Targeting ferroptosis inhibitor protein to promote cancer cell ferroptosis
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Targeting ferroptosis inhibitor protein to promote cancer cell ferroptosis
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
New strategy for cancer treatment: Targeting ferroptosis inhibitor protein to promote cancer cell ferroptosis.
During the development of multicellular organisms, there are a variety of predetermined and precisely controlled programmed cell death, such as apoptosis (Apoptosis) , programmed necrosis (Necroptosis) , cell death (Pyroptosis) , and ferroptosis ( Ferroptosis) and so on.
Ferroptosis is a new type of iron-dependent programmed cell death discovered by the Brent Stockwell laboratory of Columbia University in 2012. It is induced by excessive accumulation of peroxidized lipids . Its morphological characteristics and effects The method and molecular mechanism are quite different from other forms of programmed death.
At the same time, there are multiple pathways against ferroptosis in cells(especially cancer cells), such as glutathione peroxidase 4(GPX4)mediated by glutathione(GSH)-specific catalyzed Oxidizes lipids to inhibit ferroptosis.
In October 2019, the Marcus Conrad team of the Helmholtz Munich Research Center in Germany published a paper in Nature [1] , identifying FSP1 as a new type of potent ferroptosis inhibitor independent of glutathione . The antioxidant form of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ) promotes cancer cell resistance to ferroptosis.
Induction of ferroptosis is a promising approach for the treatment of refractory cancers, and the CoQ-FSP1 pathway is a potential target to relieve cancer cell ferroptosis resistance.
On May 12, 2023, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley published a research paper titled: Identification of structurally diverse FSP1 inhibitors that sensitize cancer cells to ferroptosis in the Cell Sub-Journal Cell Chemical Biology [2] .
This study identified several FSP1 inhibitors, the most potent of which was ferroptosis sensitizer 1 (FSEN1) .
FSEN1 selectively sensitizes cancer cells to ferroptosis by targeting FSP1 and it also interacts with other ferroptosis-inducing Agents play a synergistic effect to further trigger ferroptosis.
These findings provide new tools for advancing FSP1-targeting ferroptosis-inducing cancer therapeutic strategies and also highlight the value of combinatorial therapeutic options targeting FSP1 and other ferroptosis defense pathways.

Induction of ferroptosis is a promising approach to treat refractory cancers, and FSP1 promotes cancer cell resistance to ferroptosis by producing an antioxidant form of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ) . Despite the important role of FSP1 in regulating ferroptosis, few molecular tools targeting the CoQ-FSP1 pathway exist.
In this latest study, the research team identified several structurally distinct FSP1 inhibitors through a series of chemical screens.
The most potent of these compounds is ferroptosis sensitizer 1 (FSEN1) , a noncompetitive inhibitor that selectively sensitizes cancer cells to ferroptosis by targeting inhibition of FSP1.
Furthermore, synthetic lethality screens revealed that FSEN1 can synergize with endoperoxide-containing ferroptosis inducers , such as dihydroartemisinin , to trigger ferroptosis .
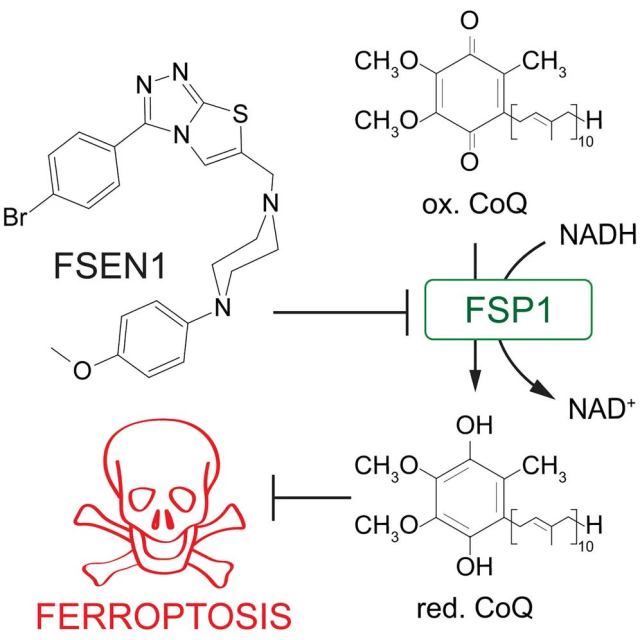
These findings provide new tools for advancing FSP1-targeting ferroptosis-inducing cancer therapeutic strategies and also highlight the value of combinatorial therapeutic options targeting FSP1 and other ferroptosis defense pathways.
Paper link :
1. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1707-0/
2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.04.007
Targeting ferroptosis inhibitor protein to promote cancer cell ferroptosis
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



