14 new targets for new drugs approved in 2021
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
14 new targets for new drugs approved in 2021
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
14 new targets for new drugs approved in 2021
Recently, drug regulatory agencies in various countries have released 2021 new drug approval reports.
The report shows that in 2021, drug regulatory agencies in the United States, Japan, and the European Union have approved a total of 59 new drugs, of which 50 new drug indications have mature mechanisms and targets.

Recently, the journal Nature Reviews Drug Discovery published a short report listing 14 new targets among all new drugs approved in 2021.
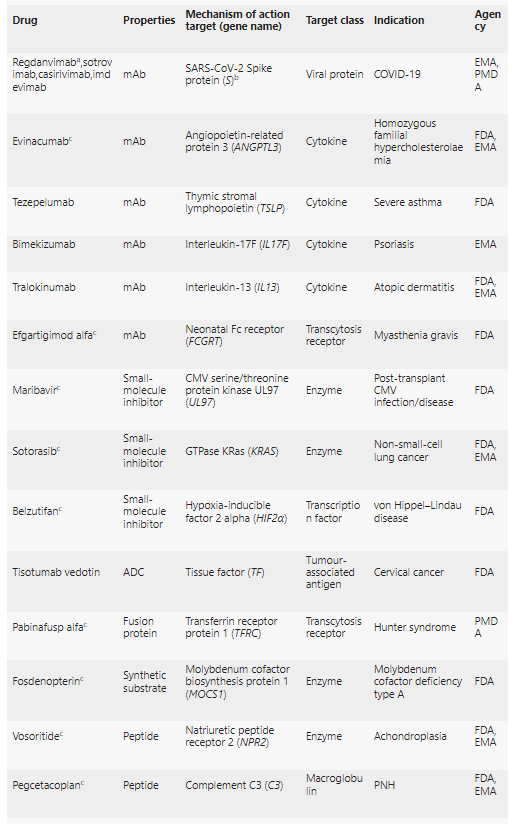
1. Novel coronavirus spike protein
In 2021, a total of 4 monoclonal antibodies have been approved against the new coronavirus spike protein, namely Regdanvimab, sotrovimab, casirivimab, and imdevimab.
Regdanvimab, trade name Regkirona, was developed by Celltrion and works by intravenous infusion. Approved in the European Union in November 2021 for the treatment of adults with COVID-19 who do not require supplemental oxygen but are at high risk of disease progression.
Sotrovimab, marketed under the brand name Xevudy and developed by GlaxoSmithKline and Vir Biotechnology, works by intravenous infusion. Sotrovimab was approved in May 2021 for the treatment of adults and adolescents (12 years and older, weighing at least 40 kg) with COVID-19 who do not require supplemental oxygen and are at risk of developing severe disease.
Casirivimab/imdevimab, trade name REGEN-COV, is a combination drug for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19, consisting of two humanized monoclonal antibodies, casirivimab and imdevimab. REGEN-COV was developed by American biotech company Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and is primarily administered by intravenous infusion or subcutaneous injection. In November 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for casirivimab and imdevimab together for the treatment of mild-to-moderate patients 12 years of age or older who weigh at least 40 kg and develop Patients at severe risk of COVID-19.
2. Angiopoietin-related protein 3 (ANGPTL3)
Evinacumab, trade name Evkeeza, is a monoclonal antibody developed by Regeneron in the United States. In February 2021, Evinacumab was approved in the United States for the treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) .
ANGPTL3 can slow down the fat hydrolysis function of some enzymes in the human body, and Evinacumab can directly target and block ANGPTL3, thereby accelerating lipolysis and lowering cholesterol levels.
The efficacy and safety of evinacumab was evaluated in a 24-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 65 participants with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) . In the trial, 43 participants received 15 mg/kg of evinacumab every 4 weeks and 22 received placebo. All participants were concurrently taking other lipid-lowering therapies. The results showed that at week 24, participants receiving evinacumab had an average 47 percent decrease in LDL-C, compared with an average 2 percent increase in participants in the placebo group.
3. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP)
Tezepeluma, traded under the trade name Tezspire, is a humanized monoclonal antibody jointly developed by AstraZeneca and Amgen. In December 2021, Tezepeluma was approved for the add-on maintenance treatment of severe asthma in patients 12 years and older.
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) , an epithelial cytokine produced in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli, plays a key role in the development and persistence of airway inflammation. Tezepelumab directly targets and inhibits TSLP activity, thereby preventing further development of asthma.
In a phase III clinical trial, tezepelumab in combination with standard of care significantly reduced the risk of disease progression compared with placebo in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma. Currently, tezepelumab is also being investigated for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
4. Interleukin-17F (IL17F)
Bimekizumab, trade name Bimzelx, is a humanized anti-IL17A, anti-IL-17F and anti-IL17AF monoclonal antibody developed by the Belgian pharmaceutical company UCB. In 2021, Bimekizumab will be approved in the European Union for the systemic treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults.
Two large phase III clinical trials published in the journal NEJM showed that bimekizumab was superior not only to adalimumab but also to secukinumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
5. Interleukin-13 (IL13)
Tralokinumab, traded under the trade name Adtralza, is a humanized monoclonal antibody developed by AstraZeneca and LEO Pharma. Tralokinumab was approved in the EU and UK in June 2021 for the systemic treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults and in the US in December 2021 for the treatment of insufficient control of the disease with topical prescription therapy or the use of these therapies is not recommended of adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
Tralokinumab targets the cytokine interleukin 13, and data from a pivotal Phase III trial showed that tralokinumab compared with placebo in adolescents (ages 12-17 years) with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) Treatment can effectively control the disease and significantly improve the quality of life of patients.
6. Neonatal Fc receptor
Efgartigimod alfa, traded under the trade name Vyvgart, is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting neonatal Fc receptors, developed by argenx. In December 2021, Efgartigimod alfa was approved in the United States for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis in adults with positive anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibodies.
Efgartigimod alfa targets neonatal Fc receptors and inhibits their circulation of immunoglobulin G (IgG) back into the blood, resulting in a reduction in overall levels of IgG, including the abnormal acetylcholine receptor ( AChR) antibodies present in myasthenia gravis.
The safety and efficacy of efgartigimod alfa was evaluated in a 26-week clinical study of 167 participants with myasthenia gravis who were randomly assigned to receive efgartigimod alfa or placebo. The study showed that efgartigimod alfa was effective in improving symptoms in patients compared to participants who received a placebo.
7. CMV serine/threonine protein kinase UL97 (UL97)
Maribavir, traded under the trade name Livtencity, is an oral small molecule inhibitor developed by GlaxoSmithKline and ViroPharma. Maribavir was approved in the United States in November 2021 for the treatment of post-transplant cytomegalovirus infection/disease unresponsive to available cytomegalovirus antiviral therapy in patients 12 years of age and older and weighing at least 35 kg.
Maribavir is a cytomegalovirus pUL97 kinase inhibitor that works by blocking the activity of human cytomegalovirus pUL97 kinase, thereby blocking viral replication.
In a phase III, multicenter, open-label, active-controlled trial, 352 transplant recipients with cytomegalovirus infection who did not respond to treatment (with or without resistance) were randomized to receive maribavir or investigator-specified treatment for up to eight weeks. Cytomegalovirus DNA levels were below measurable levels in 56% of the 235 participants receiving maribavir at the end of Week 8, compared to 24% of the 117 participants receiving the investigator-assigned treatment .
8. GTPase KRas
Sotorasib, marketed under the name Lumakras, is an oral small molecule inhibitor developed by Amgen. Sotorasib was approved in the U.S. in May 2021 for the treatment of adult patients with KRAS G12C-mutated locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have received at least one prior systemic therapy.
Sotorasib is the first targeted therapy approved for tumors with any KRAS mutation, which accounts for approximately 25% of NSCLC mutations.
The efficacy of sotorasib was evaluated in a study of 124 patients with locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. These patients had disease progression after receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors and/or platinum-based chemotherapy. The results showed that sotorasib had an objective response rate of 36 percent, with 58 percent of participants having a response duration of six months or longer.
9. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF2α)
Belzutifan, traded under the trade name Welireg, is an oral small molecule drug developed by MERCK. Belzutifan was approved in the U.S. in August 2021 for the treatment of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) -related renal cell carcinoma (RCC) , central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastoma, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET) .
A phase II clinical study published in NEJM showed that belzutifan showed good antitumor activity in patients with VHL disease-related renal cell carcinoma and non-renal cell carcinoma tumors, and was safe and tolerable.
10. Tissue factor (TF)
Tisotumab vedotin, traded under the trade name Tivdak, is an antibody-conjugated drug developed by the Danish biotech company Genmab. Tisotumab vedotin was approved in the United States in September 2021 for cervical cancer treatment.
The antibody portion of tisotumab vedotin binds and forms a complex with tissue factor, a molecule expressed on the surface of cancer cells. This complex is then taken up into cells, where tisotumab vedotin is broken down by proteolytic cleavage, releasing MMAE, which stops the cell cycle and kills the cell by apoptosis.
Previous studies have shown that the objective response rate (ORR) of tisotumab vedotin in the treatment of recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer was 24%, the median PFS was 4.2 months, the 6-month PFS rate was 30%, and the median OS was 12.1 months, The 6-month OS rate was 79%.
11. Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC)
Pabinafusp alfa, trade name IZCARGO, is an enzyme replacement therapy developed by JCR Pharmaceuticals of Japan. In March 2021, Pabinafusp alfa was approved in Japan for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II) .
Gene mutations in MPS II patients result in defects or deletions of key metabolic proteases, resulting in the accumulation of toxic metabolites in lysosomes. Many patients develop severe symptoms in the central nervous system, resulting in poor neurocognitive development of patients, affecting their independence and quality of life.
In a phase 2/3 clinical trial conducted in Japan, all 28 patients showed significant reductions in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations of heparan sulfate (HS), a central response to MPS II, after 2 weeks of treatment biomarkers of symptoms, thereby meeting the primary endpoint of the trial. At the same time, the treatment also significantly improved the patient’s physical symptoms.
12. Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis protein 1 (MOCS1)
Fosdenopterin, traded under the trade name Nulibry, is an intravenous drug developed by Origin Biosciences. Fosdenopterin was approved in the U.S. in February 2021 for the treatment of type A molybdenum cofactor deficiency.
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency type A is a rare genetic disorder in which cyclic pyropterin monophosphate ( cPMP) is not produced in the body , resulting in death. Fosdenopterin is an intravenous drug that replaces missing cPMPs. cPMP is a precursor of molybdenum pterin and is required for the enzymatic activities of sulfite oxidase, xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase and aldehyde oxidase.
Fosdenopterin’s effectiveness was demonstrated in a pilot study of 31 patients, with 84 percent of participants who received fosdenopterin surviving at three years compared to 55 percent of those who did not.
13. Natriuretic peptide receptor 2 (NPR2)
Vosoritide, traded under the trade name Voxzogo, is a peptide drug developed by BioMarin Pharmaceutical. Vosoritide was approved in the EU in August 2021 for the treatment of achondroplasia in people 2 years of age and older with an unclosed epiphysis, respectively, and in the United States in November 2021 for the treatment of achondroplasia in people 5 years and older with achondroplasia and growth in children with open epiphysis (growth plates) .
FGFR3 is a receptor that normally downregulates cartilage and bone growth when activated by proteins called acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Vosoritide acts by binding to the B-type natriuretic peptide receptor (NPR-B) , which reduces the activity of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) .
Participants aged 5 years and older with achondroplasia with open epiphysis were studied in a one-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III study. 121 participants were randomly assigned to receive subcutaneous injections of vosoritide or placebo. At the end of the year, the researchers measured the participants’ annual growth rate, or rate of growth in height. Participants who received vosoritide were an average of 1.57 centimeters taller than those who received a placebo.
14. Complement C3 (C3)
Pegcetacoplan, traded under the trade name Empaveli, is a peptide drug developed by Apellis. Pegcetacoplan was approved in the United States in May 2021 for the treatment of adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) .
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is characterized by destruction of red blood cells, anemia (the inability of red blood cells to deliver enough oxygen to tissues) , blood clots, and impaired bone marrow function (inability to make enough blood cells) . Pegcetacoplan, the first drug to treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, binds and inhibits complement protein C3.
The effectiveness of pegcetacoplan was evaluated in a study that enrolled 80 participants with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and anemia who had been taking eculizumab, a previously approved treatment for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Treatment of hemoglobinuria. The results showed that pegcetacoplan was more effective than eculizumab.
Overall, from a therapeutic perspective, 9 of the 14 new targets (64%) are for drugs to treat various rare diseases. In the future, as humans pay more attention to rare diseases, there may be more new targets.
References
1. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41573-022-00057-7
14 new targets for new drugs approved in 2021
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



