Do people with low immunity need to be vaccinated against COVID-19?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Do people with low immunity need to be vaccinated against COVID-19?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Do people with low immunity need to be vaccinated against COVID-19?
Should Immunocompromised People Get the COVID-19 Vaccine?
Did it work?
In order to answer this question, the School of Biomedical Sciences, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, and the Shenzhen Advanced Technology Research Institute recently published a paper entitled: Vaccine-induced protection against SARS-CoV-2 requires IFN-γ-driven cellular immune in Nature Communications , a sub-journal of Nature . response research paper.
This study shows that COVID-19 mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 can provide sufficient immunity against COVID-19 virus in the absence of antibodies and no induction of humoral immunity, demonstrating the importance of cellular immunity in the prevention of COVID-19 pneumonia.
It also further emphasizes the importance of vaccination in immunocompromised populations .

Professor Huang Jiandong from the School of Biomedical Sciences of the Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine of the University of Hong Kong , Assistant Professor Zhu Xuan from the Department of Microbiology, and Associate Researcher Zhang Baozhong from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology are the corresponding authors of the paper.
Wang Xiaolei, a postdoctoral fellow at the School of Biomedical Sciences, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, HKU, Yuan Zitai , a postdoctoral fellow at the Department of Microbiology, Dou Ying , Hu Jingchu , a master student , and Li Renhao , a doctoral student , are the first authors of the paper.
Based on the humanized K18-hACE2 mouse model, this study constructed a B cell-deficient transgenic mouse (μMT) , and through this model, it proved that COVID-19 mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 can induce effective expression in this gene-deficient mouse. Protective immunity against many different variants of the new coronavirus.
This study further demonstrated that this protective immunity was attributed to interferon-γ-mediated cellular immunity, and that both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells contributed to this cellular immunity.
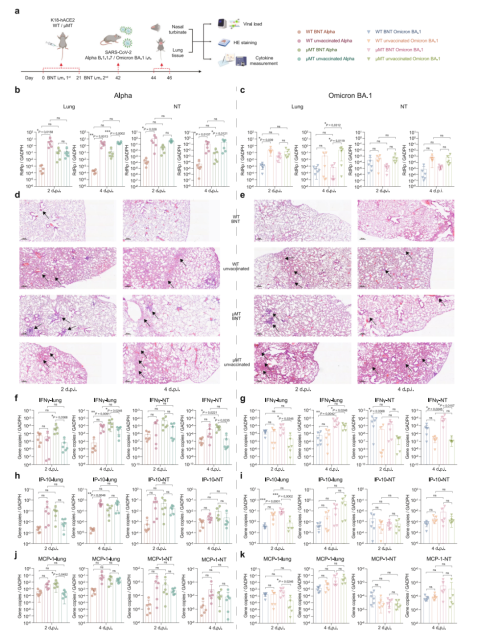 Figure 1. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine elicits significant protective immunity in C57BL/6 j μMT mice
Figure 1. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine elicits significant protective immunity in C57BL/6 j μMT mice
The research team confirmed through the antibody-deficient mouse model that the replication ability of Alpha and Omicron BA.1 variant viruses was inhibited in the lungs and nasal cavities of immunized wild-type and deficient mice. Lung pathology was milder in the vaccinated group of mice compared to unvaccinated mice.
After further analysis, the team found that the expression of the cytokine interferon-γ was significantly increased in the vaccinated antibody-deficient mice compared with the non-immunized group.
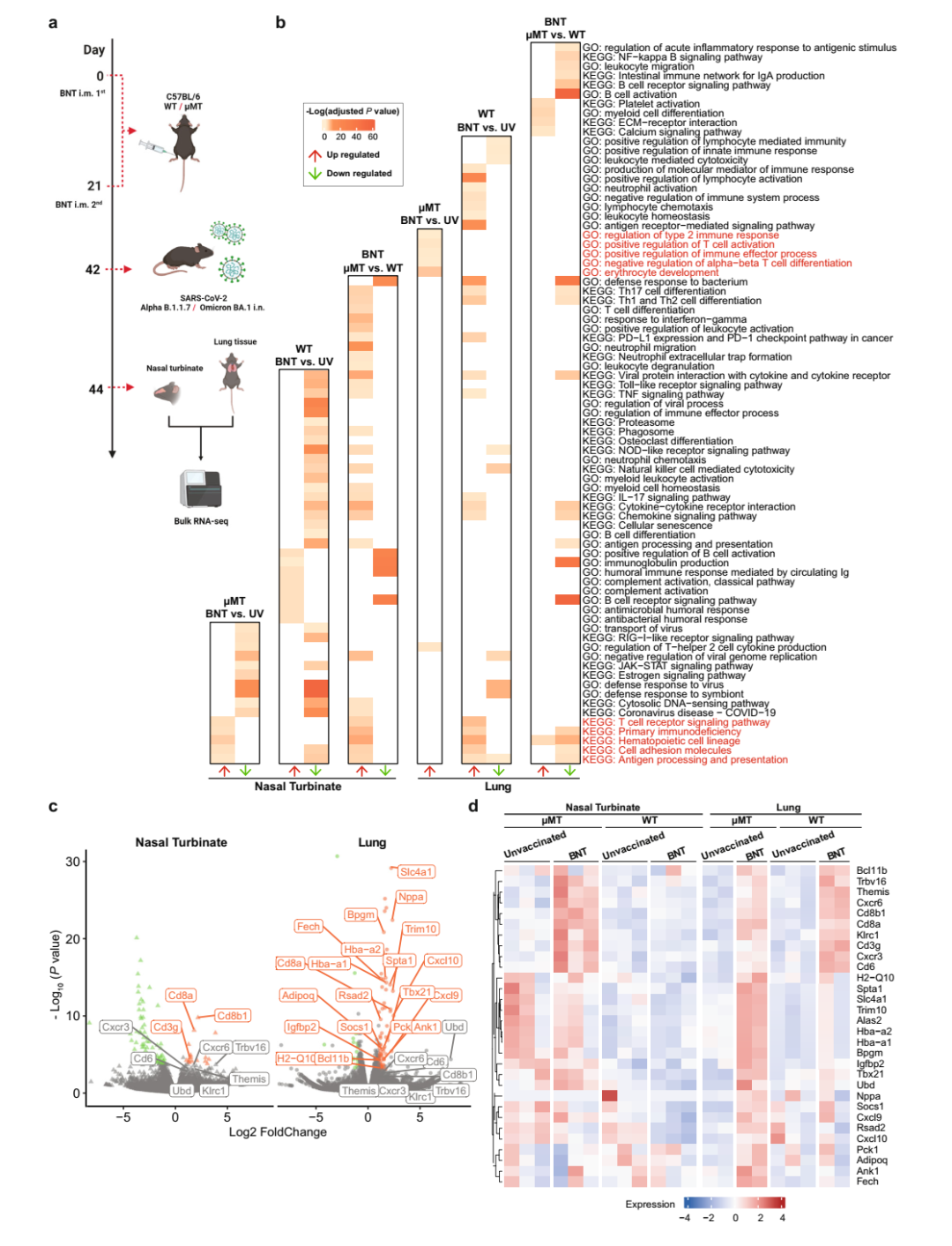 Figure 2. Transcriptome profiles of BNT162b2-vaccinated μMT mice after SARS-CoV-2 challenge determined by RNA-Seq
Figure 2. Transcriptome profiles of BNT162b2-vaccinated μMT mice after SARS-CoV-2 challenge determined by RNA-Seq
The research team further analyzed the results of RNA sequencing and confirmed that in the lungs and nasal cavity of antibody-deficient mice, due to the lack of mature B cells, only genes involved in T cell activation and T cell receptor signaling pathways were significantly up-regulated under vaccination .
CD8+ T cells were highly enriched in vaccinated antibody-deficient mice compared with unvaccinated deficient mice.
In addition, the cxcr6 gene, which is highly associated with tissue memory T cells, was also highly expressed in vaccinated antibody-deficient mice.
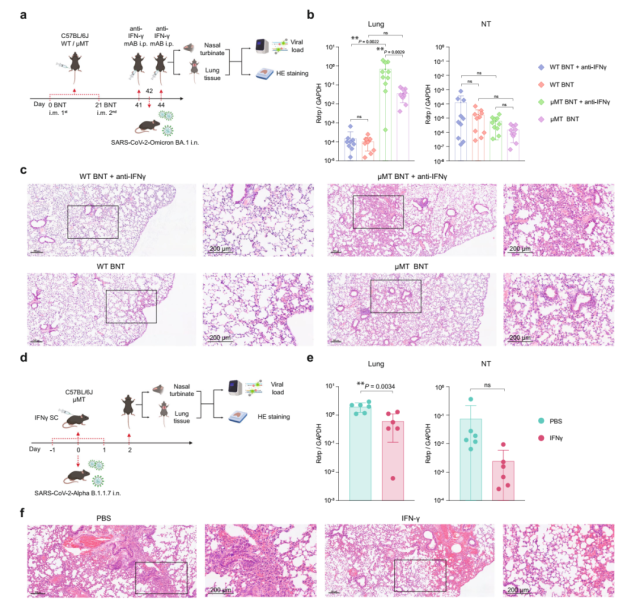 Figure 3. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are required for vaccine-induced immune responses to clear SARS-CoV-2 in nose and lung tissues of μMT mice
Figure 3. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are required for vaccine-induced immune responses to clear SARS-CoV-2 in nose and lung tissues of μMT mice
The research team then used interferon-gamma depletion antibodies to demonstrate that the ability of the Omicron BA.1 variant virus to replicate in the lungs of vaccinated antibody-deficient mice compared with normal conditions under conditions of restricted interferon-gamma production Improvement by 19.3 times.
Consistent with this result, vaccinated antibody-deficient mice developed more severe lung lesions under conditions of restricted production of interferon-γ.
In addition, we also demonstrated that subcutaneous injection of interferon-γ to unimmunized antibody-deficient mice can inhibit the replication of 2019-nCoV and alleviate the symptoms of mice.
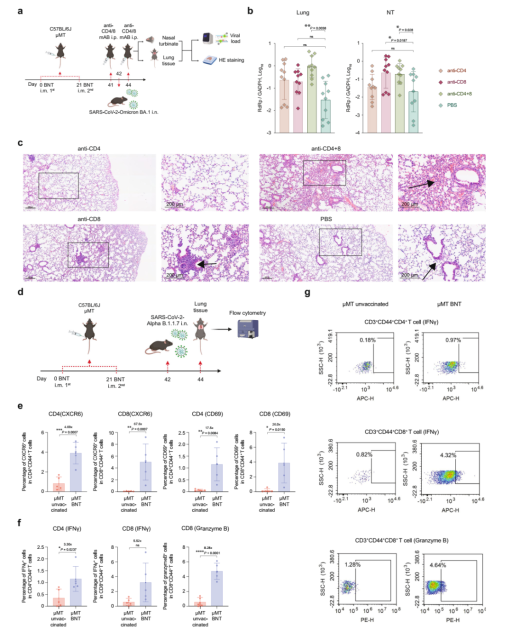 Figure 4. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine induces protective immunity against Omicron BA.5.2 in C57BL/6 J and K18-hACE2 μMT mice
Figure 4. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine induces protective immunity against Omicron BA.5.2 in C57BL/6 J and K18-hACE2 μMT mice
Finally, the research team concluded through flow cytometry analysis that after infection with the virus, the number of resident memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in lung tissue was significantly higher in vaccinated antibody-deficient mice than in unimmunized mice .
And in the lungs of vaccinated antibody-deficient mice, the expression levels of interferon-γ and granzyme B in CD8+ T cells were 5.5 and 8.3 times higher than those in the control group, respectively.
These data confirm the previous conclusion that COVID-19 mRNA vaccine induced a strong cellular immune response in antibody-deficient mice after infection with the new coronavirus.
Paper link :
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-39096-y
Do people with low immunity need to be vaccinated against COVID-19?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



