Pembrolizumab treats advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Pembrolizumab treats advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma
Pembrolizumab treats advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma. Pembrolizumab completely breaks through the dilemma of advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma treatment, long-term survival is coming soon.
At present, there are more and more immunotherapy drugs that can be used in clinical practice. For example, many new drugs have also carried out clinical research on first-line immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in lung squamous cell carcinoma, and achieved good results.
The results of the KEYNOTE-407 study have attracted a lot of attention as soon as it came out. The most important reason is that pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy has brought better curative effects for patients with advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), regardless of the patient’s PD -L1 expression status.
At the European Lung Cancer Conference (ELCC) in 2021, the three-year survival data of the KEYNOTE-407 study was announced. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the latest data of the KEYNOTE-407 study and the comprehensive breakthrough brought by pembrolizumab for advanced squamous NSCLC. .
Pembrolizumab completely breaks through the dilemma of advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma treatment
Prior to the publication of the results of the KEYNOTE-407 study, the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma was the weakest link in the entire field of lung cancer treatment. Precision targeted therapy and anti-angiogenesis therapy have brought survival benefits to patients, but in the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma, the former There is no opportunity for application, and the latter has a higher risk of application. Advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma is in a dilemma of stagnant treatment, and the therapeutic effect has not been improved.
It has been observed from early clinical studies that immunotherapy can bring significant survival benefits to patients in the second-line and above treatment of advanced NSCLC. Based on this premise, the KEYNOTE-407 study adopts a classic research design. Pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy is compared with traditional chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma, with overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) as the The common primary endpoint, and both achieved double-positive results, have made a major breakthrough in the efficacy and survival of this part of patients.
Immunotherapy is closely related to the molecular pathological characteristics of tumors. The contribution of the KEYNOTE-407 study is that, without requiring PD-L1 expression to be positive, it is the first to prove that advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma can still benefit from immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy. It can be said that this breakthrough has made lung squamous cell carcinoma a tumor that can fully benefit from immunotherapy.
Fully understand the significance of the 3-year OS rate of 29.7% in the KEYNOTE-407 study
The 3-year survival data of the KEYNOTE-407 study showed that the 3-year OS rate of the pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy group was 29.7%. This result brings unexpected joy and once again highlights the “extra-long standby” of immunotherapy. The characteristics of pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy also show that pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy still maintains a clear survival advantage after long-term follow-up.
To further refine the data of the study, first of all, the KEYNOTE-407 study did not require that the PD-L1 expression of the enrolled patients must be positive. Therefore, such good results are still obtained in this case, which adds a lot of confidence in clinical treatment.
Second, in the KEYNOTE-407 study, 49.1% of the patients in the chemotherapy alone group received PD-(L)1 inhibitor treatment after disease progression. In this case, pembrolizumab combined chemotherapy group and chemotherapy alone group The median overall survival times were 17.2 months and 11.6 months, and the absolute benefit was 5.6 months. The 3-year OS rate was 29.7% and 18.2%, respectively.
After adjusting for de-crossing factors, the combined treatment group had greater survival benefits than the chemotherapy group alone. The median OS of the two groups was 17.1 and 9.1 months (HR=0.59), further indicating that pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy can give patients The survival benefit brought is extremely huge.
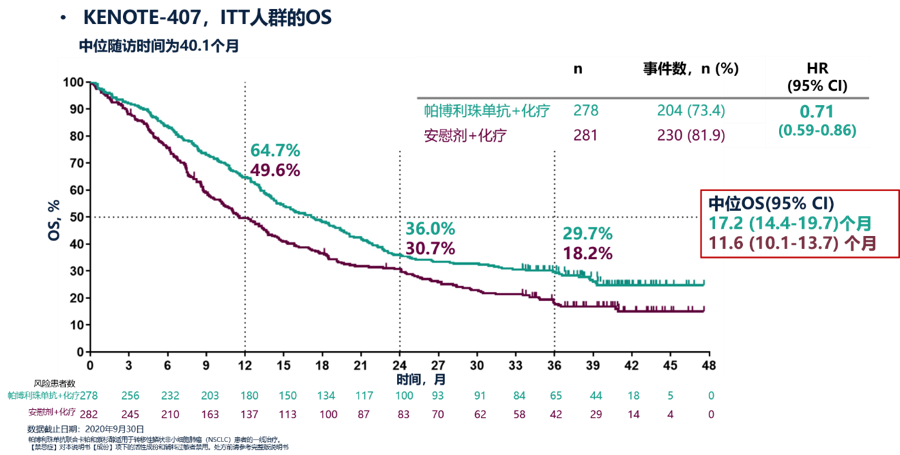
KEYNOTE-407 studies OS in ITT population[1]
Third, nearly 20% of patients in the KEYNOTE-407 study completed 35 cycles (2 years) of pembrolizumab treatment. The 35 cycles of treatment were the initial pre-set of the study. The drug can be stopped as soon as it progresses. Under this design, not only has OS and PFS been significantly improved, but it also makes patients feel that the treatment of malignant tumors can still be discontinued. This has great psychological comfort to patients, after all, there is still a lot of pressure on lifelong medication.
Fourth, the ORR of these patients who completed 35 cycles of dosing is as high as 92.7%, and the median DOR has not yet been reached. The 1-year OS rate after completion of pembrolizumab treatment (3-year OS rate from randomization) It is 96.0%, and the 1-year PFS rate is 82.6%. These results can be said to be unprecedented, and from another perspective, using the efficacy of the patient’s initial medication to predict the long-term benefit of the patient from immunotherapy may become a very good prediction of the efficacy. factor.
Pembrolizumab is the first-line immunotherapy for advanced squamous NSCLC in China
Immunization combined chemotherapy has become the main theme of the first-line treatment of advanced squamous NSCLC. When the patient’s economic and physical conditions permit, immune combined chemotherapy should be used as the first-line standard treatment.
The global data of the KEYNOTE-407 study clearly shows that compared with chemotherapy alone, pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy has a better survival advantage. The data of Chinese patients is also the same, and even more prominent.
The data from the KEYNOTE-407 study of the Chinese population shows that compared with the global data, the Chinese population data seems to be better. For example, the progression-free survival time is 8.0 months compared to 5.1 months in the global data (HR=0.57), and the Chinese population data is 8.3 months compared to 4.2 months (HR=0.32), the risk of disease progression or death is even greater, and the advantage is greater. This may be different from the race’s response to drugs, or the Chinese doctors’ perception of the side effects of immunotherapy It is related to higher processing power.
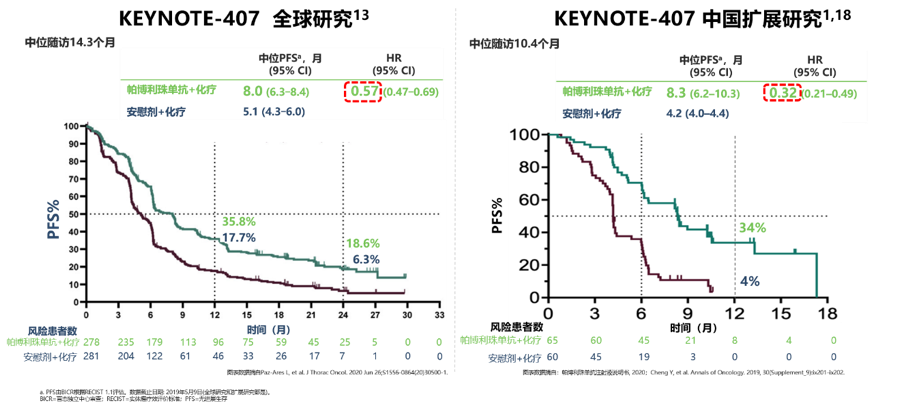
KEYNOTE-407 studies PFS data of global and Chinese population [2]
In the case of subsequent cross-over immunotherapy in the chemotherapy-only group, the survival benefit of the Chinese population is also consistent with global data, and the risk of death from the disease is even greater. In the Chinese population, the median OS of the two groups is 17.3 months. And 12.6 months (HR=0.44), which is a very significant benefit for patients with advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma. In addition, in the Chinese population, pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy also brought an improvement in the objective response rate (ORR: 78.5% vs 41.7%), allowing patients to have a longer duration of response (median DOR: 8.9 vs 3.5 Months).
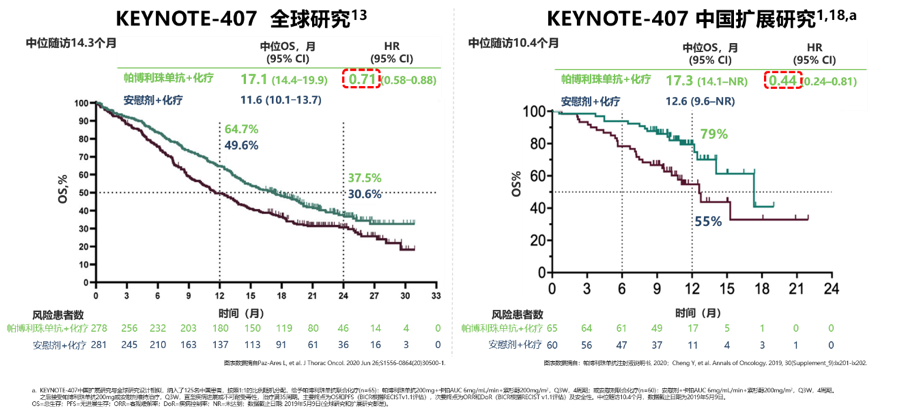
KEYNOTE-407 studies the OS data of the global and Chinese population [2]
At present, there are more and more immunotherapy drugs available in the clinic. For example, many Chinese domestic new drugs have also carried out clinical studies of first-line immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in lung squamous cell carcinoma, and achieved good results. But so far, the survival data of these studies are not yet mature.
We look at the efficacy of drugs, survival is the last word, and safety must be paid more attention. The shortcoming of Chinese domestic drugs at this stage is that the survival data is not yet mature, and the safety data is not as sufficient as the KEYNOTE-407 study. The greater contribution of the KEYNOTE-407 study is that it has opened up a new path for the treatment of patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma, including the application of Chinese domestic drugs.
In short, in the first-line treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma, the data of the KEYNOTE-407 study is the most mature. I hope that the follow-up and analysis of the KEYNOTE-407 study can provide us with more highlights. Peking Union Medical College Hospital is one of the KEYNOTE-407 research centers. From the research, we have also seen some patients who have benefited, including the benefits of survival and the guarantee of quality of life. This is what we particularly want to see.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



