PNAS: Vitamin C Improve T cell effect by 380%!
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
PNAS: Vitamin C Improve T cell effect by 380%!
PNAS: Vitamin C Improve T cell effect by 380%! Improve T cell killing effect by 380%! This common vitamin may become a good partner for PD-1.
In the clinic, researchers began to taste more treatment methods to find substances and drugs that increase the therapeutic effect of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.
As PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors are used more and more clinically, what is most interesting for doctors and patients is how to improve the therapeutic effect of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. The current clinical data show that when only PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy is used, the patient’s effective rate is only 10% to 30%, which is obviously not an ideal data.
Therefore, in clinical practice, researchers have begun to taste more treatment methods to find substances and drugs that increase the therapeutic effect of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. It was found that: Vitamin C, a common vitamin, can help improve the therapeutic effect of PD-1 inhibitors!

This latest result is also on “PNAS” (picture source: PNAS official website)
DNA methylation is mainly to protect the stability of the genome, so as to ensure that there will be no errors in replication. But in the process of tumor occurrence and development, cancer cells will become hypomethylated, so that they can replicate quickly and become more active. As early as in previous studies, it was found that vitamin C can prevent tumor demethylation by enhancing the activity of enzymes (10-11 translocation enzyme, TET) in the human body, thereby exerting an anti-cancer effect.
In this study, the researchers found that vitamin C can increase the activity of immune cells-indicating that vitamin C may be a broad-spectrum drug that increases the effect of immunotherapy. Vitamin C may be the best demethylation inhibitor in conjunction with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
In this study, vitamin C can help improve the therapeutic effect of PD-1 inhibitors mainly in three aspects:
First, after using high-dose vitamin C to treat lymphoma cells, the immunogenicity of lymphoma cells can be significantly improved, and the killing rate of immune cells against lymphoma cells can be increased by 40%! At the same time, after treating the CD8+ T cells of 3 healthy people with vitamin C, it was found that its killing effect on lymphoma cells was increased by 380%!
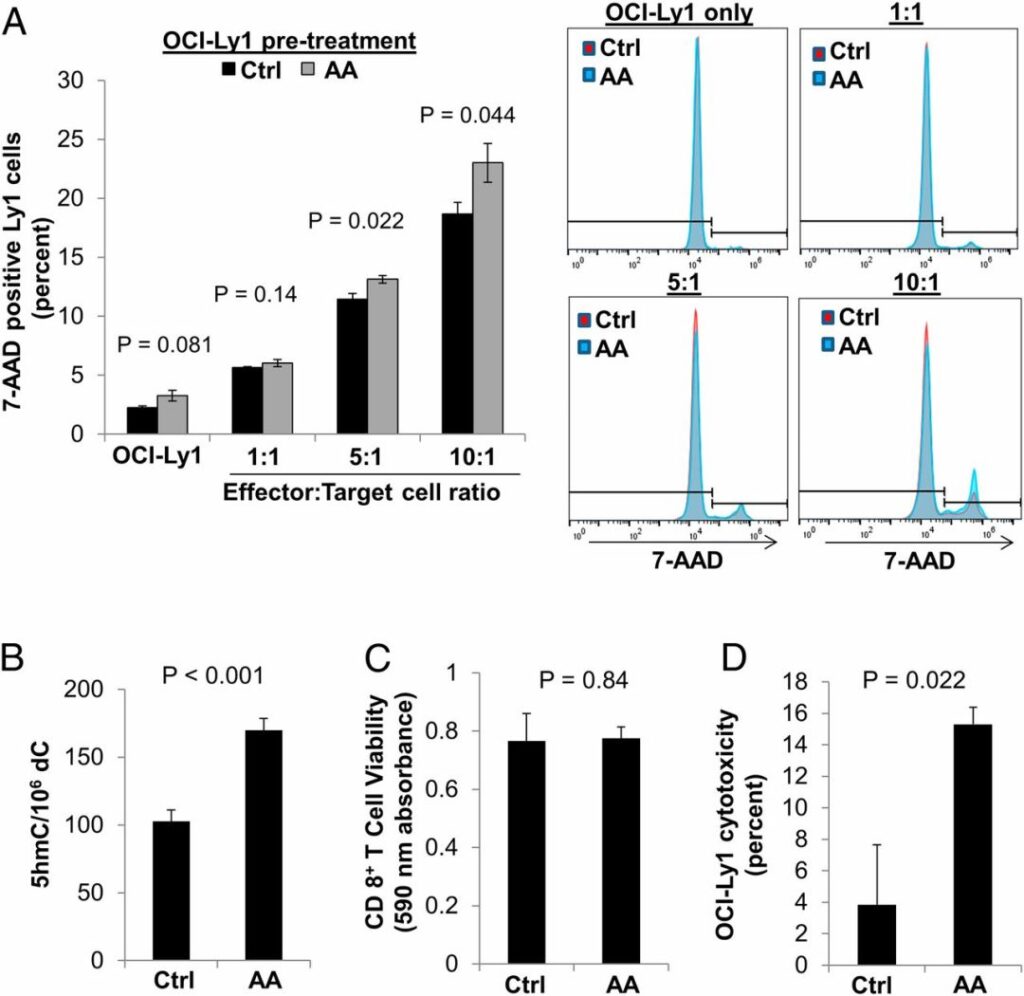
Compared with the control group, vitamin C treatment can significantly increase the killing rate (picture source: High-dose ascorbic acid synergizes with anti-PD1 in a lymphoma mouse model)
The second point is that it can increase the infiltration of immune cells into tumors. We all know that if immune cells want to play a killing effect, they must be in contact with tumor cells. However, for solid tumors, a difficulty in treatment is that the tumor will form its own immune microenvironment locally, which prevents immune cells from entering the tumor. Effective killing is formed around. But vitamin C can help immune cells to enter the surrounding tumor tissues, including macrophages and T cells, which may effectively improve the effect of immunotherapy.
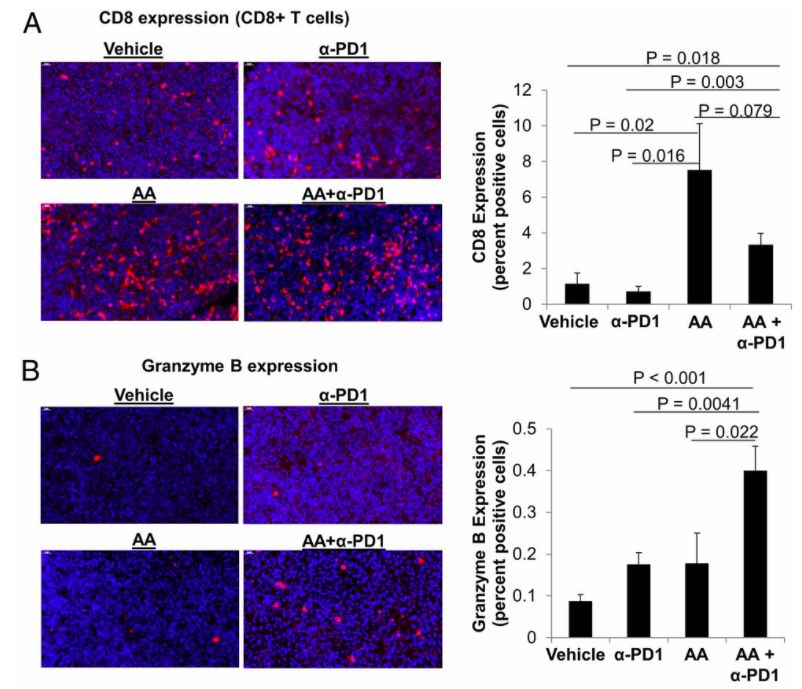
In the tumor microenvironment treated with vitamins, immune cells are more immersed, and at the same time, it can promote the release of cytokines and help immune cells to perform better (Image source: High-dose ascorbic acid synergizes with anti-PD1 in a lymphoma mouse model)
In addition to the above effects, the most important point of vitamin is that when it is used in combination with PD-1 inhibitors, it can also activate other immune cells in the body, including NK cells. NK cells are known as the first line of defense against tumors and are also an important indicator of cancer prognosis. When activated, they can also inhibit the occurrence and development of tumors.
For immune checkpoint inhibitors, there are still several problems: 1. Cancer cells are usually low in immunogenicity, which makes it difficult to identify; 2. The tumor microenvironment has an inhibitory effect on immune cells; 3. Cancer cells have an inhibitory effect on immune cells. A variety of immune cells have an inhibitory effect. These all limit the therapeutic effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
But vitamin C can help solve these problems, which may be a good breakthrough. It can perfectly solve the above problems, as shown in the figure below, can help immune cells to better eliminate cancer cells.
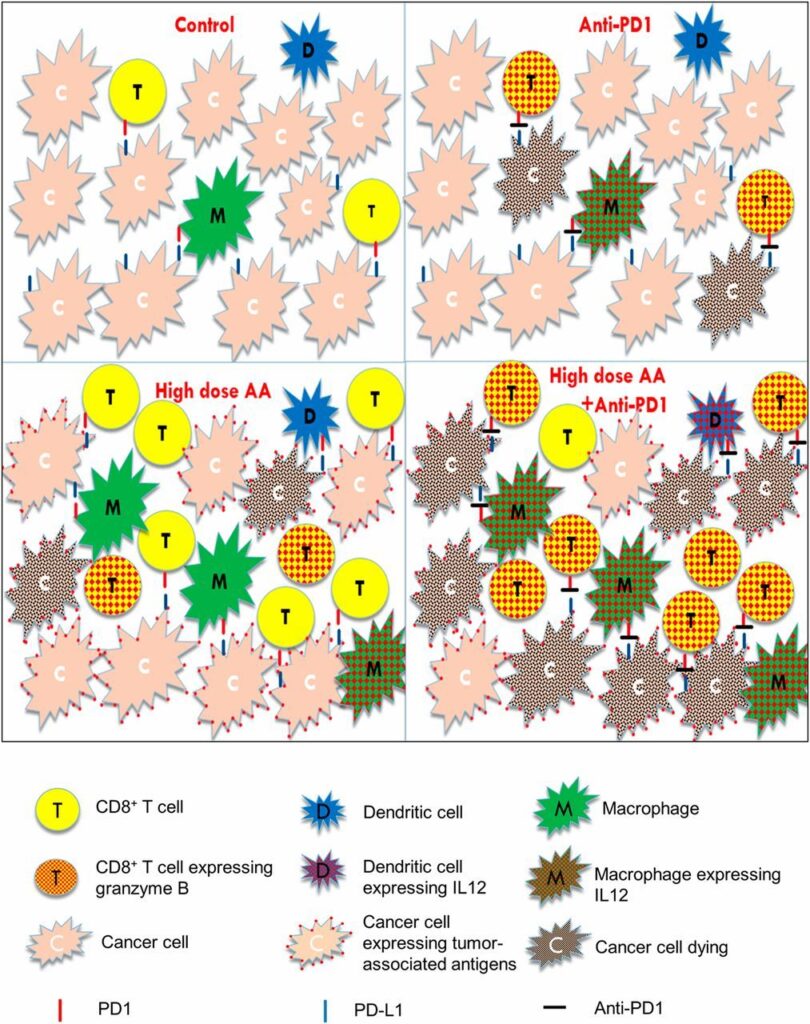
Of course, this is only a theoretical study. The researchers also pointed out the need to further confirm the connection between immune cell subgroups and vitamin C, and how to use vitamin C to help improve the therapeutic effect. Previous clinical trials have shown that: For cancer patients, intravenous infusion of vitamin C at a dose of 1 to 1.25 g/kg can effectively reduce the side effects and toxicity of chemotherapy. This may be related to the anti-tumor effect of vitamin C.
From the results of this experiment, high-dose vitamin C may be one of the important drugs to enhance PD-1 inhibitor therapy, and it may also be one of the combination drug options for immunotherapy. However, it should be noted that the daily supplement of vitamin C does not reach the therapeutic level dose.
As more and more drugs and immunotherapy have a combined effect, it is believed that the effect of immunotherapy will get better and better, helping more tumor patients to cure cancer.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



