Pfizer Q1: 16 regulatory approvals expected in 18 months
- Did Cloud Seeding Unleash a Deluge in Dubai?
- News draftScientists Identify Gut Bacteria and Metabolites that Lower Diabetes RiskNews draft
- OpenAI’s Model Matches Doctors in Assessing Eye Conditions
- UK: A Smoke-Free Generation by Banning Sales to Those Born After 2009
- Deadly Mutation: A New Monkeypox Variant Emerges in the DRC
- EPA Announces First-Ever Regulation for “Forever Chemicals” in Drinking Water
Pfizer Q1: 16 regulatory approvals expected in 18 months
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Pfizer Q1: 16 regulatory approvals expected in 18 months. What are the latest developments to watch?
Recently, Pfizer announced its financial results for the first quarter of 2022. During the conference call, the company’s executives highlighted recent advances in key clinical development programs in the areas of COVID-19, inflammation and immunology, infectious diseases, oncology and rare diseases.
The latest research and development progress of the COVID-19 vaccine
Comirnaty, an mRNA vaccine jointly developed by Pfizer and BioNTech, was used as a booster to significantly increase neutralizing antibody levels against the Omicron variant in children aged 5-11. The neutralizing titer against Omicron BA.1 subspecies was increased 36-fold, and it also showed potent neutralizing activity against other Omicron subspecies.
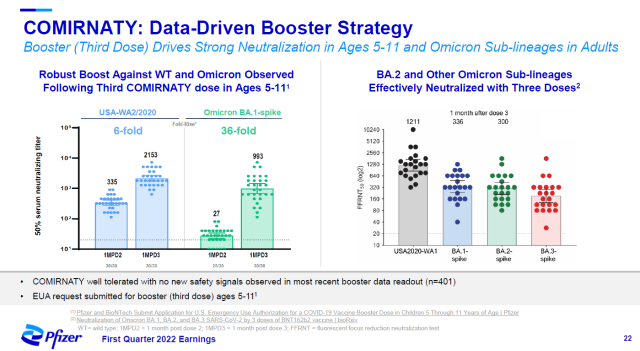
▲The role of Comirnaty enhancement needles in children aged 5-11 (Image source: Pfizer official website)
In addition, in people over 50 years of age, real-world data from Israel showed that receiving a second booster dose during the Omicron epidemic significantly reduced the risk of hospitalization, severe illness, or death due to COVID-19. At present, more than 15 countries around the world have recommended vaccination of the second booster dose in high-risk groups.
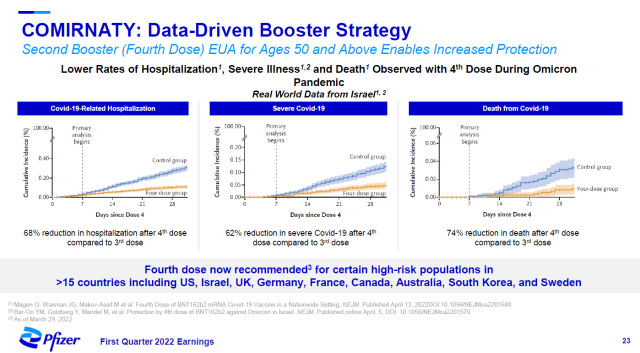
▲ Comirnaty’s second dose booster reduces the risk of hospitalization, severe COVID-19, and death in people over 50 years old (Image source: Pfizer’s official website)
Potential ‘best-in-class’ oral ulcerative colitis drug
Pfizer completed its acquisition of Arena Pharmaceuticals on March 11 this year. The company’s lead drug is the next-generation oral S1P modulator etrasimod, which specifically binds to S1P receptors 1, 4, and 5 and may have a better efficacy/safety profile.
In two Phase 3 clinical trials in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis, etrasimod met both the primary and key secondary endpoints. Patients achieved statistically significant improvements in clinical remission after 12 and 52 weeks of treatment.
Pfizer said that etrasimod’s mechanism of action has the potential to treat inflammatory diseases other than ulcerative colitis, and clinical trials to test the efficacy of etrasimod in the treatment of Crohn’s disease, alopecia areata, atopic dermatitis, and eosinophilic esophagitis have all entered Phase 2 clinical trials development stage.
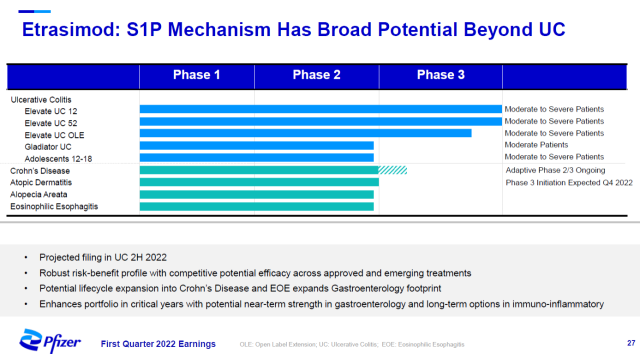
▲Etrasimod’s clinical development project (Image source: Pfizer’s official website)
Several clinical trials of JAK3/TEC selective inhibitors are progressing positively
A feature of Pfizer’s JAK3/TEC-selective inhibitor, ritlecitinib, is that it avoids inhibition of JAK1, JAK2, and TYK2 activity. These are the main targets of existing oral JAK inhibitors, which are effective in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, but also bring some side effects.
Ritlecitinib may reduce drug side effects while still suppressing intrinsic drivers of widespread immune-inflammatory disease. In a phase 3 clinical trial for the treatment of alopecia areata, ritlecitinib has met the primary efficacy endpoint of improving scalp hair regrowth, with a significantly higher proportion of patients in the ritlecitinib group than in the placebo group with ≤20% scalp hair loss after 6 months of treatment.
The company expects to submit a New Drug Application (NDA) for ritlecitinib in the treatment of alopecia areata in the second quarter of this year.
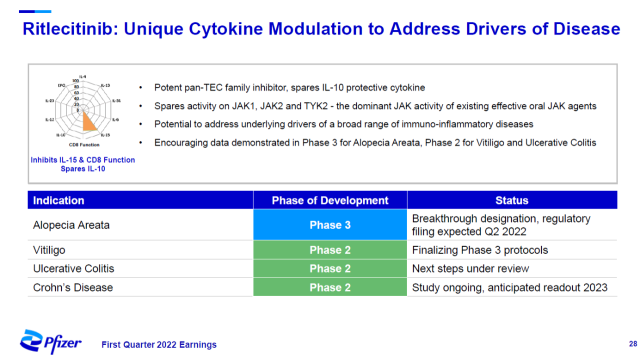
▲Introduction to Ritlecitinib (Image source: Pfizer official website)
In a phase 2b clinical trial for the treatment of vitiligo, patients received significant improvement in the Facial Vitiligo Area Severity Index (F-VASI) after 48 weeks of treatment. Pfizer expects to initiate a Phase 3 clinical trial in the second half of this year.
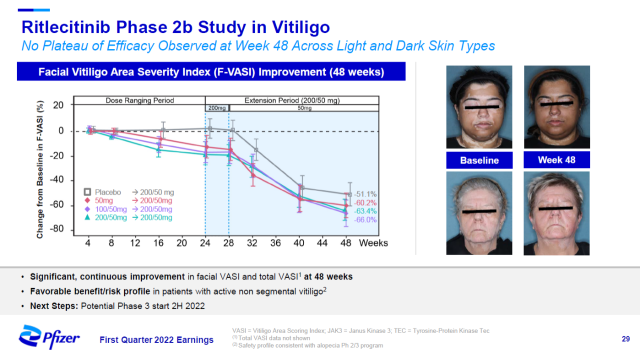
▲ The results of the Phase 2b clinical trial of Ritlecitinib in the treatment of vitiligo (Image source: Pfizer official website)
Potential ‘best-in-class’ anti-RSV therapy
Pfizer recently reached an agreement with ReViral to acquire ReViral for about $525 million to acquire its respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) therapy sisunatovir.
Sisunatovir is an oral anti-RSV drug that blocks the fusion of RSV with the cell membrane by binding to the F protein of RSV, preventing the virus from infecting cells.
In a virus-challenged Phase 2 clinical trial in healthy volunteers, it met the primary endpoint of significantly reducing the volunteers’ viral load. This therapy has been granted Fast Track status by the US FDA.
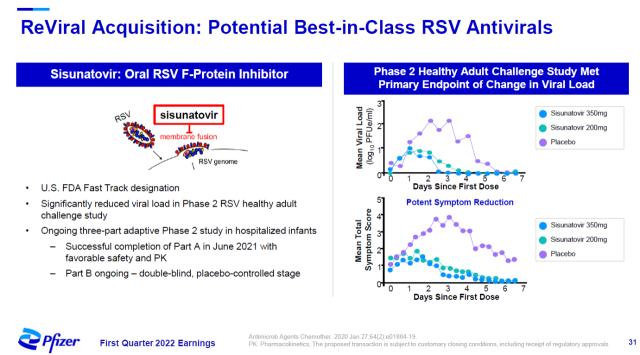
▲Introduction to Sisunatovir (Image source: Pfizer official website)
In the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, the third-generation ALK inhibitor has a positive effect for 3 years
At the recently concluded AACR annual meeting, Pfizer announced the 3-year follow-up results of its third-generation ALK inhibitor lorlatinib (Lorbrena).
The trial results showed that lorlatinib reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 73% compared with the active control group.
The therapy also recently received regulatory approval in China for the treatment of ALK-positive locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.
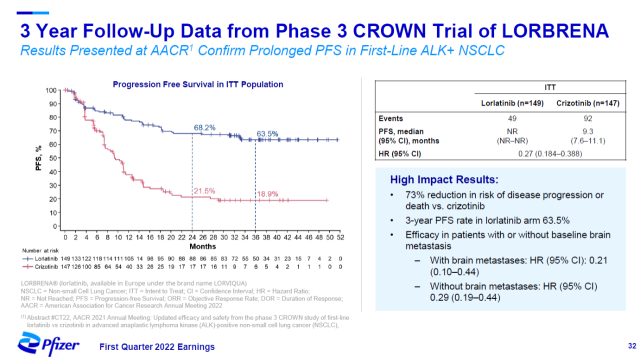
▲ Lorlatinib significantly reduces the risk of disease progression or death in patients (Image source: Pfizer official website)
Lorlatinib has also shown good effects in preventing brain metastases due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Results of 3-year follow-up showed that in intention-to-treat patients, lorlatinib reduced the risk of developing brain metastases by 92% compared with active controls.
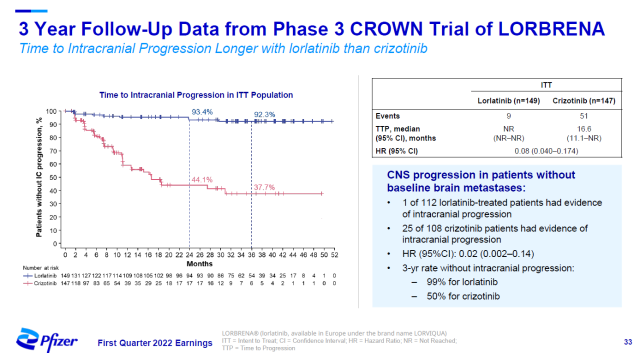
▲ Lorlatinib significantly reduces the risk of cancer brain metastases (Image source: Pfizer official website)
Multiple strategies to treat all types of hemophilia
In the treatment of hemophilia, Pfizer’s gene therapy for hemophilia B has shown positive results in Phase 1b/2 clinical trials, with an average annual bleeding rate of 0.1 in patients who were followed for 3-5.5 years after treatment. ~0.9.
The therapy will receive pivotal clinical trial results in the first quarter of 2023. The company’s gene therapy for hemophilia A has been cleared by the FDA and is expected to restart pivotal clinical trials in the third quarter of this year.
In addition, the company’s development of marstacimab, a candidate therapy that does not directly target coagulation factors, is a monoclonal antibody that targets tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI).
TFPI is an anticoagulant protein, and targeted inhibition of the function of TFPI provides a new subcutaneous prophylaxis for hemophilia A and B patients, regardless of the presence or absence of antibodies against the clotting factor.
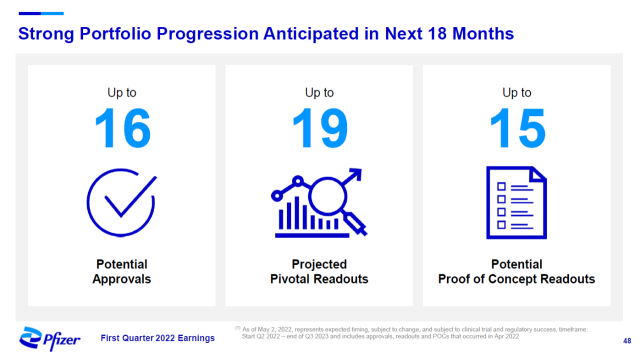
source: Pfizer official website
Pfizer said it expects to receive up to 16 regulatory approvals, up to 19 pivotal clinical trial results, and up to 15 proof-of-concept trial results over the next 18 months.
The company’s financial report also introduced the company’s operating status, limited space, this article will not introduce them one by one.
References:
[1] PFIZER REPORTS FIRST-QUARTER 2022 RESULTS. Retrieved May 3, 2022, from https://s28.q4cdn.com/781576035/files/doc_financials/2022/q1/Q1-2022-PFE-Earnings-Release.pdf
[2] First Quarter 2022 Earnings Teleconference. Retrieved May 3, 2022, from https://s28.q4cdn.com/781576035/files/doc_financials/2022/q1/Q1-2022-Earnings-Charts-FINAL-(1). pdf
Pfizer Q1: 16 regulatory approvals expected in 18 months. What are the latest developments to watch?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.