Research found: Electrical stimulation can speed up wound healing
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Research found: Electrical stimulation can speed up wound healing
Research found: Electrical stimulation can speed up wound healing. Electrical stimulation can increase the permeability of blood vessel walls and help blood vessels to transport white blood cells and oxygen to the wound, thereby speeding up wound healing. This research also provides new insights into how new blood vessels grow.
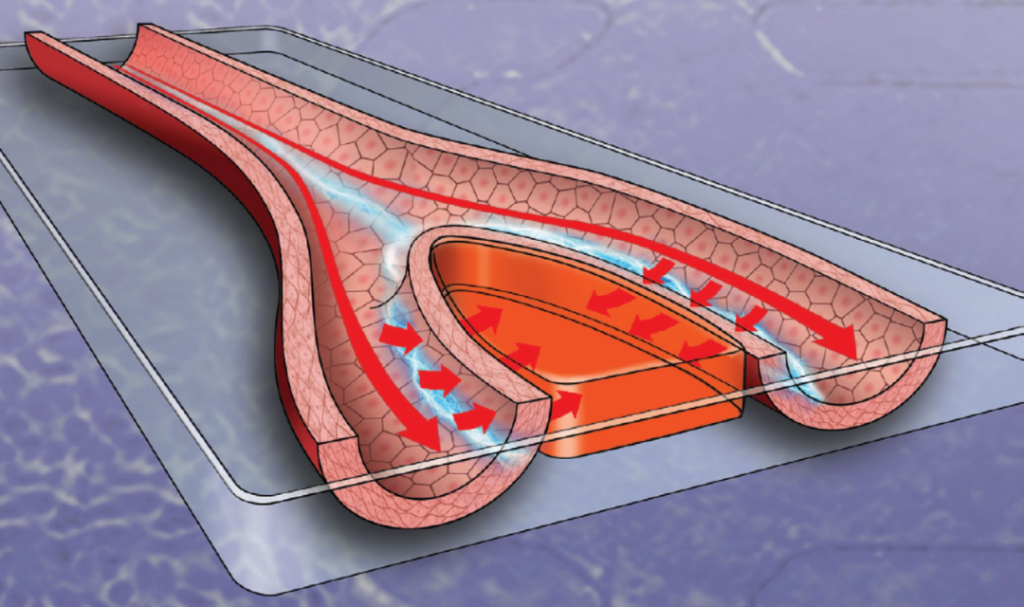
Blood vessels are essential for wound healing. They are distributed throughout the body and carry nutrients, cells and chemicals, which can help control inflammation caused by injuries. Of which oxygen
And white blood cells are the two key components that are transported by blood vessels to protect the human body from foreign invaders.
But when an injury occurs (for example, a finger is cut), the blood vessel structure at the wound site is destroyed, which also interrupts the blood vessel’s ability to help the wound heal. As part of the healing process, blood vessels grow on their own almost like the branches of a tree.
As blood vessels begin to grow, they damage the skin and cells and re-establish a healing barrier. But how to make this healing process better and faster? Is there any benefit to doing this?
Recently, researchers from Ohio State University in the United States published a research paper titled “Direct current electric field regulates endothelial permeability under physiologically relevant fluid forces in a microfluidic vessel bifurcation model” in Lab on a Chip magazine.
The study shows that electrical stimulation can increase the permeability of blood vessel walls, help blood vessels to transport white blood cells and oxygen to the wound, thereby speeding up wound healing. This research also provides new insights into how new blood vessels grow.

With fluid flowing, electrical stimulation provides a constant voltage and accompanying current. Previously, there was speculation that electrical stimulation of blood vessels would make blood vessels grow better.
One of the main methods for blood vessels to heal wounds is to allow molecules and cells to move on the walls of blood vessels. If the blood vessel is cut, it will cause blood loss. At this time, the blood vessel needs to transport blood cells to reach the position and start to repair the wound.
The research team conducted experiments with human cells and found that electrical stimulation of blood vessels found that the permeability of blood vessels increased significantly, which may be a physical marker of new blood vessel growth.
The findings of this preliminary study are exciting, indicating that electrical stimulation increases vascular permeability, and that the increase in vascular permeability allows these blood-derived cells to reach the wound site faster. The research team suspects that this may be due to electrical stimulation. A protein that holds blood vessel cells together.
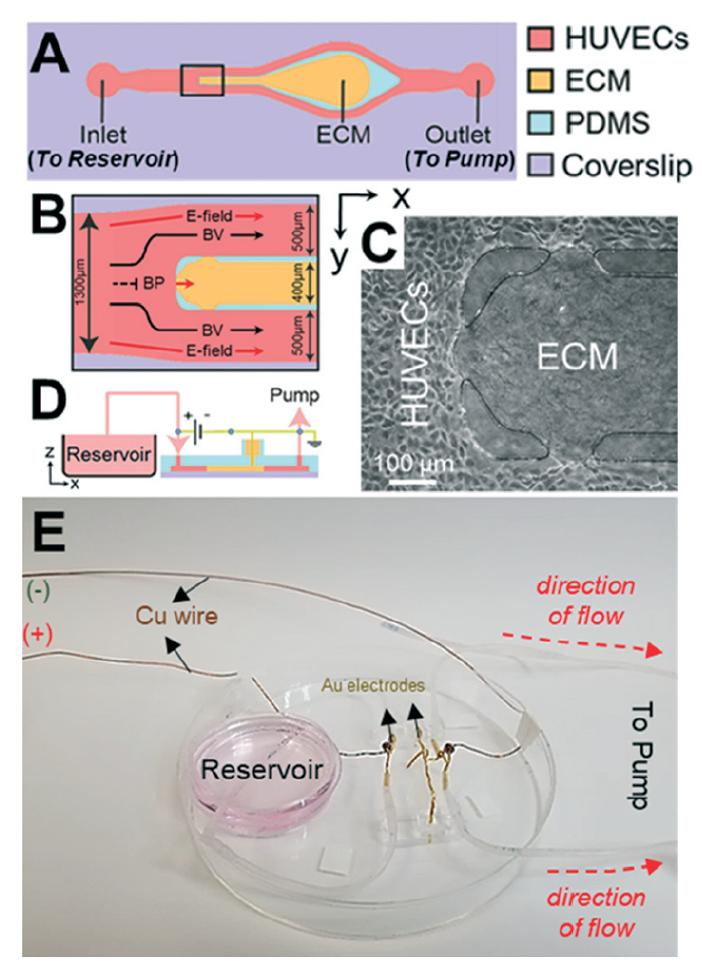
Overall, this work shows that electrical stimulation may help control infections at the wound site and speed up wound healing. It shows that changing the vascular permeability through electrical stimulation is a potential method to speed up wound healing.
In addition, in January 2021, Nature Medicine published two papers back to back, showing that Electrical stimulation of the brain can treat obsessive-compulsive disorder and depression.
Click for details: Electrical stimulation of the brain can save people suffering from mental illnesses such as obsessive-compulsive disorder and depression.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



