- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
COVID-19 Vaccines in the world and related information
COVID-19 Vaccines in the world and related information. China and U.S. companies lead to the development of COVID-19 vaccines in the world.
Currently there are 5 different technical routes for COVID-19 vaccine:
01. Inactivated vaccine
Technical route:
Inactivated vaccines are the most traditional classic technical route: culture the new coronavirus in vitro and then inactivate it to make it non-toxic, but the “corpses” of these viruses can still stimulate the body to produce antibodies and make immune cells remember The appearance of living a virus. At present, three inactivated COVID-19 vaccines in some countries have entered clinical studies. Among them, the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine developed by Wuhan Institute of Biological Products has entered phase 2 clinical studies.
Advantages:
The advantages of inactivated vaccines are that the preparation method is simple and fast, and the safety is relatively high. It is the usual means to deal with the transmission of acute diseases. Inactivated vaccines are very common. The commonly used hepatitis B vaccines, inactivated polio vaccines, inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccines, and DPT vaccines in China are all inactivated vaccines.
Disadvantages:
However, inactivated vaccines also have disadvantages, such as large vaccination doses, short immunization period, and single immunization route. The most terrible disadvantage is that it sometimes causes antibody-dependent enhancement effects (ADE) and aggravates viral infections. This is one This is a serious adverse reaction that will lead to the failure of vaccine development.
02. Adenovirus vector vaccine
Technical route:
Adenovirus vector vaccine uses modified and harmless adenovirus as a carrier, loaded with the S protein gene of the new coronavirus to make an adenovirus vector vaccine to stimulate the body to produce antibodies. The S protein is the key “key” for the new coronavirus to invade human cells. The harmless adenovirus wears the S protein hat and pretends to be fierce, allowing the body to produce immune memory. The COVID-19 vaccine that Academician Chen Wei’s team is doing in the second phase of clinical trials is an adenovirus vector vaccine, which is a relatively mature vaccine technology route.
Advantages:
The advantages of adenovirus vector vaccines are: safety, high efficiency, and fewer adverse reactions. This vaccine has a successful precedent: Previously, the “recombinant Ebola virus disease vaccine” independently developed by the team of Academician Chen Wei and Tianjin Kangsino Biotechnology Co., Ltd. also used adenovirus as a vector.
Disadvantages:
This vaccine also has disadvantages. The development of recombinant virus vector vaccines needs to consider how to overcome “pre-existing immunity”. Take the “recombinant COVID-19 vaccine” that entered clinical trials as an example. This vaccine uses type 5 adenovirus as a carrier, but most people have been infected with type 5 adenovirus during growth, and there may be antibodies that can neutralize the adenovirus vector in the body. , Which may attack the vector and reduce the effect of the vaccine. In other words, the safety of the vaccine is high, but the effectiveness may be insufficient.
03. Nucleic Acid Vaccine (mRNA or DNA vaccine)
Technical route:
Nucleic acid vaccines include mRNA vaccines and DNA vaccines. They directly inject genes, mRNA or DNA encoding S protein into the human body, and use human cells to synthesize S protein in the human body to stimulate the body to produce antibodies. In layman’s terms, it is equivalent to handing over a detailed virus file to the body’s immune system. The mRNA COVID-19 vaccine approved by Moderna of the United States for Phase II clinical trials is a nucleic acid vaccine.
Advantages:
The advantages of nucleic acid vaccines are: there is no need to synthesize proteins or viruses during development, the process is simple, and the safety is relatively high. Nucleic acid vaccines are new technologies for vaccine research and development that are actively being explored all over the world. At present, there is no human-use nucleic acid vaccine on the market in the world. Some high-level corrections in China have carried out research on this route.
Disadvantages:
The technology of this vaccine is too new, and there is no successful precedent, so we don’t know where there may be pits in the development process! From an industrial point of view, although the production process itself is not complicated, most countries in the world have a relatively weak foundation in this field, and a stable and controllable large-scale production supply chain has not yet been formed. So its shortcomings are: there is no successful precedent, most countries are unable to produce on a large scale, and it may be difficult to spread to low-income countries because of the high price.
04. Recombinant protein vaccine
Technical route:
Recombinant protein vaccine, also known as genetic engineering recombinant subunit vaccine. It uses genetic engineering methods to mass-produce the S protein, which is the most likely antigen of the new coronavirus, and inject it into the human body to stimulate the body to produce antibodies. It is equivalent to not producing a complete virus, but separately producing the “keys” of many key components of the new coronavirus and handing it over to the body’s immune system. some countries has mastered the technology for mass production of high-quality and high-purity vaccine proteins. This is a technical route that can produce vaccines on a large scale and quickly.
Advantages:
The advantages of recombinant subunit vaccines are: safety, high efficiency, and large-scale production. This route has a successful precedent, and the more successful genetic engineering subunit vaccine is the hepatitis B surface antigen vaccine.
Disadvantages:
The disadvantage of recombinant subunit vaccines is that it is difficult to find a good expression system. Its antigenicity is affected by the selected expression system, so the expression system needs to be carefully selected when preparing the vaccine.
05. Attenuated influenza virus vector vaccine
Technical route:
The attenuated influenza virus vector vaccine uses an attenuated influenza virus vaccine that has been approved for marketing as a carrier, carrying the S protein of the new coronavirus, and co-stimulating the human body to produce antibodies against the two viruses. Simply put, this vaccine is a fusion virus formed by the low-toxicity influenza virus wearing the COVID-19 virus S protein “cap”, which can kill two birds with one stone, and can prevent influenza and COVID-19. When the epidemic of COVID-19 pneumonia overlaps with influenza, its clinical significance is very great. Since the attenuated influenza virus is easy to infect the nasal cavity, this vaccine can be vaccinated only by nasal drip.
Advantages:
The advantages of the attenuated influenza virus vector vaccine are: one vaccine prevents two diseases, less frequent vaccination, and simple vaccination method.
Disadvantages:
Live attenuated virus vaccines are a very important type of vaccine. Our usual live attenuated vaccines are: Japanese encephalitis live attenuated vaccine, hepatitis A live attenuated vaccine, measles live attenuated vaccine, rubella attenuated Live virus vaccine, live attenuated varicella vaccine, oral rotavirus live attenuated vaccine, etc. But the disadvantage of live attenuated vaccines is that the development process is long.
It should be noted that this technical route does not directly attenuate the new coronavirus into a vaccine, because it requires long-term virus culture and passage attenuation and screening; instead, it uses the attenuated influenza virus vaccine as a carrier. , The disease-causing S protein on the new coronavirus is transferred to the attenuated influenza virus vaccine through bioengineering methods, which can save a lot of virus culture, passage, attenuation and screening time.
COVID-19 Vaccines in the world and related information
China: 6 COVID-19 vaccines:
China is the first country to begin the development of COVID-19 vaccines. Therer are 5 vaccines are approved by Chinese government.
More than 500 million people have been vaccinated without serious adverse reactions till May 23, 2021.

There are 6 vaccines that have been approved by China CDC:
- China National Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. (SINOPHARM) :
- Beijing Bio-Institute;
- Wuhan Bio-Institute;
- Beijing Kexing Zhongwei Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
- PLA Academy of Military Sciences and CanSino Biologics
- Anhui Zhifeilongkoma Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- Kangtai Biological Products Co., Ltd.
China: 6 COVID-19 vaccines:
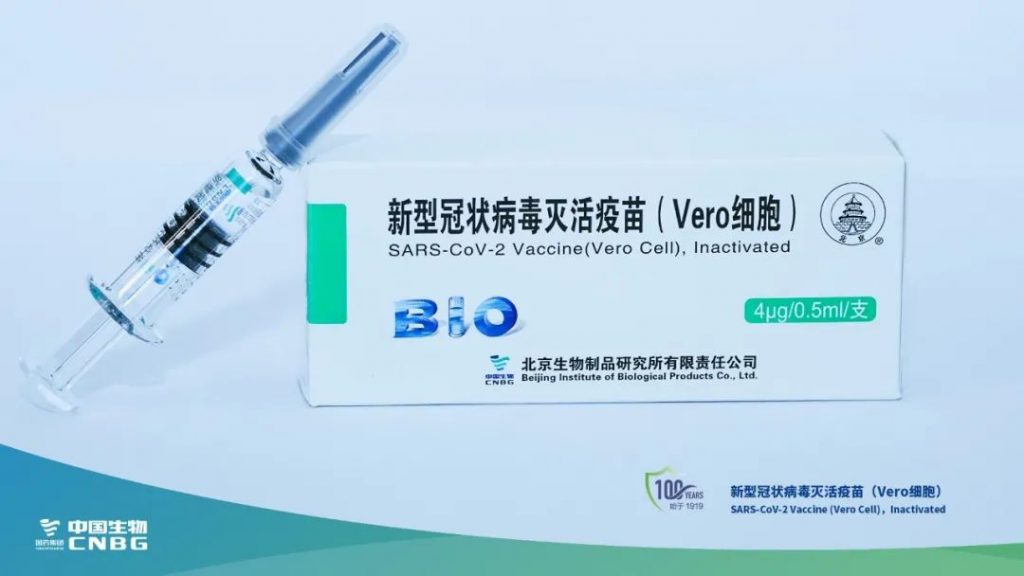
1. Beijing Bio-Institute (SINOPHARM)
- Inactivated vaccine (Vero Cell)
- Approved on Dec. 31, 2020
- Two doses
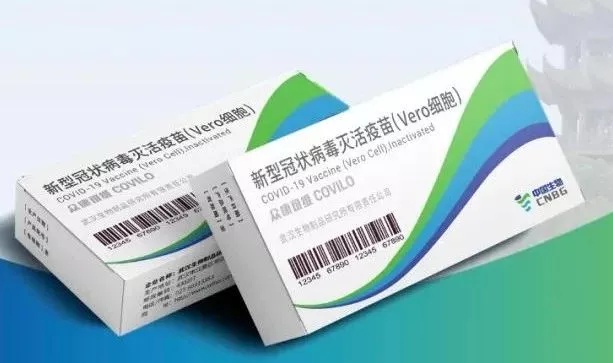
2. Wuhan Bio-Institute (SINOPHARM)
- Inactivated vaccine (Vero Cell)
- Approved on Feb. 25, 2021
- Two doses
3. Beijing Kexing Zhongwei Biotechnology Co., Ltd.,
- Inactivated vaccine (Vero Cell)
- Approved on Feb. 05, 2021
- Two doses

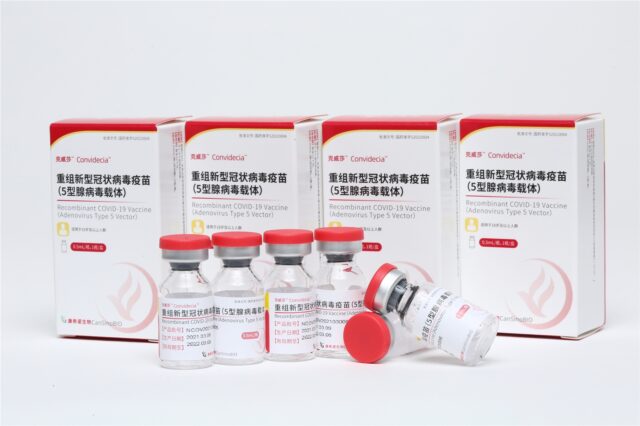
4. PLA Academy of Military Sciences and CanSino Biologics
- Recombinat vector vaccine (Adenovirus Type 5 Vector)
- Approved on Feb. 05, 2021
- One doses
4. Anhui Zhifeilongkoma Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- Recombinant protein vaccine (CHO Cell)
- Approved on Mar. 18, 2021
- Three doses
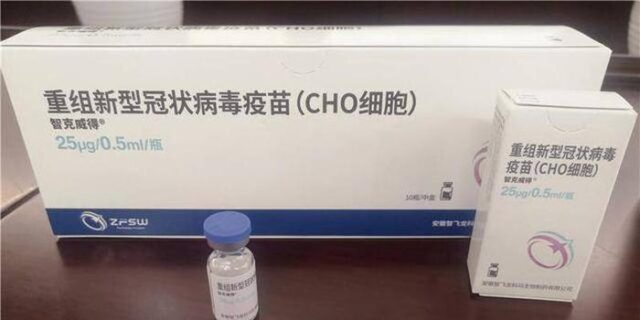
6. Kangtai Biological Products Co., Ltd.
- Inactivated vaccine (Vero Cell)
- Approved on May 15, 2021
- Two doses

COVID-19 Vaccines in the world and related information
U.S. COVID-19 Vaccines:
1. Pfizer Inc.
- Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine
- mRNA vaccine
- Approved on Dec 11, 2020 by U.S. FDA
- Two doses
2. Moderna TX, Inc.
- Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine
- mRNA vaccine
- Approved on Dec 18, 2020 by U.S. FDA
- Two doses
3. Janssen Biotech Inc.
- Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine
- Recombinat vector vaccine
- Approved on Feb. 27, 2021 by U.S. FDA
- One doses
4. Novavax Inc.
- Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine
- Recombinant protein
- Estimated Approval on 3rd quarter of 2021 by U.S. FDA
- Storage: Regular Fridge temperature
- Two doses
Other vaccines
AstraZeneca
-
AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine: manufactured by AstraZeneca
-
COVISHIELD COVID-19 vaccine: manufactured by Serum Institute of India
-
ChAdOx1-S recombinant vaccines developed by AstraZeneca and Oxford University
Russia:
-
Satellite V (Sputnik V) developed by the National Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology in Gamalea, Russia;
-
Satellite Light (Sputnik Light) developed by the National Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology in Gamalea, Russia;
COVID-19 Vaccines in the world and related information



