Questions about high tibial osteotomy (HTO)
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Questions about high tibial osteotomy (HTO)
Questions about high tibial osteotomy (HTO). Eight questions you need to know about high tibial osteotomy (HTO)! Knee arthritis is the most common joint disease in the elderly. Its incidence increases with age and usually causes repeated knee joint swelling and pain.
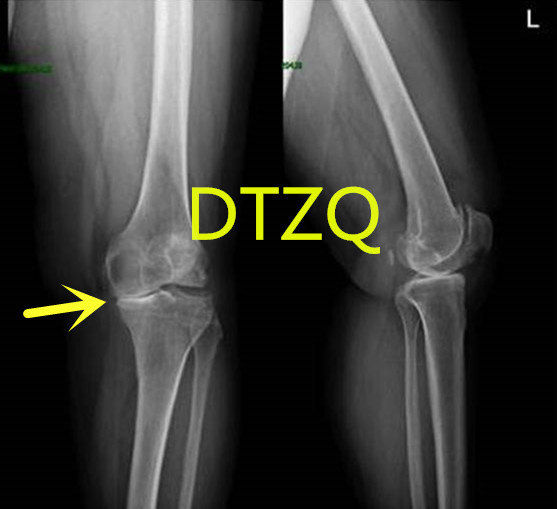
01 What is knee arthritis, what are its manifestations, and how to treat it?
Knee arthritis is the most common joint disease in the elderly. Its incidence increases with age. It usually causes symptoms such as recurrent knee joint swelling and pain, restricted movement, etc., which can lead to joint deformation and “O-shaped legs” or “X-shaped legs” and other deformities.
Its current main treatment method is step treatment. Early-stage patients are treated conservatively, using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, exercise, etc. to relieve pain and delay the progression of the disease. When joint disease is severe, joint replacement may be considered. For relatively young patients, high knee osteotomy can be performed for treatment.
02 What is high tibial osteotomy? What are the characteristics?
High Tibial Osteotomy (High Tibial Osteotomy), referred to as HTO, refers to high tibial osteotomy to correct uneven force lines, improve symptoms, relieve pain, and retain bone to the maximum extent, reduce bone damage, thereby delaying the knee bone The progression of arthritis. Patients can go to the ground early after the operation, and recover quickly, with complete preservation of knee joint function.
This operation has a long history and was first proposed by Jackson et al. in 1958 to treat varus deformity and knee osteoarthritis. The effect is good.
03 How is HTO surgery done?
There are two types of surgery: closed high tibial osteotomy and open tibial high osteotomy:
At present, the main clinical practice is to open high tibial osteotomy. Simply put, the tibia adjacent to the knee joint is cut internally, with a dilator at a certain angle in the middle, and strong internal fixation to make the legs straight. The line of force passes through the outer compartment of the knee joint to slow down the wear on the inner side of the knee joint.
Closed osteotomy (cwhto):
Closed osteotomy was proposed by Jackson in the 1950s.
Aadvantages:
1) The bone surface of the osteotomy site is completely in contact, and the postoperative healing is fast and the healing speed is fast. The results show that bone grafts are not required during surgery, which can reduce the pain and economic burden of patients and avoid the formation of the lower patella after surgery.
③ As the surgical site is close to the varus deformity, the deformity can be corrected obviously;
④The recurrence rate of varus deformity is low.
Note:
①To close the osteotomy end, fibula osteotomy is required, which is easy to damage the common peroneal nerve;
②The angle is not easy to control after correction, and sometimes requires multiple osteotomies;
③Oseotomy causes more bone loss and easily leads to limb shortening; ④It is difficult and requires high technical requirements for doctors.
Open wedge osteotomy (owhto):
With the continuous development of internal fixation technology, the choice of bone graft materials has become more and more extensive, and owhto has become more and more popular. The uneven settlement theory suggests: owhto can well correct the force lines of both lower limbs of the knee joint in single chamber.
The advantages are:
- 1) It can better correct the force lines of the two bone surfaces and better correct the deformity.
- 2) No need for osteotomy to reduce the risk of common peroneal nerve injury;
- 3) There is no bone defect during the operation, and the lower limbs will not shorten;
- 4) The surgical incision is small, no muscle separation is required, and the operation is difficult;
- 5) If the operation fails or needs to be modified later, it is easier to switch to TKA[10].
Precautions:
- Surgery may require bone grafting, which may lead to delayed union or nonunion of fractures;
- It may lead to low patella and increased pressure in the joint cavity;
- Postoperative joint stability is difficult to control, and the recurrence rate of deformity is high.
- Which patients are suitable for high tibial osteotomy? Which patients are not suitable for it?
HTO indications mainly include:
- A. Relatively young patients under 65 years old (female under 60 years old)
- B. BMI<30kg/m2;
- C. The range of motion of the knee joint is normal, and the knee joint is stable;
- D. The lesion is limited to the inner compartment, and the outer compartment is normal;
- E. Conservative treatment is invalid for more than half a year without surgical contraindications.
- F. The flexion deformity is less than 10°F, the tibial varus deformity is greater than 5°, and the medial angle of the proximal tibia is less than 85°
The main contraindications are: ①Age >65 years old, with poor general condition and cannot tolerate surgery; ②Patients with basic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease; ③Patients with multiventricular disease; ④BMI>30kg/m2; ⑤Severe, Knee ligament rupture, septic arthritis in patients with rheumatoid or rheumatoid arthritis 6 exposure of tibia and femur articular surfaces and long-term smoking.
05 What is the effect after HTO?
According to reports in the literature, 95% of patients had no other surgery within 5 years after osteotomy, 91.6% of patients had no other surgery 10 years after surgery, and more than 90% of patients had no other surgery 10 years after HTO. That is, in most patients, the effect of knee-sparing surgery can be maintained for more than 10 years.
The postoperative recovery is fast and the effect is good. On the second day after the operation, they can walk on crutches and will be discharged after three or four days. You can walk slowly in one and a half months.
06 Apart from HTO, what other surgical methods can patients choose?
(1) Unicondylar replacement (UKA)
Only replace the inner part of the articular surface, which can correct mild varus, preserve the ligaments, and relieve the pain of the inner joint. It is suitable for the simple internal measurement of cartilage wear.
(2) TKA:
Replace the entire articular surface, correct the line of force, the prosthesis has a long life, and the effect is positive. It is suitable for patients with total knee cartilage wear and varus deformity.
07 What are the possible postoperative complications of HTO?
A comprehensive physical examination and medical history collection before surgery, strict control of the indications and contraindications for surgery, selection of appropriate internal fixation methods, and good postoperative rehabilitation training will help reduce complications and improve patient prognosis. Most patients recover well after HTO, but there are also some complications, such as deep vein thrombosis of lower limbs, common peroneal nerve injury, surgical incision infection, tibial plateau fracture, lower patella, injury of ligament around knee joint, loose internal fixation, bone and tendon Membrane compartment syndrome and so on.
08 How is HTO progressing?
In recent years, with the popularization of knee-protection concepts, HTO, as a special minimally invasive surgery, has become more and more popular for its advantages of simple operation, convenient operation, easy to master, less bleeding, less postoperative complications, and significant clinical effects. The more patients accept it. At the same time, HTO combined with arthroscopy, as a safe and effective surgical method, is also favored by more and more patients. The choice of preoperative patients, the function of the knee joint, the choice of surgical methods, the goodness of internal fixation and the correction of the postoperative line of force are important factors that affect the efficacy of HTO. However, it is believed that with the development of technology, 3D technology can be used to correct HTO force lines more accurately in the future, thereby reducing pain after surgery, delaying the progression of knee arthritis, and bringing more benefits to patients.
(sourceinternet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



