Difference between male and female symptoms of Delta variant infection?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Difference between male and female symptoms of Delta variant infection?
Difference between male and female symptoms of Delta variant infection? What is the difference between male and female symptoms of Delta variant infection?
As the COVID-19 epidemic spreads, “atypical symptoms” may increase the difficulty of early detection and blocking infection.
“As the virus continues to mutate, the most common symptoms of COVID-19 infections have changed.” On July 29, “The Lancet-Digital Medical” released the latest research from King’s College London, UK. Previously, it was the research team who proposed that the “most typical symptom” of the COVID-19 is loss of taste/olfaction. Immediately, countries including China included it as a “list of symptoms to be monitored.”
Currently, 99% of new cases in the UK are infections with the Delta strain. The symptoms of infected persons are becoming more and more like flu. The most common symptoms are headache, sore throat, runny nose, fever, and persistent cough (in descending order of the number of reports).
“We need to expand the’symptom list’ so that early warning signals can be issued.” The research leader, Professor Tim Spector of Genetic Epidemiology, King’s College London, pointed out.
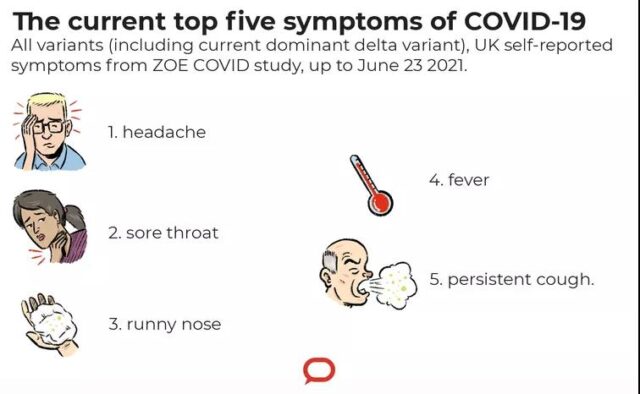
Picture from The Conversation
The symptoms of COVID-19 infection have changed again and again
The aforementioned study at King’s College London, UK, is called the “Covid Symptoms Study” (Covid Symptoms Study), which started in the spring of 2020. At that time, the college cooperated with Massachusetts General Hospital and Zoe Global, a health science company, to develop an application software that allowed users to report their health status daily.
The research team established a model that combined the user’s age, gender, body mass index, and symptoms such as loss of smell or taste, cough, fatigue, and loss of appetite to predict whether it is a COVID-19 infection.
In May 2020, “Natural Medicine” published the team’s preliminary research results, claiming that the prediction accuracy rate is nearly 80%. At the same time, model analysis shows that loss of taste or smell is the primary indicator for predicting COVID-19 infection; followed by extreme fatigue and acute muscle pain. Fever and cough are the fourth and fifth judging indicators.
In February of this year, King’s College London updated its “recommendations”, stating that the typical symptoms of COVID-19 should be expanded to 7 types, including cough, fever, loss of taste or smell, fatigue, headache, sore throat and diarrhea (in no particular order).
Symptoms of COVID-19 infection vary by gender and age
According to an article published by “The Lancet-Digital Medical” on July 29, after infection with the Delta strain, the symptoms of COVID-19 changed again.
Tim Spector told the Daily Mail that the research team analyzed the data collected by the software on 18,299,000 adult infected persons. Among them, 15,049 people tested positive for nucleic acid. Relevant data was collected 3 days after the first symptoms appeared.
The results show that:
First, the infection symptoms of medical workers are specific.
The software collects and analyzes, and there are 18 main reported symptoms of COVID-19 infection. The core symptoms of workers in the medical industry include loss of smell, chills, persistent cough, headache, and chest pain. Other symptoms include abnormal muscle pain, diarrhea, and fatigue.
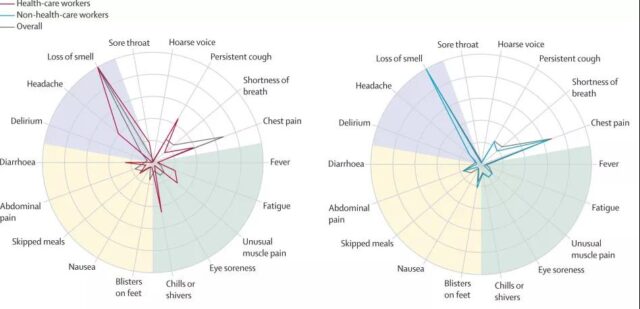
Picture description: The red line is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection by medical industry workers; the blue is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection by non-medical workers; the gray line is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection for the entire population.
Second, there are differences in the symptoms of male and female infections.
After being infected, men are more likely to experience shortness of breath, fatigue, chills and fever. Loss of smell or taste, chest pain, and persistent cough seem to be the most common among women infected.
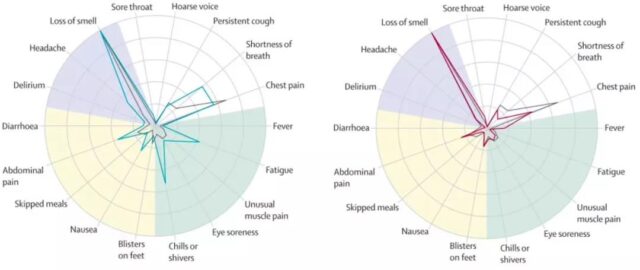
Picture description: The blue line is the radar table for reporting symptoms after male infection; the red is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection for women; the gray line is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection for the entire population.
Third, people 80 years and older are more likely to report diarrhea. Loss of taste/olfaction is rare in this age group.
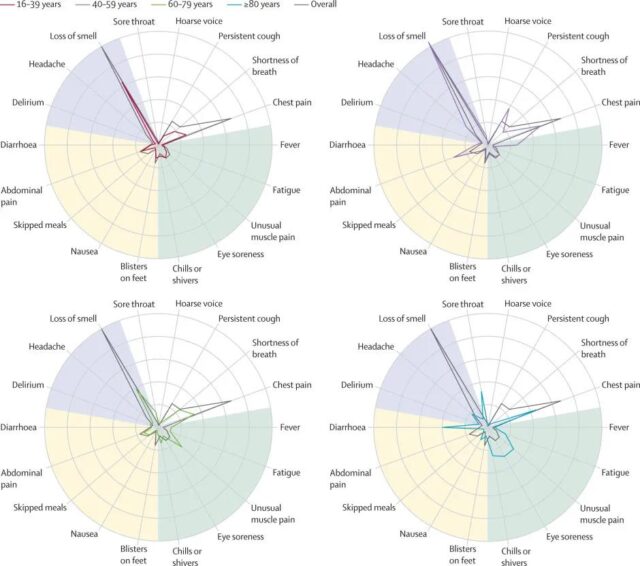
Picture description: The green line is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection for people 60-79 years old; the blue is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection for people over 80 years old; the gray line is the radar table for reporting symptoms after infection for the entire population.
Fourth, after infection with the Delta strain, the most common symptoms are headache, sore throat and runny nose.
“It is especially important to note that the incidence of loss of smell or taste has dropped to ninth.” said one of the main authors, Professor Claire Stevens, King’s College London, UK.
Laura Herrero, director of the Virology and Epidemiology Research Program at Griffith University in Australia, did not participate in the above-mentioned research. She wrote that the main symptoms of the COVID-19 infection have changed due to many reasons.
First of all, in the spring of 2020, more data collected by the software will come from patients and relatives, who may be more severely ill and have correspondingly more and more severe symptoms.
Secondly, after the COVID-19 vaccine is widely vaccinated, the proportion of people aged 20-50 in the total infected population has increased. Even if people in this age group are infected with the disease, the symptoms are generally mild.
Again, this may be related to virus mutation and evolution.
John Brownstein, an epidemiologist at Boston Children’s Hospital in the United States, commented that this study highlights the value of mobile devices in real-time surveillance of epidemics. However, the disadvantage is that users of mobile devices are often younger and it is difficult to obtain real infection data of the elderly.
Should the monitoring symptoms be updated?
The “medical community” found that the World Health Organization (WHO) description of the symptoms of COVID-19 is different from the previous studies.
The WHO updated its guidelines on May 31, 2021, stating that the most common symptoms of COVID-19 include fever, dry cough, and fatigue. Secondly, some infected people may experience muscle pain, sore throat, diarrhea, conjunctivitis, headache, loss of taste or smell, skin rash, discoloration of fingers or toes. Severe symptoms are difficulty or shortness of breath, chest pain or pressure in the chest, loss of speech or motor function.
Claire Stevens believes that what needs to be advertised is that there are many symptoms of COVID-19 infection, and everyone’s performance may be different, and the list of monitored symptoms should be expanded.
British media believe that expanding monitoring of symptoms may significantly increase the burden on the British medical system. The research team also said that if the “list of typical symptoms” is increased from 3 to 7, the positive detection rate may increase from the current 46:1 to 95:1. “But every time a positive patient is screened, it is saving lives.”
Tim Specter emphasized that the increase in the number of people between the ages of 20 and 29 in the UK has been very significant. “If young people find that they have flu-like symptoms, please stay at home and receive a nucleic acid test as soon as possible.”
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



