Breast cancer treatment: Monoclonal antibodies | double antibodies | ADC
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Breast cancer antibody treatment: Monoclonal antibodies | double antibodies | ADC
Breast cancer antibody treatment: Monoclonal antibodies | double antibodies | ADC. According to statistics from the International Association for Research on Cancer, approximately 685,000 people worldwide will die of breast cancer in 2020.
Among female-related cancer deaths, breast cancer accounts for approximately 15.5%. And in 2020, approximately 2.3 million people worldwide will be diagnosed with breast cancer, which has surpassed lung cancer to become the number one killer of women’s health.
However, what is gratifying is that from 2007 to 2016, the mortality rate of breast cancer has been decreasing at a rate of 1.8% per year. This is mainly due to the advancement of medical technology. The current treatment of breast cancer mainly includes surgery, radiotherapy, Chemotherapy, hormone therapy and targeted therapy, among which targeted therapy not only provides patients with a variety of options, but also greatly improves the survival of patients.
1. The landscape of breast cancer antibody therapy
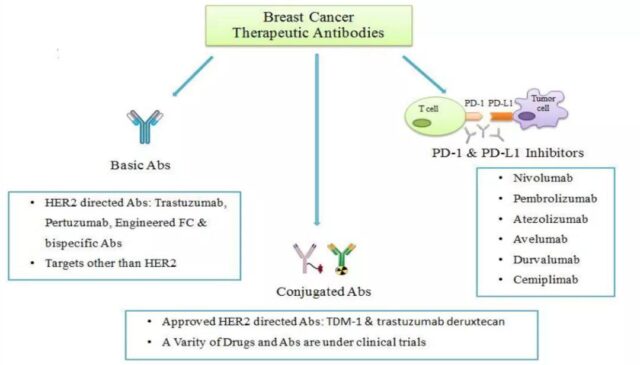
The antibodies currently approved or in clinical use for the treatment of breast cancer can be divided into three categories:
1) Naked antibodies targeting tumor surface antigens
This type of antibody mainly blocks tumor cell growth related signal pathways by binding to HER2 or other antigens on the tumor surface, thereby inhibiting tumor growth, or killing tumor cells through antibody-mediated ADCC and other effects;
2) Antibody conjugated drugs
This type of antibody also targets the antigen on the surface of tumor cells, but the antibody is coupled with small molecule toxicants or radiopharmaceuticals. After the antibody binds to the antigen on the tumor cell surface, it enters the tumor cell through endocytosis, and releases small molecules through lysosomes or enzymes. Toxic or radiopharmaceutical, thereby killing tumor cells;
3) Immune checkpoint inhibitory antibodies represented by PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies
These antibodies inhibit the inhibitory PD-1 or PD-L1 of the immune system, and then stimulate the immune response of the body’s immune system, and ultimately kill or inhibit tumor cells through the immune system.
2. Single/dual antibodies in breast cancer treatment
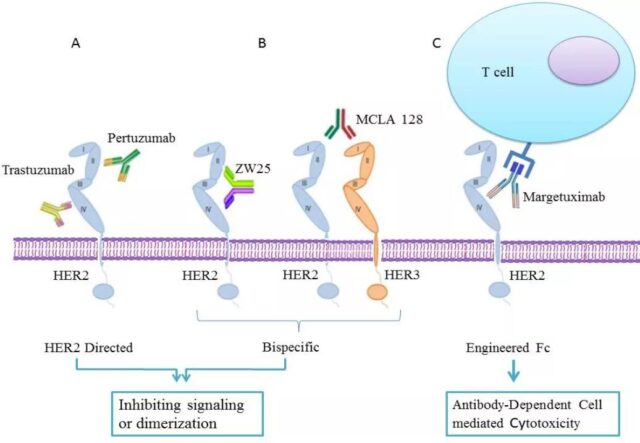
Targeting HER2
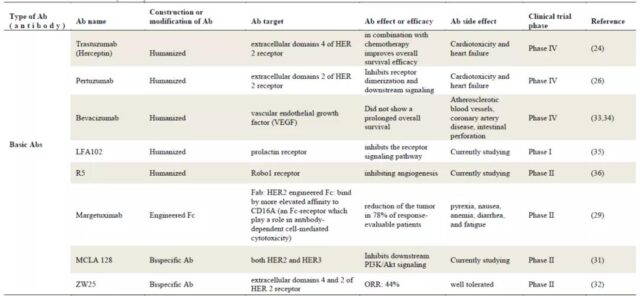
HER2 is expressed in 15-20% of breast cancer patients, so this target is an ideal target for breast cancer treatment. There are currently two monoclonal antibodies targeting HER2 (trastuzumab and Pertuzumab). Monoclonal antibody) was approved to be marketed for the treatment of breast cancer. These two antibodies target the fourth and second domains of HER2, respectively.
At the same time, there are currently several antibodies against HER2 under clinical evaluation, such as Margetuximab, MCLA128 and ZW25.
Margetuximab
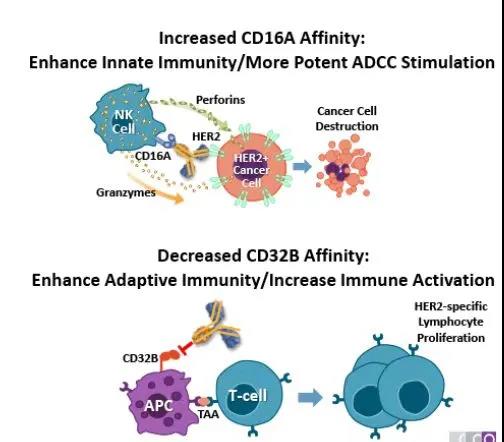
Margetuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the fourth domain of HER2. Unlike Trastuzumab, this antibody modifies Fc (F243L/R292P/Y300L/L235V/P396L) to enhance the antibody’s ability to bind to CD16A. , Thereby increasing the ADCC effect mediated by the antibody, and at the same time the antibody reduces the affinity for CD32B, thereby enhancing the body’s immune response. The drug has been approved by the FDA in December 2020 for the treatment of adult metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer in combination with chemotherapy.
MCLA128
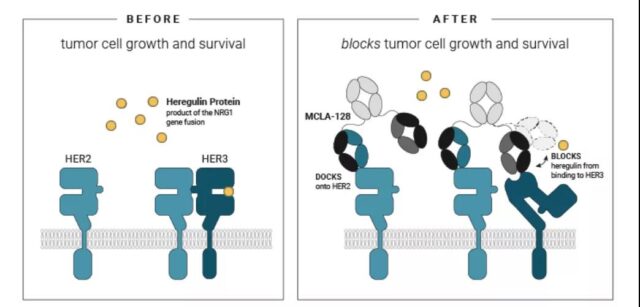
MCLA 128 is a bispecific antibody targeting HER2 and HER3. After the antibody binds to HER3, the antibody can block the binding of NRG1 protein to HER3; even at high NRG1 protein levels, it can also block HER2/HER3 dimerization; therefore, it can block the dimerization of HER2/HER3. It interrupts the activation of the downstream signals of HER2/HER3, thereby inhibiting the growth of tumor cells. In addition, the antibody modified Fc to enhance the ADCC effect mediated by the antibody, and further enhance the killing of tumor cells. The antibody is currently in 1/2 clinical trials.
ZW25
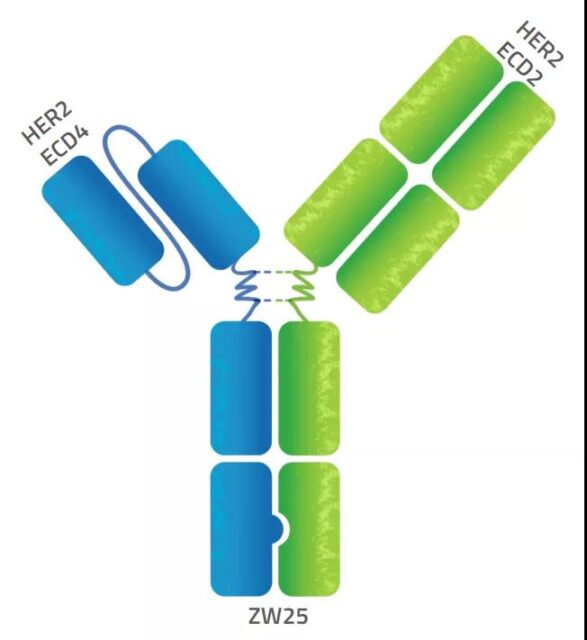
ZW25 is a bispecific antibody developed based on Zymeworks’ AzymetricTM platform. It can simultaneously bind to two non-overlapping epitopes (second domain and fourth domain) of HER2, which is called biparatopic binding. This unique design produces multiple mechanisms of action, including dual HER2 signal blockade, increased endocytosis of antibodies to increase the binding and removal of HER2 protein from the cell surface, and effective effector functions. The antibody is currently in clinical phase 2 and was introduced by BeiGene in China.
Antibodies that target other antigens
In addition to the HER2 target, there are other targets currently under development for the treatment of breast cancer, such as VEGF, PRLR (prolactin receptor), Pobo1 receptor and so on.
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets VEGF. It was approved by the FDA in 2004 for the treatment of colorectal cancer. This antibody mainly binds to VEGF to block tumor angiogenesis, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. In clinical trials, the antibody is used to treat HER2-negative breast cancer, but clinical results show that it cannot significantly prolong the survival rate of patients.
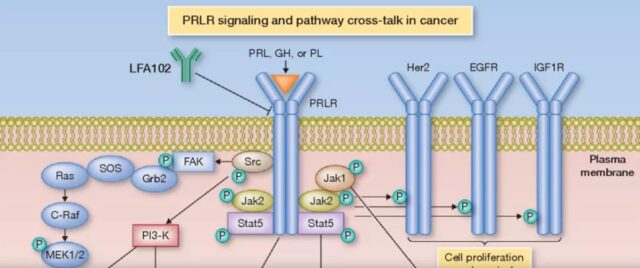
LFA102: is a humanized monoclonal antibody to PRLR, which mainly binds to the extramembrane domain of prolactin receptor. PRLR is a type I cytokine receptor, which will activate the downstream Jak/Stat, PI3-kinase/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways when combined with PRL, GH or PL, which will lead to the proliferation of tumor cells. LFA102 binds to PRLR and inhibits the combination of PRL, GH or PL, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of tumors, and further kills tumor cells through the ADCC effect of antibodies.
R5 is a monoclonal antibody targeting Robol receptor. Robo1 belongs to the immunoglobulin Ig supergene family and is a transmembrane signaling protein, which is the most clearly studied receptor for Slit2. The Slit2/Robo1 signaling pathway is involved in the regulation of angiogenesis and plays an important role in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
3. ADC treatment of breast cancer
Compared with naked antibodies, the ADC field has more targets for the treatment of breast cancer.
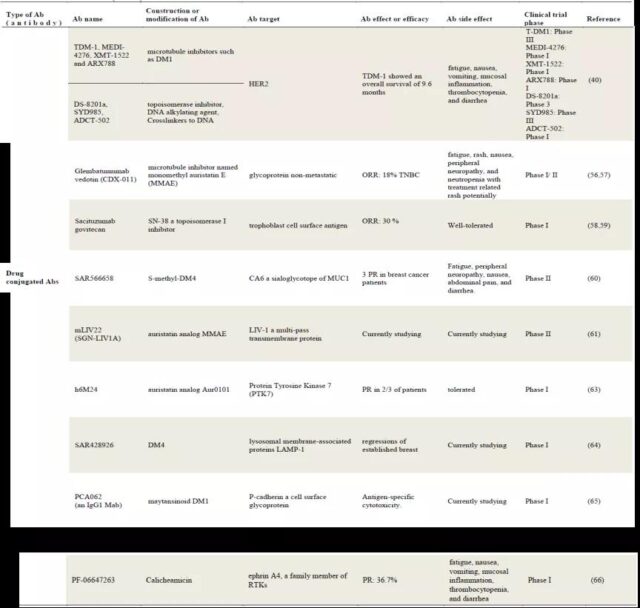
In addition to HER2, there are glycoprotein non-metastatic, trophoblast cell surface antigen, CA6 (sialylated MUC1), LIV-1 (a multiple transmembrane protein), PTK7 (Protein tyrosine kinase 7), LAMP-1 (lysosomal surface-associated protein), P-cadherin (a cell membrane surface glycoprotein) and ephrinA4 (a member of the PTKs family).
At present, two ADC drugs targeting HER2 have been approved by the FDA-TDM-1 and DS-8201a.
TDM-1
It is trastuzumab, the small molecule cytotoxin DM1 is a microtubule inhibitor. TDM1 targets the fourth domain of the HER2 receptor, and through receptor-mediated internalization and subsequent lysosomal degradation, results in the release of cytotoxic catabolites containing DM1 in cells. The combination of DM1 and tubulin destroys the intracellular microtubule network, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death.
In 2013, the FDA approved TDM1 for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients who had previously received trastuzumab and taxane alone or in combination; in 2019, the FDA approved TDM1 for taxane and trastuzumab Adjuvant treatment for HER2-positive early breast cancer patients with residual aggressive disease after anti-neoadjuvant therapy. MEDI-4276, XMT-1522 and ARX788, similar to TDM1, are ADC drugs that target HER2 and carry microtubule inhibitors, and are currently under clinical evaluation.
DS-8201a
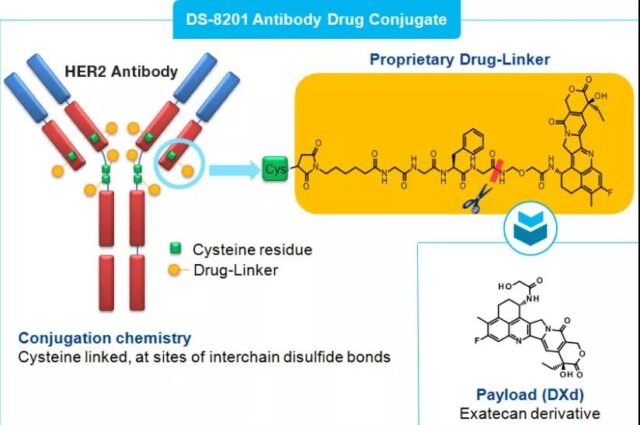
It is constructed by humanized HER2 monoclonal antibody trastuzumab coupled to a new topoisomerase I inhibitor camptothecin derivative (DX-8951 derivative DXd) via a peptide-based linker. It binds to HER2 on the surface of tumor cells through trastuzumab, enters tumor cells through HER2-mediated endocytosis, and is phagocytosed by intracellular lysosomes. Subsequently, the lysosomal enzyme cleaves the polypeptide linker, releases the loaded DXd, inhibits the activity of topoisomerase I, and then induces DNA damage and cell apoptosis, and exerts an effective anti-tumor effect.
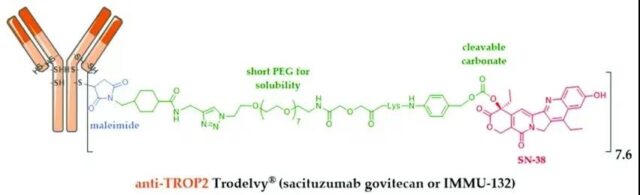
Sacituzumab govitecan
It is an ADC drug formed by coupling a humanized IgG1 antibody targeting the TROP-2 antigen and the metabolically active product SN-38 of the chemotherapy drug irinotecan (a topoisomerase I inhibitor). It will be released on April 2020. Approved by the FDA for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) that has received at least 2 therapies in the past. This is the first TROP-2 antibody conjugate drug approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with metastatic triple-negative breast .
TROP-2 is a cell surface glycoprotein encoded and expressed by the TACSTD2 gene. Its expression in normal tissues is very low, and it is overexpressed in a variety of malignant tumors. It mainly promotes tumor cell growth, proliferation and metastasis by regulating calcium ion signal pathway, cyclin expression and reducing fibronectin adhesion. TROP2 can also interact with β-catenin in the Wnt signaling cascade, and play a role in the transcription of nuclear oncogenes and cell proliferation.
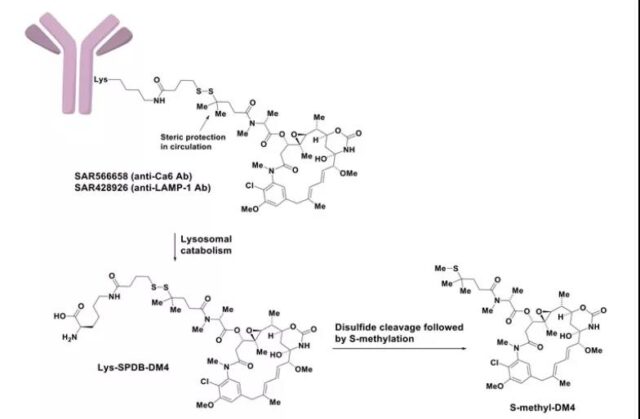
SAR566658
It is an ADC drug targeting CA6 (tumor-associated glycosylation of MUC-1), consisting of a huDS6 antibody that binds to CA6 and DM4 (Maytansine-derived microtubule inhibitor). In a phase I clinical trial involving 114 patients, 60% of patients in the 190 and 90 mg/m2 dose groups on the first and eighth days had tumor regression; at 150 and 120 mg/m2 doses In the biweekly administration group, 35% of patients experienced tumor regression.
In addition to the ADC drugs introduced above, there are currently many ADC drugs targeting different targets of breast cancer in clinical trials, which will not be described in detail here. See the table below for specific information.
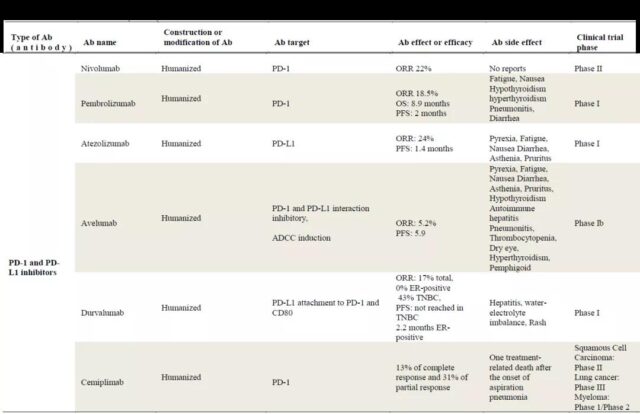
4. PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies
Progress in breast cancer treatment
PD-1 (CD279) is a member of the CD28 family, which mainly plays an immunosuppressive role and plays an important role in the immune escape of tumor cells.
PD-1 is expressed on a variety of immune cells, including NKT cells, B cells and DC cells. The interaction of PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 (CD274/B7-H1) can inhibit the proliferation and survival of T lymphocytes, and can promote the programmed death of T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Factors inhibiting PD-1 or PD-L1 can effectively stimulate the body’s immune response and inhibit or kill tumor cells through the immune system.
At present, a number of PD-1 and PD-L1 related antibodies have been approved for marketing, and they have also achieved good efficacy in different indications. Their research progress and efficacy in breast cancer are shown in the following table.
Summary
The development of antibody technology has brought great success to the treatment of breast cancer. At present, there are mainly three types of antibody-related drugs that are being clinically explored for the treatment of breast cancer.
The first category is antibodies targeting tumor surface antigens, including monoclonal antibodies such as trastuzumab and pertuzumab that have been approved for marketing, and bispecific antibodies such as MCLA128 and targets targeting Her2 and Her3. ZW25 to a different domain of Her2;
The second category is ADC drugs that target tumor cell surface antigens. At present, three ADC drugs have been approved for the treatment of breast cancer, two of which target Her2 (TDM-1 and DS-8201a), and one targets TROP- 2 (Sacituzumabgovitecan), and there are many ADC drugs targeting other targets under clinical evaluation, such as CA6, LIV-1, PTK7, LAMP-1, P-cadherin and ephrin A4;
The third type is an antibody that activates the body’s immune system, PD-1 or PD-L1. These antibodies use immune-related cells to kill tumor cells by activating the immune system.
Of course, in addition to the above-mentioned antibody monotherapy for breast cancer, there are currently a variety of combinations of drugs being explored, including the combination therapy of trastuzumab and pertuzumab with small molecule drugs, PD-1 antibody and Combination therapy with paclitaxel and other drugs.
Therefore, the treatment of antibodies in the field of breast cancer can be described as a hundred flowers blooming! We also hope that more and more treatment options will come out to bring good news to breast cancer patients!
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



