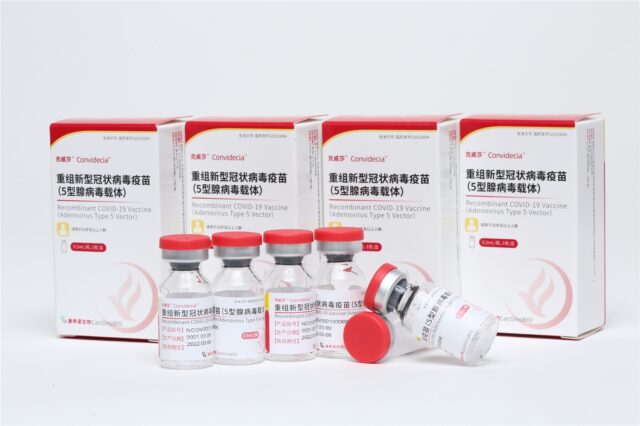
CanSino’s COVID-19 vaccine is included in WHO’s emergency use list (EUL)
- A Persistent Crisis: The Looming Specter of Drug Shortages in United States
- Rabies: The fatality rate nearly 100% once symptoms appear
- Human Brain Continues to Grow: Study Shows Increase in Size and Complexity
- CRISPR Genome Editing: From Molecular Principles to Therapeutic Applications
- Metformin Helps Immune System Better Recognize Cancer Cells
- Highlights of Prostate Cancer Research at the 2024 EAU Congress
CanSino’s COVID-19 vaccine is included in WHO’s emergency use list (EUL)
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
CanSino’s COVID-19 vaccine is included in WHO’s emergency use list (EUL).
On May 19, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced on the 19th that the adenovirus vector COVID-19 vaccine developed by China’s CanSino Bio has been approved by the WHO for emergency use authorization and included in the Emergency Use List (EUL).
This is China’s third COVID-19 vaccine listed on the WHO emergency use list after Sinopharm and SINOVAC vaccine, and it is also China’s first adenovirus vector COVID-19 vaccine and single-dose COVID-19 vaccine in the list.

It is reported that in the first half of 2021, CanSino Bio’s adenovirus vector COVID-19 vaccine has completed the submission of the letter of intent and the pre-review meeting procedure before submission, and started rolling data evaluation, becoming a “Chinese candidate” on the emergency use list.
After months of rigorous review and on-site inspections, technical reviews and relevant responses, WHO finally included the vaccine on the emergency use list.
According to public information, the vaccine was established in January 2020 and took the lead in launching clinical trials worldwide.
In May of that year, the results of clinical Phase I and Phase II trials were published in the world-renowned medical journal The Lancet.
In August of the same year, the vaccine obtained China’s first COVID-19 vaccine invention patent authorization. In February 2021, CanSino Bio’s adenovirus vector COVID-19 vaccine was approved for marketing with conditions in China, and has successively obtained emergency use approvals in Mexico, Pakistan, Chile, Argentina, Ecuador, Hungary, Indonesia, Kyrgyzstan and other countries.
Industry insiders believe that CanSino Bio’s adenovirus vector COVID-19 vaccine has been approved by the WHO for emergency use authorization, and will expand the list of vaccine libraries of the WHO-led “COVID-19 Pneumonia Vaccine Implementation Plan” (COVAX), which can be purchased and distributed by United Nations agencies. countries in need, giving more low- and middle-income countries the opportunity to accelerate vaccine deployment.
This will help deal with the current surge in the number of COVID-19 infections globally, insufficient vaccine supply, and slow progress in vaccination, and take a solid step towards making China’s COVID-19 vaccine a global public good, accessible and affordable in developing countries.
In addition, CanSino Bio has developed two other COVID-19 vaccines that are also in clinical trials, of which the inhaled adenovirus vector COVID-19 vaccine has received particular attention.
According to the information previously disclosed by CanSino Bio, the inhaled COVID-19 vaccine has been approved for clinical use in March 2021, and by the end of 2021, the clinical phase I/II trial has been completed.
The results of the world’s first publicly-published mucosal immunity clinical trial of the COVID-19 vaccine previously released by The Lancet showed that the aerosol inhalation inoculation of the COVID-19 vaccine of CanSino was well tolerated and did not cause any serious adverse reactions related to the vaccine.
28 days after the first intramuscular injection, aerosol boosting can induce strong immunoglobulin and neutralizing antibody responses, and the immune effect is better.
The results of previous studies on sequential strengthening have shown that after inoculation with 2 doses of inactivated vaccine and then 1 dose of inhaled COVID-19 vaccine, the level of neutralizing antibodies increased by about 300 times.
Last month, CanSino Bio announced on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange that the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine developed by the company has also obtained approval for drug clinical trials from the State Drug Administration.
Related News:
- CanSino: COVID-19 Booster shot increases neutralizing antibodies about 8 times
- CanSino released Phase 1 data of nebulized inhalation COVID-19 vaccine
- Argentina approved emergency use of China’s CanSino COVID-19 Vaccine
- COVID-19 Vaccine Company: Cansino obtained EU GMP certification
- Adenovirus Vector Recombinant vaccine: CanSinoBio VS AstraZeneca
CanSino’s COVID-19 vaccine is included in WHO’s emergency use list (EUL)
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.