The virulence of the new coronavirus variant will become weaker in the future
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
- New Ocrevus Subcutaneous Injection Therapy Shows Promising Results in Multiple Sclerosis Treatmen
- Dutch Man Infected with COVID-19 for 613 Days Dies: Accumulating Over 50 Virus Mutations
The virulence of the new coronavirus variant will become weaker in the future
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Controversy | The virulence of the new coronavirus variant will become weaker in the future.
As early as the early days of the outbreak in Wuhan, it was heard that the more infectious the virus, the weaker its virulence, and eventually it would evolve towards a weakening of its virulence.
This logically makes sense. The virus can only rely on the host to maximize its copy number. The virulence is too strong.
Once infected, bedridden or quickly killed, there is not much chance to contact more people and spread. power is limited.
In order for the virus to coexist with humans, the transmissibility must become stronger and the toxicity weakened, which is also reflected in the Omicron variant.
However, is there a correlation between the transmissibility and pathogenicity of the virus? Will the new coronavirus necessarily evolve in a direction of less virulence? This is a highly controversial topic, and today we look at some different points of view.
Antigen map of COVID-19 mutants
Recently, a pseudovirus neutralization test was used to evaluate the neutralizing antibody titers of recovered sera from unvaccinated patients with COVID-19s against various COVID-19 mutants.
Except for the sera of patients infected with Beta mutants, the sera of patients with other mutants targeted Homologous viruses had the highest neutralizing antibody titers.
Infection with the original strain or Alpha strain, serum neutralizing antibodies have the broadest neutralizing ability, while infecting other mutant strains, serum neutralizing antibodies show more strain specificity.
The neutralization ability of Omicron mutants by the sera of survivors infected with other mutants was greatly reduced.
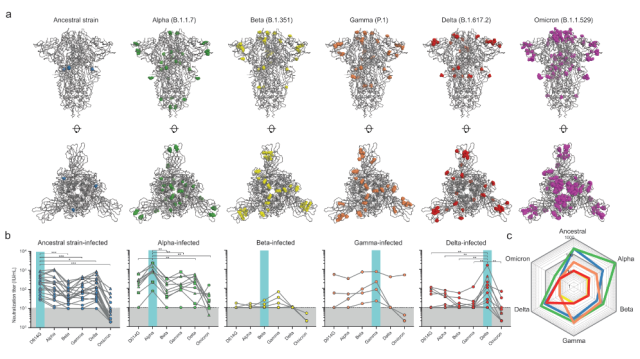
Gene differences and serum antibody neutralization responses of new coronavirus variant strains
The antigen map ( angenetic cartography ) of the new coronavirus variant can be drawn through the data of serum neutralizing antibodies to reflect the changes in the antigenic properties of the pathogen. In this figure, the small squares represent the sera of the infected variant, and a grid represents the 2-fold change in antibody titer.
In the influenza virus antigen map, it is generally believed that if the antigenic distance of the mutant strains is less than 3 units, that is, the antibody titer change is less than 8 times, then the antigenic properties of the two mutant strains are similar.
The COVID-19 antigen map reflects that the COVID-19 variant strains before the emergence of Omicron belong to the same antigenic cluster, while Omicron belongs to a new antigenic cluster .
The distant antigenic units of the Omicron mutant and other mutants suggest that the current high infection rate of Omicron is at least partly due to its antigenic immune escape, and the development of specific vaccines for it is very necessary [1] .
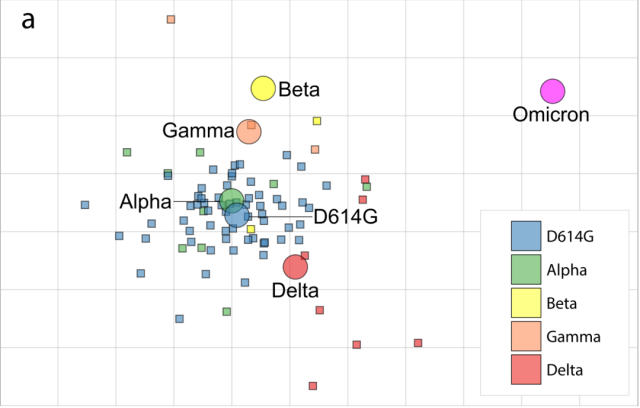 Antigen map of COVID-19 mutants
Antigen map of COVID-19 mutants
There is no regularity in the evolution of viruses
On April 13, 2022 , Mr. Rao Yi once posted on his official account platform to refute the view that “the more widespread the virus is, the milder the symptoms” , thinking that the virus is infectious, antigenic, pathogenic, and human symptoms. , with no correlation. The virus will not be more infectious or weaker because of the longer the epidemic.
The mutation of the virus is also irregular. It may become mild for a while, but it may also become severe.
Virus mutation itself is not directional, but is subject to selection. If the infectivity is enhanced after mutation, it is easy to spread. Only an appallingly high virus fatality rate can stop the spread of a vicious strain by killing the sick.
The mortality rate of the new coronavirus is only a few percent or a few tenths of a percent, so there is no possibility that the person’s symptoms are strong and the transmission rate is low.
The full text is explaining a basic fact that there is no law in the evolution of viruses, and there is uncertainty.
Virulence evolution
On March 14, 2022 , Nikolaos I. Stilianakis et al. published an article in Nature Reviews Microbiology Antigenic evolution will lead to new SARS-CoV-2 variants with unpredictable severity , saying that despite the milder infection of Omicron variants and the improvement of herd immunity Hopes for a weakening of the epidemic are greatly enhanced, however, the extremely low pathogenicity of the Omicron variant may be merely an accident, and uninterrupted rapid antigenic evolution may produce new variants that escape existing immunity and are more severely pathogenic.
One of the most persistent myths about pathogen evolution is that viruses will evolve towards less virulence without sacrificing the host.
The immune evasion and transmissibility of viruses are under strong evolutionary pressure, but virulence is altered by complex interactions between pathogens and hosts.
Viruses evolve toward greater transmissibility, which may sometimes be accompanied by high virulence, for example, if a high viral load not only facilitates transmission, but also increases pathogenicity, the virus may move toward higher virulence direction of evolution.
If pathogenicity is only manifested in the late stages of infection after the typical transmission window, e.g. influenza, HIV, HCVD, etc., then it has a limited role in viral fitness and the evolution of the virus will not choose to move towards weak pathogenicity .
Predicting the evolution of virulence is complicated, and the virulence of future variants cannot be predicted by virtue of the low pathogenicity of Omicron. Unfortunately, future mutants are likely to combine the reinfection ability acquired by immune escape with high virulence.
Antigen evolution
Another common misconception is that widespread vaccine or infection-triggered immunity must guarantee mild pathogenicity in the future.
This view completely ignores the evolution of antigens – viruses that continually modify antigenic properties in the face of host immune stress.
Rapid antigen evolution can lead to immune escape, thereby reducing the immune system to prevent infection and severe disease. At the population level, antigen evolution and immune escape increase the odds of severe infection and disease severity.
Omicron has clearly proved that the new coronavirus can acquire a large number of antigenic mutations in a short period of time.
Compared with the original Wuhan strain, there are 50 amino acid mutations in Omicron, 37 mutations in Spike protein, and 15 mutations in the RBD region.
The antigenic properties are completely different from the previous mutants. The explosive spread of Omicron in highly immune populations suggests that these mutations make Omicron highly susceptible to infecting individuals previously immune to infection or vaccines.
In September 2020, after a short period of evolutionary stabilization, new coronavirus variants carrying a large number of differentiated antigens began to appear. At least 3 early variants, Beta, Gamma, Delta, have obvious immune escape mutations, and there is no existing evidence that the evolution of the new coronavirus antigen will slow down in the future. Instead, the variants currently in focus are just the tip of the iceberg in the evolution of the virus.
Hundreds of new coronavirus lineages will dissociate from each other over time, and evolutionary theory predicts that the probability of immune escape of virus variants will increase in the future.
Adaptive evolution
Viral fitness was quantified by the effective infection number Rt. The effective infection number is different from the base infection number R0.
The effective number of infections Rt refers to the total number of new infections caused by infected individuals in only one group and not all people are susceptible to infection.
Therefore, the most adaptable virus is the one that infects the largest number of hosts. In a situation where all people are susceptible, the virus achieves increased fitness by becoming more infectious.
The evolution of the early COVID-19 mutants is along this road, Alpha, and Delta are nearly 50% more infective than the original strain, thus quickly replacing the original strain and dominating the population.
In highly immune populations, the mere increase in infectivity has a relatively weak effect on transmissibility, since the barrier to transmission in this case is the host’s resistance to infection.
Correspondingly, as the population has higher immunity, the novel coronavirus will likely optimize the transmissibility ( Rt ) more by increasing the ability to re-infect the immune population, rather than becoming more infectious.
In this way, an increase in herd immunity may accelerate the rate of antigenic evolution, leading to an increased risk of re-infection and the probability of disease severity following re-infection.
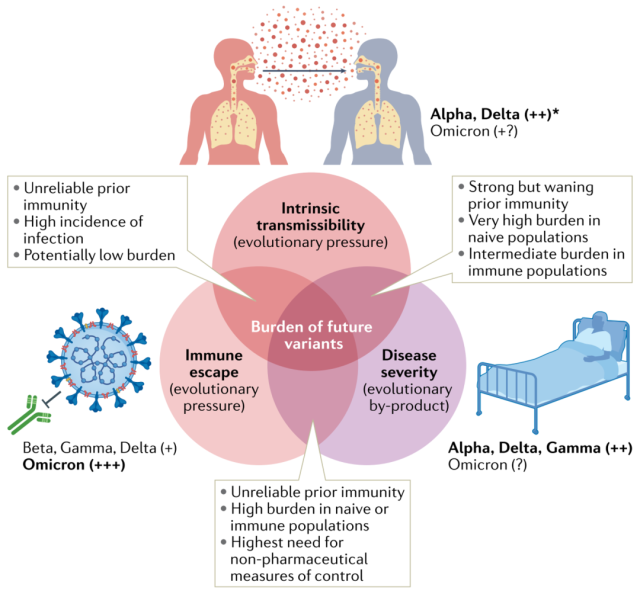 The impact of the interaction between virus transmissibility, disease severity, and immune escape of variant strains on the future population load of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The impact of the interaction between virus transmissibility, disease severity, and immune escape of variant strains on the future population load of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Summary
The virulence of the new coronavirus variant will become weaker in the future.
The super-transmissibility of the new coronavirus Omicron in the population provides infinite possibilities for the mutation and recombination of the virus, resulting in the emergence of new highly adaptable mutant strains. No one can predict which direction the pathogenicity of the new variant strains will go in the future, and everything is possible.
In the absence of highly effective drugs to block the spread of the virus, it is very necessary to increase the vaccination rate of the population and take restrictive measures to delay the emergence of new mutant strains.
Vaccination is an effective means, and isolation and prevention and control are also effective means, and there is no need to oppose the two.
The protection effect of the vaccine is good, then the physical prevention and control will be weakened. Vaccine prevention is ineffective, and physical prevention and control can only be tightened. The virus is emotionless, and it doesn’t listen to anyone’s expectations to decide where to go next.
There is a price we have to pay, because the most rigorous aspect of biological systems is that exceptions and surprises are always allowed .
How to balance the supremacy of life and survival and development, will there be no accidents… The threat posed by the COVID-19 is far more than the biological level, but more about the tearing and opposition of cognition.
References
1. Mapping the antigenic diversification of SARS-CoV-2
2. The title image is from Google Gallery
The virulence of the new coronavirus variant will become weaker in the future
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



