Cancer stem cell marker ALDH1A1 to promote breast cancer
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Cancer stem cell marker ALDH1A1 to promote breast cancer
Cancer stem cell marker ALDH1A1 to promote breast cancer.
A new mechanism for cancer stem cell marker ALDH1A1 to promote breast cancer by remodeling the immune microenvironment.
More and more studies have shown that in a small part of a variety of tumor tissues, a small part of cells with particularly strong tumorigenicity, extremely low differentiation, and self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation characteristics of stem cells are called “cancer stem cells (Cancer Stem Cells). Cells, CSCs)”.
Aldehyde dehydrogenas 1A1 (Aldehyde dehydrogenas 1A1, ALDH1A1) is one of the important biomarkers of breast cancer stem cells (Breast Cancer Stem Cells, BCSCs).
Studies have found that ALDH1A1 is also a predictor of breast cancer development and poor prognosis, and its expression and enzyme activity have important regulatory effects on tumor development.
However, the specific mechanism of how ALDH1A1 promotes breast cancer progression and how to maintain the characteristics of BCSC is still unclear.
Solving this problem will bring new hope for us to design specific anti-tumor drugs that target cancer stem cells.
On December 1, 2021, Researchers from Fudan University Cancer Hospital published an online research paper entitled ALDH1A1 activity in tumor-initiating cells remodels myeloid-derived suppressor to promote breast cancer progression in Cancer Research , revealing that ALDH1A1 relies on its enzyme activity to promote breast cancer progression .
The remodeling and tumor-promoting effects of breast cancer immune microenvironment and its specific molecular mechanisms help us better clarify the influence of BCSC marker ALDH1A1 on the occurrence and development of breast tumors, and provide new ideas for the clinical treatment of malignant breast cancer.
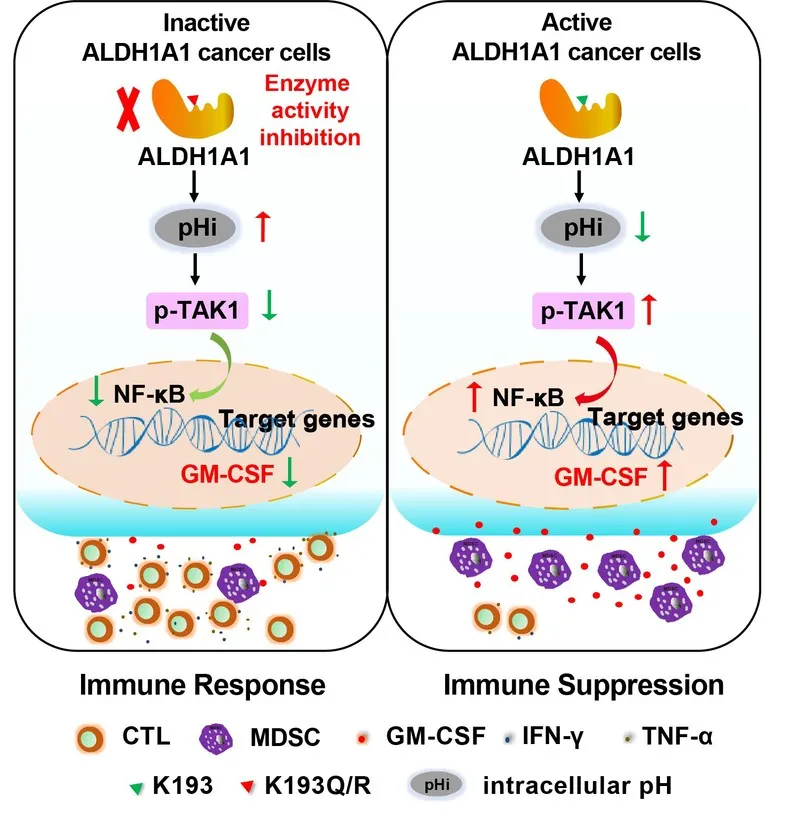
In order to analyze the remodeling effect of ALDH1A1 on the immune microenvironment of breast cancer, the authors constructed a triple-negative breast cancer stable cell line that overexpressed wild-type ALDH1A1 (with enzyme activity) and K193Q/R mutant (with no enzyme activity).
Proliferation function test and in vivo breast orthotopic transplantation tumor test found that ALDH1A1 relies on its aldehyde dehydrogenase activity to play a role in promoting BCSC self-renewal and tumor growth.
Immune cell staining and flow cytometry analysis showed that ALDH1A1-dependent enzyme activity promotes the enrichment of MDSCs in the tumor microenvironment, and MDSCs inhibits CD8+ T cell immune activity to promote tumor growth; moreover, it inhibits ALDH1A1 enzyme activity and knockdown Their expressions all showed the opposite effect.
Due to the low proliferation rate of CSCs and high resistance to immune-mediated killing, when a large number of ordinary tumor cells are eliminated by the immune system, CSCs can still escape the damage of the immune system, and in this immune escape process, except for tumor stem cells Heterogeneity and genetic variation continue to increase, and changes in the tumor immune microenvironment also play an indispensable role; this study found that the BCSC biomarker ALDH1A1 regulates MDSCs and active CD8+ T cells.
In terms of mechanism, they found that ALDH1A1 relies on its enzyme activity to lower the pH value in tumor cells, thereby activating the TAK1-NFkB signaling pathway, increasing the secretion of granulocyte macrophage stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in tumor cells, and then inducing the tumor microenvironment With the increase of MDSCs, the increase of MDSCs finally inhibited the anti-tumor immune activity of CD8+ T cells to promote breast tumor growth.
Aiming at the specific mechanism that ALDH1A1 exerts to promote breast cancer, they designed a combination therapy strategy to more efficiently target the treatment of malignant breast cancer.
They used gemcitabine, a chemotherapeutic drug that can eliminate MDSCs, and disulfiram, an inhibitor of ALDH1A1 enzyme activity, alone or in combination to treat orthotopic breast transplantation tumors in mice with healthy immune function and human-derived breast tumor transplantation tumors (PDX) with immunodeficiency. Rat model.
The results show that the combined treatment effect is better than any single-agent treatment effect. The combined use has a better anti-tumor effect and more effectively inhibits the growth of breast tumors.
At the same time, the combined treatment can better inhibit ALDH + BCSCs and immunity in tumor tissues.
Infiltration of MDSCs in the microenvironment.
Overall, this study found that ALDH1A1 relies on enzyme activity to reduce pHi in breast tumor cells to activate the TAK1-NFkB signaling pathway, which in turn leads to increased secretion of GM-CSF, induces MDSC amplification and reduces anti-tumor immunity, thereby promoting the development of breast tumors.
These research results help us better clarify the impact of BCSC marker ALDH1A1 on the occurrence and development of breast cancer and its specific molecular mechanisms, and provide direct evidence for the interaction between BCSC and MDSCs with ALDH enzyme activity, and provide direct evidence for the clinical treatment of breast cancer. Provides a new effective therapeutic target.
As soon as the paper was published, Lorenzo Galluzzi and others reviewed their work in Trends in Immunity with the title “MDSCs sneak CSCs out of immune-surveillance” and gave a high evaluation, believing that this study is to break the recruitment of CSCs.
MDSCs, which in turn promote the vicious circle of CSCs dryness, provide a new perspective.
Breaking this vicious circle can reshape the body’s immune surveillance of CSCs, thereby controlling the progression of tumors.
Doctoral student Liu Cuicui from Fudan University Cancer Hospital is the first author of the paper; Professor Liu Suling from Fudan University Institute of Biomedical Research/Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Associate Researcher Zhang Lixing from Fudan University Cancer Hospital, Professor Zhang Xiaoyong from Institute of Brain Science of Fudan University and Fudan University Cancer Institute Professor Shao Zhimin from the hospital is the co-corresponding author of this article.
Reference:
https://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/81/23/5919.short?casa_token=pPNLisAmSu8AAAAA:6PvaWH1_YEmyHq3K0UiqvLh16lMuuKYMLd9N9M_lHeG36BSphG0xN9ziI6b8Ilvaa#
Cancer stem cell marker ALDH1A1 to promote breast cancer
(sourceinternet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org




