Nature: Leprosy drug amphenazine can effectively inhibit the new coronavirus
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Nature: Leprosy drug amphenazine can effectively inhibit the new coronavirus
Nature: Leprosy drug amphenazine can effectively inhibit the new coronavirus. The research team pointed out that in both human cells and hamster models, aminophenazine can effectively fight the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection, and when combined with Redecive, it has a synergistic effect in reducing virus replication.

On March 16, 2021, the Yuan Guoyong team of the University of Hong Kong and others published a research paper titled “Clofazimine broadly inhibits coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2” in Nature magazine.
The study showed that clofamizine, a drug originally used to treat leprosy, can effectively combat new coronavirus infections in human cells and hamster models, and has a synergistic effect with remdesivir.
Fenazine can be taken orally, and the manufacturing cost is relatively low. These characteristics make it a potentially attractive drug candidate for COVID-19.

In this study, the research team studied the effectiveness of triamphenazine against coronaviruses, which is a drug approved by the US FDA for marketing. It is used to treat leprosy by interfering with the nucleic acid metabolism of Leprosy bacillus. It is a second-line anti-leprosy drug. It is used to treat tumor-type leprosy and borderline leprosy. It is suitable for people allergic to sulfone drugs or when bacteria are resistant to sulfones. , The drug is not easy to cause leprosy reactions, so it can be used when other drugs cause leprosy reactions and cannot continue to be used.
The research team found that aminophenazine can reduce the replication of two coronaviruses (new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus MERS-CoV) in human and monkey cell lines and human lung tissue.
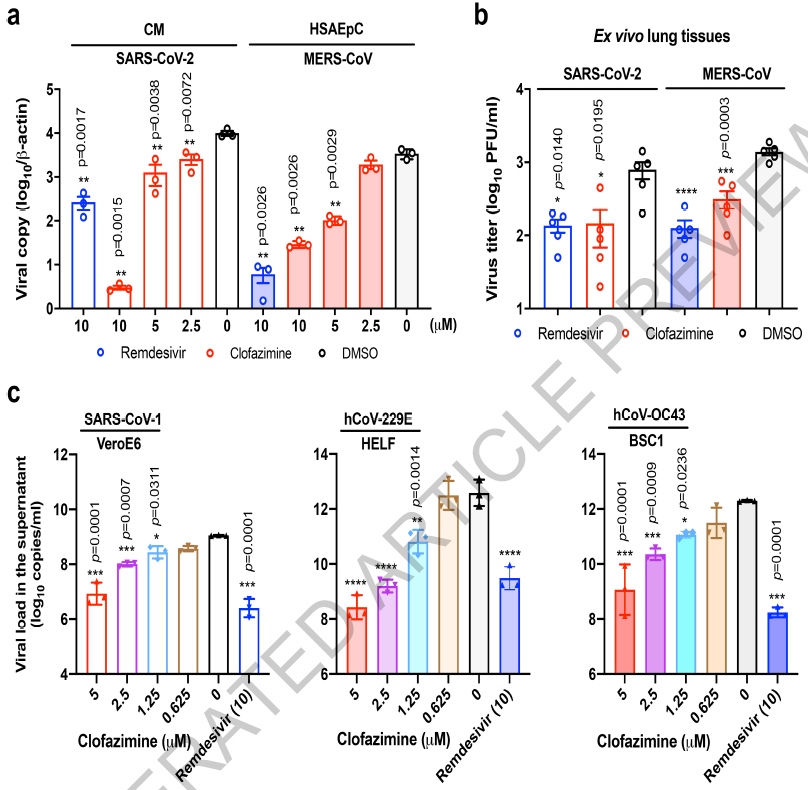
In the analysis of the drug’s antiviral effect, the research team observed that the drug targets multiple steps in the replication of the new coronavirus, including interference with the cell fusion process and the activity of viral helicase.
In the hamster model of new coronavirus infection, the use of amphenazine before or after virus exposure can significantly reduce the number of virus particles found in the lungs.
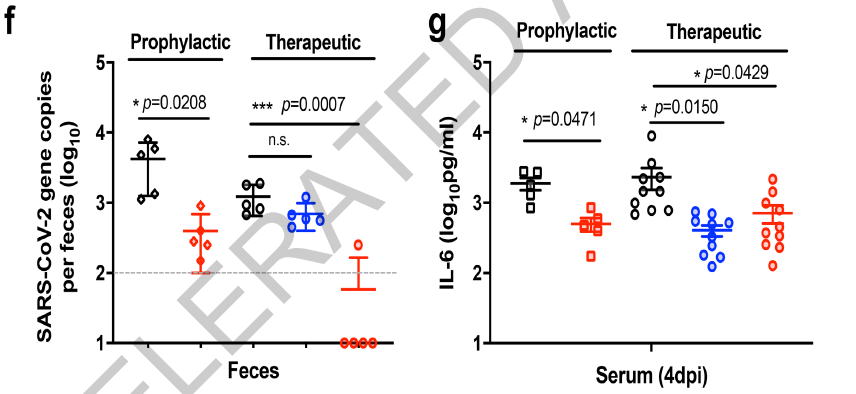
When combined with Remdesivir (Remdesivir), the two drugs have a synergistic effect in reducing virus replication. Low-dose remdesivir combined with aminophenazine can limit the improvement of the virus control effect in the hamster model.
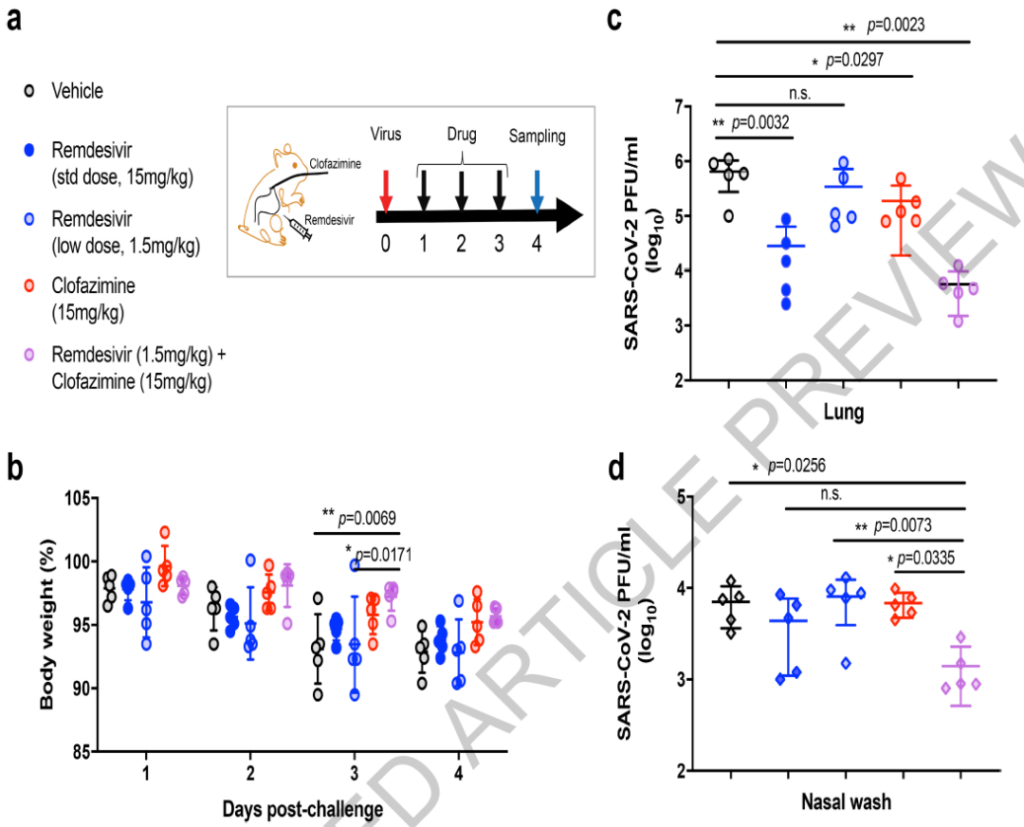
The research team pointed out that in both human cells and hamster models, aminophenazine can effectively fight the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection, and when combined with Redecive, it has a synergistic effect in reducing virus replication. Fenazine can be taken orally, and the manufacturing cost is relatively low. These characteristics make it a potentially attractive drug candidate for COVID-19. More clinical studies are now needed to determine whether it has the potential to become an alternative therapy.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



