C peptide test result analysis
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
C peptide test result analysis
C peptide test result analysis. As an endocrinologist, C peptide can be used a lot in the daily diagnosis and treatment process. So why do we need to detect C peptide? How to detect C peptide? What about the result?
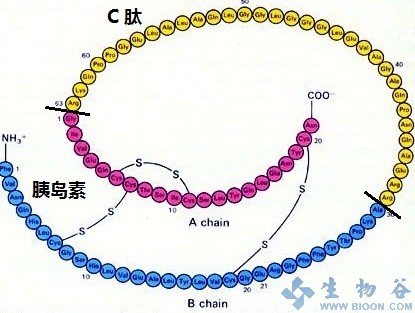
What is C peptide? Why test C peptide?
C-peptide, also known as connecting peptide, is a secreted product of pancreatic β cells. It shares a common precursor with insulin-proinsulin. A molecule of proinsulin is cleaved into a molecule of insulin and a molecule of C peptide under the action of pancreatic protease and carboxypeptidase.
C-peptide and insulin exist in the same granular capsule, and are finally secreted with equal molecular weight and released into the blood. After entering the liver from the portal vein, insulin will be taken up by the liver, and the amount of insulin will be indefinite; however, C-peptide is rarely taken up by the liver, mainly excreted directly through the urine through the kidneys, with a slower clearance rate; and compared with insulin The half-life is longer, so the concentration of the two in the blood is not equal.
The detection of C peptide level can more stably and comprehensively reflect the function of pancreatic β cells to secrete insulin, and C peptide has no cross-immune reaction with insulin, and can overcome the interference of insulin receptor.
For diabetic patients who have used exogenous insulin or have produced insulin antibodies, measuring the C-peptide level in the peripheral blood can reflect the level of endogenous insulin more accurately and timely, and can better represent the function of pancreatic β cells for guidance Treatment of diabetes.
What is the use of testing C peptide?
✦ Contribute to the clinical classification of diabetes and to understand the patient’s islet function.
✦ Because C-peptide is not interfered by insulin antibodies, for patients receiving insulin therapy, the concentration of C-peptide can be directly measured to determine the patient’s pancreatic β cell function and evaluate the clinical insulin treatment effect.
✦ Can identify the cause of hypoglycemia. For patients with frequent hypoglycemia, if C-peptide exceeds the normal range, it can be considered to be excessive insulin secretion; if it is lower than normal, it is caused by other reasons.
✦ The measurement of C-peptide level is helpful for the diagnosis of insulinoma and the evaluation of the effect of related surgery. If the serum C-peptide level is still high after the operation, it indicates that there is residual insulin tissue; if the serum C-peptide level continues to rise, it indicates that the tumor recurrence or metastasis is more likely.
✦ According to the 2020 international expert group consensus, in the management of latent autoimmune diabetes “LADA” in adults, it is recommended that patients be individually managed according to the level of C peptide:
- “C peptide <0.3 nmol/L” is recommended to follow the type 1 diabetes treatment plan and use insulin injection.
- “0.3 ≤ C peptide ≤ 0.7 nmol/L” It is recommended to follow the treatment plan for type 2 diabetes, and recommend metformin, GLP-1RA or DPP-4i, TZD and SGLT-2i oral hypoglycemic drugs treatment plan, if glycosylated hemoglobin does not meet the standard, use it in time Insulin treatment.
- “C peptide> 0.7 nmol/L” It is recommended to follow the treatment plan for type 2 diabetes, and consider using other oral hypoglycemic agents except sulfonylureas. It is recommended to repeat the C peptide test every 6 months or when blood sugar deteriorates. And once again formulate the treatment plan; and should pay attention to the identification of type 2 diabetes patients with false positive autoantibodies.
How to detect C peptide clinically?
C Peptide release test: The method is the same as the glucose tolerance test and insulin release test.
✦ Stop drugs that have an impact on the trial.
Discontinue drugs that may affect the test, such as contraceptives, diuretics, or phenytoin sodium, for 3 to 7 days before the test.
✦ Carbohydrate intake should be controlled but not excessively restricted.
The patient’s daily carbohydrate intake should not be less than 150 g since 3 days before the test, but it should be controlled within the range of 250 to 300 g and maintain normal activities.
✦ Don’t ignore the details of sugar water preparation, taking and timing.
From 7 to 9 in the morning, the patient took 75 g of anhydrous dextrose powder dissolved in 300 mL of warm water on an empty stomach for “8-10 h”, or 82.5 g of glucose with 1 molecule of water. Children are given 1.75 g per kilogram of body weight, and the total amount should not exceed 75 g.
The syrup is taken within 3 to 5 minutes. Start timing from the first mouthful of sugar, and take blood samples on the forearm to measure blood glucose and C-peptide levels before and after taking the sugar at 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h.
✦ Maintain peace and stability and accept the experiment.
During the experiment, the subjects did not drink tea or coffee, smoke, or did strenuous exercise, but they did not need to stay in bed absolutely. Blood samples should be submitted for examination as soon as possible.
✦ Fasting fingertip blood sugar is less than 10 mmol/L.
The test generally requires subjects to measure fasting fingertip blood glucose less than 10 mmol/L. If the fasting blood glucose exceeds 10 mmol/L, it indicates that the subject has high glucose toxicity inhibition. The data at this time cannot truly reflect the subject’s Islet function. Furthermore, taking sugar water orally when fasting blood sugar is too high will make high blood sugar worse and cause unnecessary damage to the subjects.
C How to analyze the results of peptide release test?
✦ C-peptide release curve of people with normal glucose metabolism: fasting plasma C-peptide is 0.3 ~ 1.3 nmol/L, and the secretion reaches the peak at 0.5 ~ 1.0 h after oral glucose, and the peak value is about 5 ~ 6 times the fasting value, and gradually after 2 ~ 3 h Return to fasting level.
✦ The main points of analyzing C peptide release test are as follows:
- Analyze the relationship between the value of each time point of the C peptide release test and the simultaneously measured blood glucose level, and whether there is relative hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance.
- Analyze the time when the peak of the C-peptide release test occurs, and whether there is a peak delay, which is characteristic of type 2 diabetes.
- When the C-peptide release curve is low, whether there is toxic inhibition of hyperglycemia on pancreatic β-cells, whether there is severe pancreatic β-cell failure, and whether it is type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes combined with insulin-related antibodies and disease course.
What are the common types of C-peptide release curves?
1. All points of the glucose tolerance test are within the normal range, but the C-peptide level is elevated, especially the fasting C-peptide, which indicates that there is fasting insulin resistance, which is more common in overweight and obese people.
The treatment plan is mainly to manage the lifestyle: proper diet control, physical exercise, weight reduction for obese people, and no hypoglycemic drugs. Check the glucose tolerance test and C-peptide release test in about 1 year. If the lifestyle is well controlled, the normal C-peptide secretion curve can be restored.
2. All points of the glucose tolerance test are in the normal range, and the fasting C-peptide level is elevated, indicating that there is fasting insulin resistance. The peak value after taking glucose is more than 5 times the fasting value, but the peak is delayed, which is the early manifestation of type 2 diabetes. Patients are prone to pre-meal hypoglycemia and are a high-risk group of diabetes.
3. Glucose tolerance test indicated impaired glucose regulation, fasting C-peptide level increased, the peak value appeared in 0.5 ~ 1.0 h, the peak value was more than 5 times the fasting value, 3 h was still high level, did not fall back to the fasting level.
The treatment plan is mainly to manage the lifestyle: proper diet control, physical exercise, weight reduction for obese people, alpha glycosidase inhibitors can be selected as hypoglycemic drugs, and metformin can also be taken orally for obese people.
4. The glucose tolerance test indicates that the fasting C-peptide level can be normal, high or low. After taking sugar, the release curve rises slowly, and the peak is delayed. The release curve still does not fall back to the fasting level after 3 hours. This is typical 2 Characteristics of type diabetes.
With the prolonged course of diabetes, the function of pancreatic islet β-cells gradually declines, the fasting C-peptide level gradually decreases, the post-prandial release curve rises more slowly, and the peak shift is more obvious.
5. The fasting C-peptide level is low, and the release curve rises slowly after taking sugar, almost in a straight line, without the characteristic of peak. After excluding glycotoxicity, the patient’s pancreatic β-cell function is very exhausted, mainly due to insufficient insulin secretion, and long-term insulin replacement therapy is required.
If it is a teenager with ketosis, type 1 diabetes is more likely;
If it is a middle-aged and elderly patient with sudden onset, weight loss, rapid progress of the disease, and repeated ketosis, adult latent autoimmune diabetes should be considered, combined with islet-related antibodies for diagnosis;
If the patient’s diabetes has a long course and has been treated with adequate blood sugar lowering drugs, the effect is getting worse. It should be considered as pancreatic β-cell failure in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Summary
The correct analysis of the C-peptide release curve of diabetic patients and the evaluation of the pancreatic β cell function of patients have important guiding significance for the classification and treatment of diabetes.
Previous studies believe that C-peptide has no biological activity and is only used to determine the function of pancreatic β-cells. However, more and more studies have shown that C-peptide can relax blood vessels, improve red blood cell deformability, strengthen the function of insulin signaling system, and promote muscles to sugar and amino acids It plays an important role in the development of glucose metabolism and diabetic complications such as diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy and cardiovascular disease.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



