How to do if a meningioma recurs after surgery?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
How to do if a meningioma recurs after surgery?
How to do if a meningioma recurs after surgery? At present, the main clinical treatment methods for recurrent meningiomas are radiotherapy and reoperation.
Meningioma is a common benign tumor in the brain, with an incidence rate of 19.2% of intracranial tumors, ranking second. It is a derivative of meninges and meningeal space that grows slowly. Clinically, many meningiomas are accidentally discovered.
The main impact of meningioma on patients is that the growth of the tumor causes compression of peripheral nerves and blood vessels. The current treatment of meningioma is mainly surgical resection. During the operation, the doctor will cut the tumor as much as possible. In recent years, with the development of micro-neurosurgical technology, the surgical effect of meningiomas has been significantly improved.
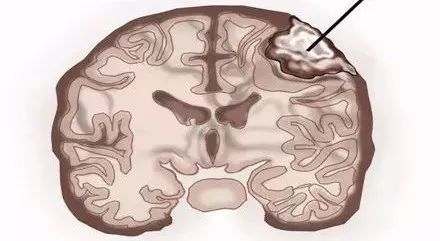
Although meningiomas are benign tumors, most patients can be cured after surgical resection, but some patients may recur. Clinically, the main reason for the recurrence of meningioma patients after surgery may be the absence of a total resection of the tumor or the erosion of the bone by the meningioma.
Although the tumor should be completely removed as much as possible during meningioma surgery, meningioma may involve nerves, blood vessels and other important intracranial tissues. During the operation, in order to avoid dysfunction of blood vessels and nerves, a part of the tumor may remain and cause tumor recurrence. Of course, if the meningioma erodes the bone, the blind full resection during the operation may also cause the corresponding neurological dysfunction, so the residual tumor body will lead to the tumor recurrence.
At present, the main clinical treatment methods for recurrent meningiomas are radiotherapy and reoperation. However, radiotherapy may cause side effects such as radiation damage and necrosis, so neurosurgeons often recommend patients to operate again.
Whether a patient with meningioma recurrence needs surgery can not be simply determined from whether the tumor is recurring, but based on the age, physical condition, symptoms and signs of the patient with meningioma. Of course, the patient’s age and the location of tumor growth may directly affect the patient’s surgical results and results.
All in all, I hope that the patient’s friends will be clear: Although meningiomas are benign tumors, they may also recur after surgery. Therefore, patients must pay attention to timely review during postoperative recovery and perform postoperative consolidation treatment to prevent recurrence
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



