Molecular level of antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Protein & Cell: The molecular level of antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine
Molecular level of antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine. On April 30, 2021, Sinopharm Zhongsheng Beijing Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd. joined Nankai University, Shanghai University of Science and Technology Institute of Immunochemistry, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital Fifth Medical Center, Tsinghua University and the Russian Academy of Sciences team in Protein& Cell Journal (IF=10.164, Biological Zone 1) published an article “Molecular deconvolution of the neutralizing antibodies induced by an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccine”.

The research team used the droplet microfluidic technology platform to construct an antibody library that maintains the natural pairing of heavy and light chains from the peripheral blood of vaccinators of the COVID-19 inactivated vaccine (trade name), and used phage display technology to screen a large number of COVID-19 from the library. Virus-binding antibodies, including multiple neutralizing antibodies; isolated antibodies bind to different positions of the spike protein on the virus surface, and some of the antibodies maintain the ability to recognize mutant proteins of various new coronaviruses, explaining the vaccinators at the molecular level The reason why serum still has a neutralizing effect on a variety of new coronavirus mutant strains.
1. The serum of the vaccinated person showed the ability to bind to the spike (S) protein on the virus surface and the ability to neutralize the virus; the second-generation sequencing of the peripheral blood PBMC immune repertoire analyzed the mutation rate of the antibody heavy chain, the diversity of the CDR3 region, and the length distribution Characteristics and the expression frequency of each germline gene family. In order to obtain information about the natural pairing of antibody heavy and light chains, the researchers used droplet microfluidic technology to encapsulate B cells so that the light and heavy chains from the same B cell assemble into single-chain antibodies, constructing the maintenance of heavy and heavy chains. A library of antibodies that naturally pair with light chains.
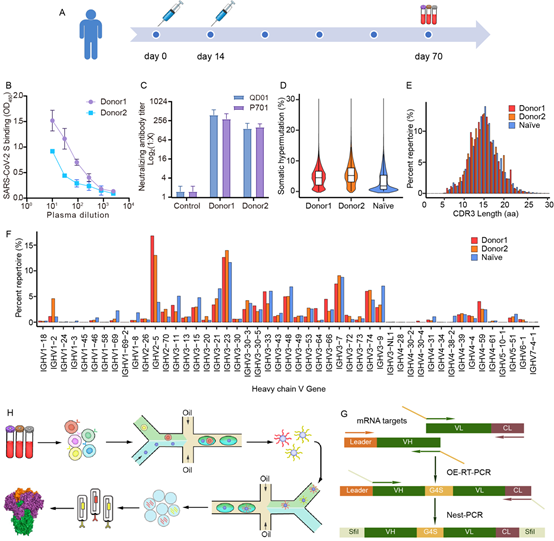
2. Next, the researchers used phage display technology to screen antibodies that bind to the spike protein on the surface of the new coronavirus from the constructed antibody library. The researchers isolated 16 virus-specific antibodies, of which 6 antibodies have good neutralizing ability. Further analysis of 5 RBD-binding neutralizing antibodies revealed that the vaccine-induced antibodies bind to different epitopes of RBD; finally, the research team evaluated the neutralizing antibodies against 12 surface protein mutants (including single point mutations and British variants and South Africa). The binding ability of the surface spike protein of the mutant strain was found to maintain the ability to bind most of the mutations, and only some antibodies had a significant decrease in binding ability to the surface spike protein of the South African mutant strain. This explained from the perspective of serum component analysis. Serum analysis results.
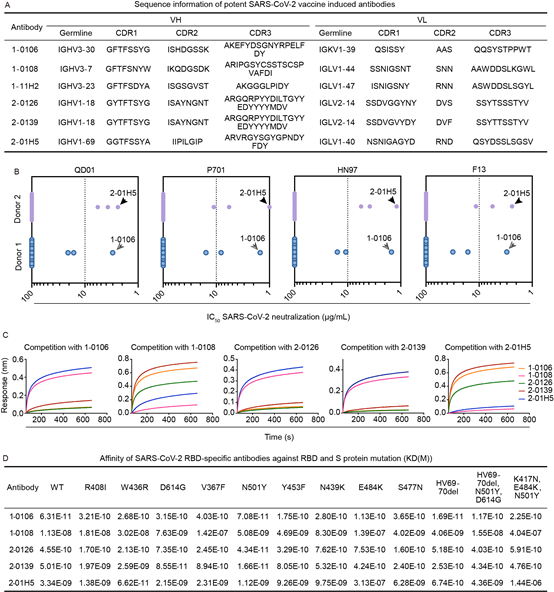
The research team has established a droplet microfluidic platform to construct a library of natural paired antibodies, combined with phage display screening, to provide an effective means to isolate natural paired antibodies of light chain and heavy chain from recovered patients or vaccinators; at the same time, from The multiple neutralizing antibodies isolated from the blood samples of inactivated vaccine vaccinators showed good binding ability on 12 new coronavirus surface protein mutants, demonstrating the potential protective ability of the new coronavirus vaccine against multiple new coronavirus mutant strains.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



