FDA approved AbbVie’s Botox for neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity in children!
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
FDA approved AbbVie’s Botox for neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity in children!
FDA approved AbbVie’s Botox for neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity in children! 12 indications in 30 years of listing! The US FDA approves AbbVie’s Botox (Botox): the treatment of neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity in children!
AbbVie recently announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Botox (botox, generic name: onabotulinumtoxinA, botulinum toxin A) for the treatment of age ≥ 5 years and anti-cholinergic Pediatric patients with insufficient drug response or intolerance, treatment of detrusor (bladder muscle) hyperactivity associated with neurological diseases. This milestone marks the 12th therapeutic indication that Botox has been approved in the United States.
It is worth mentioning that Botox is the first and only neurotoxin approved for the treatment of children with neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity. Now, for children with neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity who do not respond to anticholinergic drugs, there is a new treatment option that can be used before surgical intervention. Botox selectively prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction by blocking the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscle (in this indication, the bladder muscle), temporarily reducing muscle contraction.
Neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity occurs when the spinal cord and bladder cannot communicate effectively, which may be related to neurological diseases such as spina bifida and spinal cord injury. As a result, the bladder muscles contract involuntarily, increasing the pressure in the bladder and reducing the capacity of the bladder, which can cause frequent and accidental leakage of urine. Over time, increased bladder pressure can also cause bladder and kidney damage.
There are many causes of neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity in children, such as rhabdomyositis, spinal cord injury, and spina bifida. Among them, spina bifida is the most common, affecting about 1500-2000 babies among more than 4 million babies born in the United States each year. More than 90% of patients with spina bifida have urinary system symptoms.
The approval of the new indication is based on data from a randomized, double-blind Phase 3 study. The study was carried out in more than 100 children with neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity, evaluated the safety and effectiveness of Botox, and conducted a long-term extension study. The results of the phase 3 study showed that intramuscular injection of Botox® 200 units (not more than 6 U/kg) of detrusor can reduce the onset of urinary incontinence during the day, which is the primary end point of the study, and it decreases at the 6th week (main time point) Maximum bladder pressure and increase bladder capacity. The most common adverse reactions in the study were bacteriuria (20%), urinary tract infection (7%), white blood cell urine (7%) and hematuria (3%).
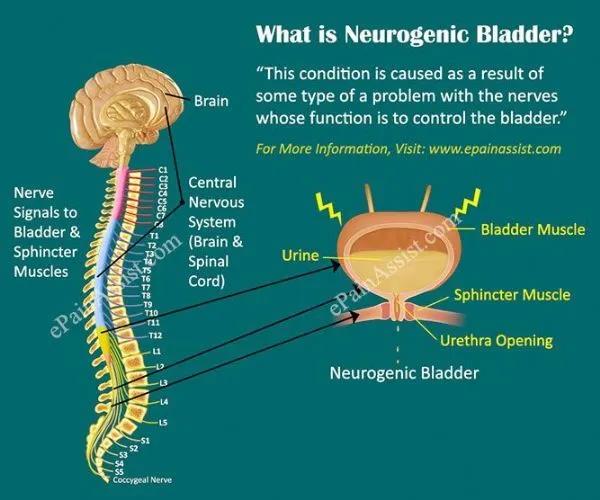
Neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity (picture source: epainassist.com)
AbbVie BOTOX® & Neurotoxins Senior Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer Mitchell F. Brin, MD, said: “Botox is the first neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity approved for inadequate disease control with anticholinergic drugs. Neurotoxins in children with chronic diseases. This milestone marks the 12th therapeutic indication for Botox approved in the United States, adding another approved use to the pediatric product portfolio.
On the basis of our 30-year Botox research and development tradition, we continue to unswervingly pursue neurotoxin innovation to address the unmet medical needs of the entire therapeutic field. “
Paul F. Austin, MD, director of the Department of Pediatric Urology at Texas Children’s Hospital and Professor of Urology at Baylor College of Medicine, said: “Many children with underlying neurological diseases may develop bladder and kidney damage over time. This highlights The importance of treatment.
When caring for children with neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity, we strive to reduce bladder pressure and increase bladder capacity. Previously, in addition to surgery, treatment options were mainly limited to anticholinergic drugs, but long-term use still requires careful consideration.
Effective management of neurogenic detrusor hyperactivity requires continuous care, and there is a high unmet need for alternative treatment options. Botox has proven safety and effectiveness, and will provide a new treatment option for pediatric patients receiving anticholinergic drugs that have not adequately managed their disease. “

Botox was developed by Allergan (acquired by AbbVie). The main ingredient of the drug is highly purified type A botulinum toxin, which is a nerve conduction blocker to treat excessive Active muscles. Botox was first approved in 1989 for the treatment of facial spasm and strabismus. In 2000, it was approved for cervical dystonia, and then further expanded to the field of beauty, including wrinkle removal, face thinning, elimination of brow lines and crow’s feet. In recent years, Botox has also been approved to treat upper limb spasm, chronic migraine, neurogenic urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, spasm, and severe underarm sweating (hyperhidrosis) and other indications.
Botox is the world’s first approved type A botulinum toxin treatment product. In the United States, Botox has been approved by the FDA for 12 therapeutic indications so far.
In the past 30 years, more than 100 million bottles of Botox® and Botox® Cosmetic (Botox A) have been sold worldwide, and more than 3,700 articles have been published in scientific and medical journals. Botox® Neurotoxin is one of the most widely studied drugs in the world.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



