over time (17) , while in the booster dose was significantly boosted after (635) (Fig. 4) .
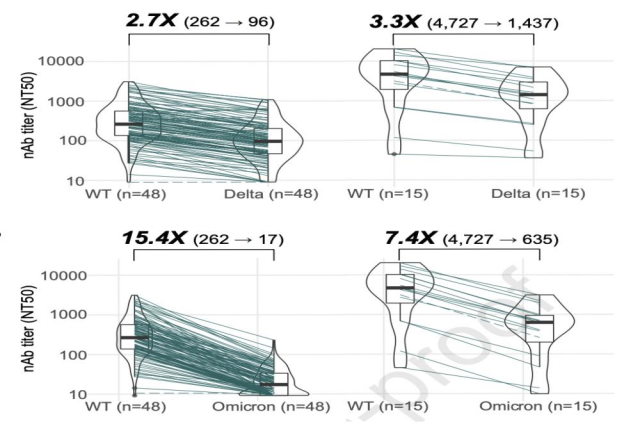 Figure 4. Results of group a (n=48 on the left) and group b (n=15 on the right)
Figure 4. Results of group a (n=48 on the left) and group b (n=15 on the right)
Looking at the data in group d, after the breakthrough infection by Omicron, the neutralizing antibody titers against wild-type, Delta, and Omicron were 1524, 467, and 387, respectively.
This shows that after the breakthrough infection by Omicron, although the activity of neutralizing antibodies against different mutants has increased, it is still far less than the effect of booster needles.
Against the progenitor wild-type strain, the post-infection neutralizing antibody titer was only 1/3 that of the booster (1524 vs. 4272) . Even against the Omicron strain itself, it was only 3/5 (387 vs 635) .
Delta breakthrough infections are different. The true virus test compares the two groups b and c and shows that:
Antibody titers obtained after breakthrough infection with delta strain rose, similar to receiving boosters;
- However, in the face of the improvement of Omicron’s immune escape ability, it is suggested that the broad-spectrum neutralization effect is not strong, and the effect is not as good as receiving a booster needle.
- Conversely, the cross-neutralization of delta after infection by the Omicron strain was also limited, with a 2.2-fold difference in potency against the original wild-type strain and the delta strain in the true virus assay.
- Among those in group A who had not been infected with Omicron, the difference was three-fold.
The article thus concludes:
In addition to increased neutralizing activity against the progenitor wild-type strain for breakthrough infections in Delta and Omicron, the degree of cross-neutralizing immunity that patients acquire is limited.
Omicron does not represent the ‘end of the pandemic’
U.S. researchers also specifically compared “face-to-face” differences in breakthrough infections between Delta and Omicron strains.
55 breakthrough infections, 35 delta, 20 Omicron.
For all patients, Delta breakthrough infection resulted in a 3.5-fold increase in neutralizing antibody titers against wild-type compared with Omicron (19806 vs. 5682) . The researchers believe that this difference is not significant, and it is estimated that the strengthening needle played a large role in it.
However, when only patients who did not receive a booster shot were analyzed, breakthrough delta infection had 10.8-fold higher neutralizing antibody titers against progenitor wild-type compared with Omicron (20481 vs 1905, P=0.037, Figure 5) .
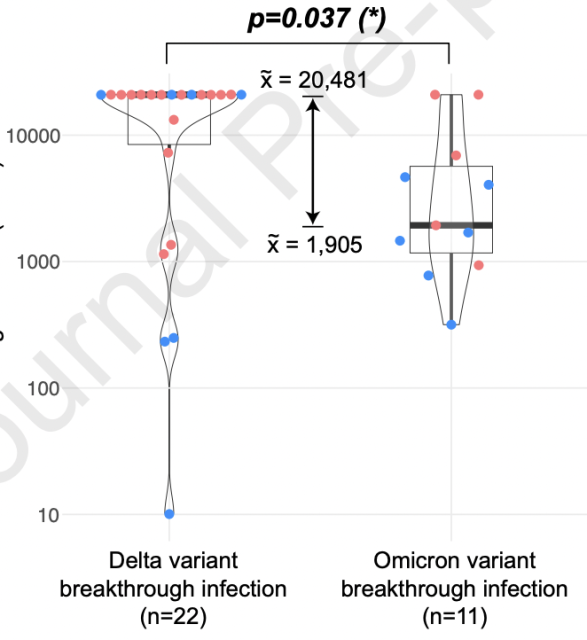
Figure 5 Comparison of neutralizing antibody titers for breakthrough infection of different strains
Further analysis found that no matter what kind of viral infection, without receiving the booster injection, the antibody titers of moderate and severe patients were 12.3 times higher than those of mild patients, and 5 times higher than those who received the booster injection.
This nicely explains part of the reason for the higher antibody titers after Delta’s breakthrough infection:
Because Omicron infection is mostly mild (28.6%) and asymptomatic (55%) , and the more severe the symptoms, the more neutralizing antibodies may be produced.
The researchers believe that at the moment of the pandemic of the Omicron strain, although it has been shown to cause mild disease, and many people think it is a sign of the end of the pandemic, the breakthrough infection of Omicron Very limited levels of neutralizing antibodies are produced.
“Thus, if another, more pathogenic variant emerges in the future, the immunity from a breakthrough infection from Omicron may not be as durable as from other variants , such as Delta , in terms of preventing infection. .”
The researchers also re-emphasized the importance of vaccination booster shots.
“There is no way to enter ‘herd immunity’ by infection”
In response to the above findings, virology expert Chang Rongshan responded to a request from the “medical community” for comment.
“Compared with various viruses in history, the mutation rate of the new coronavirus itself is not so fast, but the mutant strains are frequently found at present. The reason is that the infection base is too large, resulting in the continuous ‘evolution’ of the virus. Immune evasion is also increasing day by day.”
“In the face of these new coronavirus variants with strong immune evasion ability, natural infection cannot form ‘herd immunity’, as the above-mentioned Swedish study can prove.”
“After infection with the progenitor new coronavirus, the neutralizing antibody titer in the body was initially high, but almost all dropped significantly after 4 months. When the new variant came, the neutralizing antibody and cellular immunity produced by the previous generation of natural infection It is not enough to prevent a new round of infection, which has happened three times, with the alpha variant, the delta variant, and the Omicron variant.”
“The root cause of what appears to be ‘herd immunity’ is the high vaccination rate and booster shots. Although protection from natural infection cannot be ruled out, the effect is very limited.”
References:
[1] Neutralization Profile after Recovery from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infection,
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2201607?query=featured_home
[2] Neutralizing immunity in vaccine breakthrough infections from the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants , https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867422003294
[3] Neutralisation sensitivity of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) variant: a cross-sectional study , https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(22) 00129-3/fulltext#fig3
Is it reliable to achieve “COVID-19 herd immunity” from natural infections?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.