Nature: New COVID-19 antibody cocktail therapy
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Nature: New COVID-19 antibody cocktail therapy
Nature: New COVID-19 antibody cocktail therapy. Nature Sub-Journal: Huang Zhong’s team from Pasteur Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences and others develop COVID-19 antibody cocktail therapy.
The COVID-19 pneumonia caused by the COVID-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2) is a global pandemic. As of January 14, 2021, the cumulative number of COVID-19 pneumonia infections has exceeded 92 million, and the cumulative death toll has exceeded 1.96 million, posing a serious threat to global public health.
Neutralizing antibodies against the new coronavirus have the advantages of clear targets and significant efficacy. Ebola virus therapeutic drugs based on monoclonal antibody combinations have been approved for marketing. Therefore, the development of new coronavirus neutralizing antibodies as a potential treatment against new coronavirus pneumonia has high hopes.
Recently, Huang Zhong’s research group at the Shanghai Pasteur Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Cong Yao’s research group at the Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xie Youhua’s research group and Deng Qiang’s research group at Fudan University School of Medicine have collaborated and published the title: Development and structural basis of a two-MAb cocktail for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections.
The research developed a double antibody cocktail therapy that can be used to treat new coronavirus infections. Based on cryo-electron microscopy high-resolution structural analysis and biochemical analysis, the neutralization mechanism of 2H2/3C1 antibodies was clarified, and the new coronavirus triggered by antibodies was captured for the first time The dynamic process of the spike protein trimer through progressive allosteric rearrangement and then synergistically binding to antibodies has important theoretical significance and clinical transformational value.
The previous work of the research team found that the receptor binding domain (RBD) recombinant protein on the spike protein (S protein) of the new coronavirus can induce the production of high-titer neutralizing antibodies (Zang et al. Cell Discovery 2020).
In this study, the research team isolated 5 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies from RBD-immunized mice, and divided the 5 monoclonal antibodies into 2 groups through antibody competition experiments and mutant-based epitope identification experiments. The representative monoclonal antibodies 2H2 and 3C1 of the two antibody groups recognize different epitopes on RBD and can be combined into a non-competitive antibody pair.
The humanized 2H2/3C1 antibody combination neutralizes live SARS-CoV-2 virus in vitro with a median inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 12 ng/mL. More importantly, the 2H2/3C1 antibody combination has strong antiviral activity in the new coronavirus mouse infection model. Even if the mouse is infected with the new coronavirus 24 hours after the injection of the antibody cocktail composed of 2H2/3C1, it can still significantly reduce the virus Capacity, play a therapeutic role.
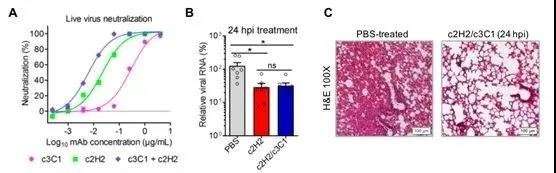
The research team also analyzed the cryo-EM structure of a series of 2H2 or 3C1 monoclonal antibody antigen-binding fragments (Fab) combined with the new coronavirus S trimer to form a complex with a resolution of 3.8 angstroms. The above structural studies have clarified the binding epitopes of 2H2 and 3C1 monoclonal antibodies, and for the first time captured the conformational change space of the new coronavirus S trimer triggered by the antibody, and the dynamic process of cooperatively binding antibodies through gradual allosteric rearrangement, revealing The 2H2/3C1 antibody cocktail synergistically neutralizes the potential molecular mechanism of the new coronavirus.
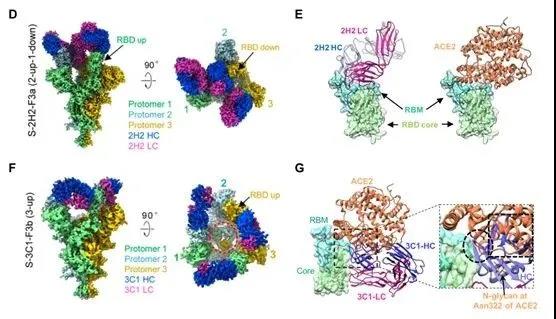
In summary, this research has developed a double antibody cocktail therapy that can be used to treat new coronavirus infections, and clarified the neutralization mechanism of 2H2/3C1 antibodies from the structural and biochemical aspects, which has important theoretical significance and clinical translational value.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



