Flu Season Update: 15000 Deaths in United States as CDC report
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Flu Season Update: 15000 Deaths in United States as CDC report
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Flu Season Update: 15000 Deaths in United States as CDC report
According to the latest statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the flu virus is still spreading at a high level in the United States.
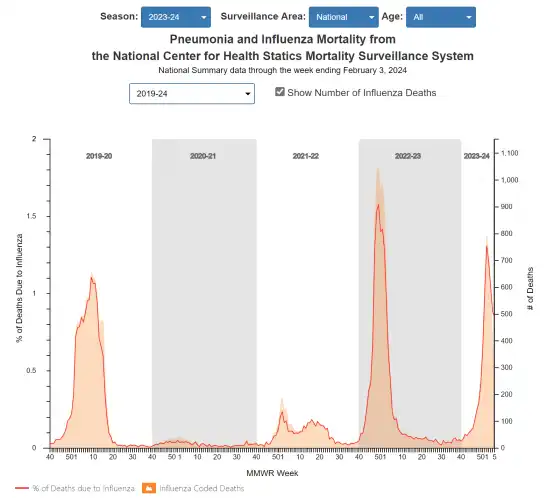
It is estimated that there have been at least 22 million flu cases so far this flu season, with 250,000 hospitalizations and 15,000 deaths.
CDC data shows that in the week ending February 3, there were over 11,000 flu-related hospitalizations nationwide, with 8 deaths in children due to flu. So far this flu season, there have been a total of 74 reported flu-related deaths in children in the United States.
The CDC recommends that everyone aged 6 months and older get a flu vaccine every year, as it not only helps prevent flu virus infection but also prevents severe illness.
The flu season in the United States typically occurs in the fall and winter, with peak activity from December to February.
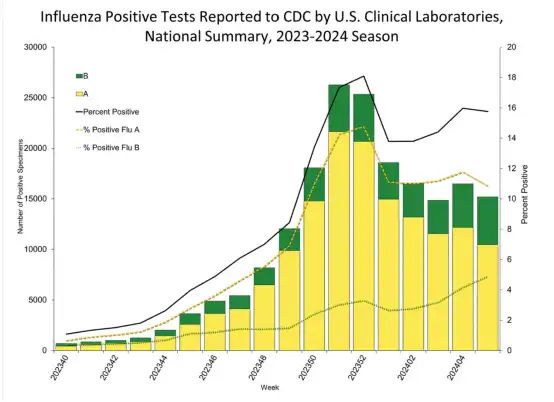
Earlier, the CDC assessed and predicted the flu season:
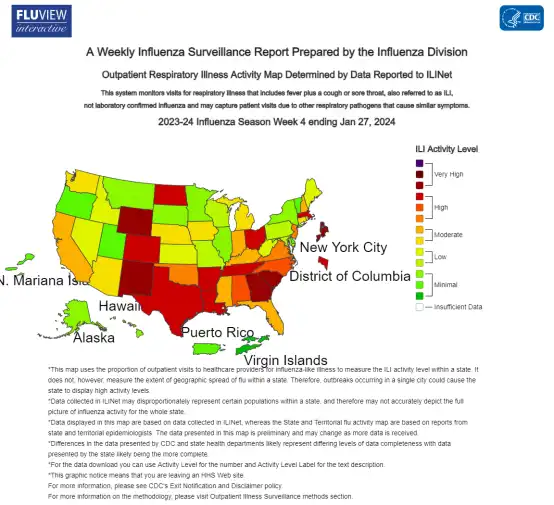
At the beginning of this month, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) updated the latest flu situation. After a few weeks of declining activity, flu activity in some parts of the country has increased, while COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) levels continue to decrease overall.
Data shows that flu activity is increasing in four states: Florida, New York, Oklahoma, and Texas. Additionally, five states (Arkansas, Kentucky, Massachusetts, North Carolina, and South Carolina) are also experiencing an increase. Wastewater monitoring shows the highest levels of COVID-19 in the southern region, with cases expected to increase in South Carolina.
A second wave of increased flu activity after the winter holidays is common, but experts say it’s difficult to accurately predict how long or how severe the entire flu season will be. The CDC states that sometimes this surge marks the beginning of a second wave, but it could also be a minor interruption before a more sustained decline.
Alicia Budd, who oversees domestic flu monitoring at the CDC, said that generally, the second wave of flu often occurs after a more significant decline, when influenza B viruses begin to exceed the main circulating influenza A viruses.
She said there is currently no evidence that this is happening, but it is too early to rule out any possibilities.
“We are still in the middle of the season,” Budd said. “It’s too early to determine our exact position on the final trajectory. We just don’t know yet. But we are still seeing a lot of flu activity.”
Most US healthcare institutions require healthcare workers to get flu vaccines.
The flu has always been a very serious seasonal respiratory infectious disease, causing 12,000 to 52,000 deaths in the United States each year (a special case in 2021-22, with 4,900 deaths). As a result, most US healthcare institutions require healthcare workers to get flu vaccines.
The proportion of Americans voluntarily receiving flu vaccines is also very high. For example, in the winter of 2023-24, the proportion of adults receiving flu vaccines was as high as 47.0%, with the elderly receiving a proportion of 72.8%; far higher than the proportion of adults receiving COVID-19 vaccines at 21.8%, and the elderly at 41.0%.
Flu Season Update: 15000 Deaths in United States as CDC report
(source:internetKwcM2aOgdxWXi6q1tlopnw, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



