Lung cancer screening can predict heart disease?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Lung cancer screening can predict heart disease?
Lung cancer screening can predict heart disease? Using CT data from lung cancer screening to predict the risk of heart disease will undoubtedly kill two birds with one stone and will not increase the medical burden.
Cardiovascular disease is the number one cause of death in the world, claiming an average of nearly 18 million lives each year, accounting for 40% of all deaths, and discoloring cancers account for only 26%, making it a veritable number one killer.
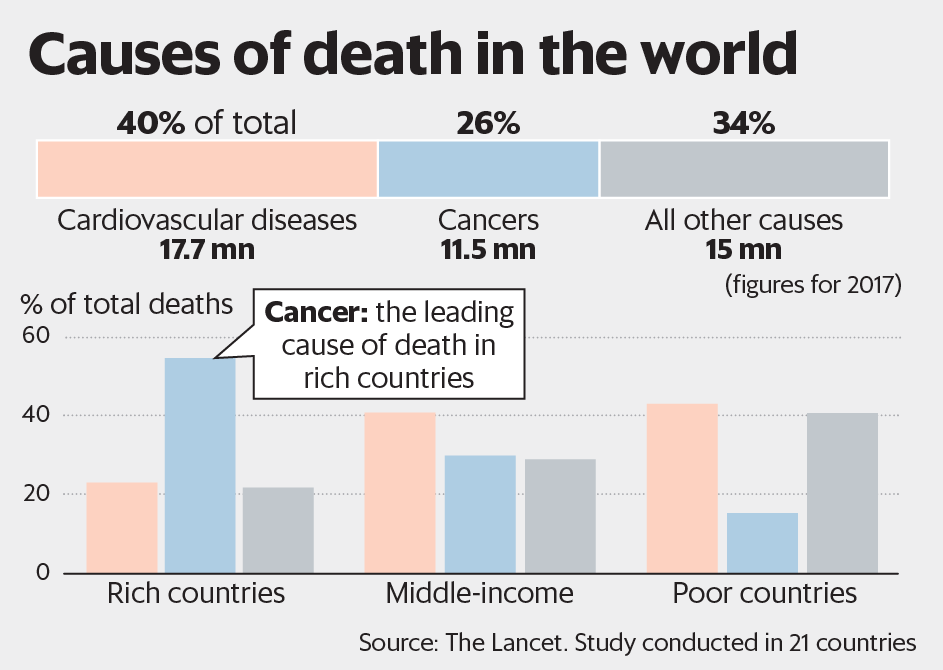
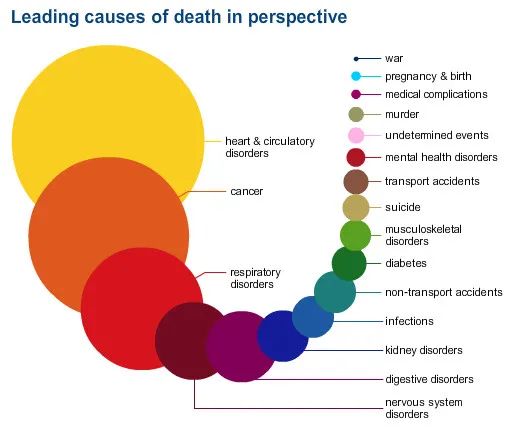
Cardiovascular disease is the number one killer of death (picture from the Internet)
There are many causes of cardiovascular disease, and smoking is one of the main causes.
According to statistics, about a quarter of deaths from cardiovascular diseases are related to smoking. Smoking can increase a person’s risk of cardiovascular disease by two to four times. The chemicals in tobacco can damage the inner walls of blood vessels and cause inflammation. Smoking can also contribute to the accumulation of atherosclerosis or plaque (consisting of fat, calcium and other substances), leading to narrowing and stiffness of the arteries.
How to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease and death has always been a key issue.
Because the base is huge, a small amount of progress in prediction and prevention can save a lot of lives and labor. Some prediction methods use questionnaires to make a comprehensive score through patient self-reports and objective medical examinations. This method is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Coronary artery calcium scan is an X-ray that uses computed tomography (CT) to create multiple images of calcium-containing plaques in the arteries. Based on these images, health professionals can create a coronary artery calcium (CAC) score to assess the patient’s heart disease risk and guide treatment.
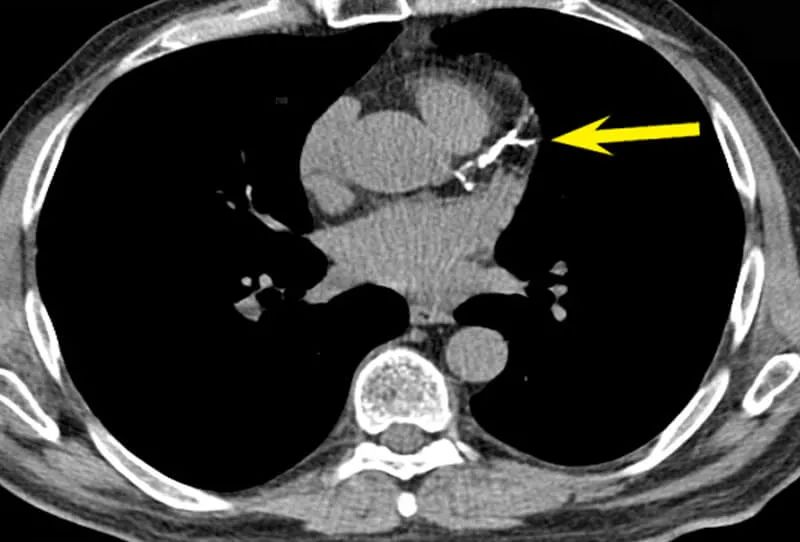
The arrow shows the calcification of the coronary artery (picture from the Internet)
However, specialized coronary scans will increase the amount of labor, wide-spreading will increase medical expenses, and unnecessary radiation. So some researchers have tried to use imaging materials from other conventional sources to predict cardiovascular disease.
As we all know, the relationship between smoking and lung cancer is also very close, and it is the most clear cause and disease relationship in medicine.
In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) currently recommends that adults aged 50-80 with a history of 20 pack years of smoking, current smoking or quitting smoking in the past 15 years should be screened for lung cancer with low-dose CT annually. If these CT data can be used to predict the risk of heart disease, it will undoubtedly kill two birds with one stone, and it will not increase the medical burden.
Learning artificial intelligence
The latest results of this study were published in the journal Radiology-Cardiothoracic Imaging.
The study used low-dose CT lung scan data from participants who participated in the national lung screening trial between August 2002 and April 2004. The study used an automated deep learning method to quantify arterial calcification signals from low-dose CT lung scans. Deep learning is a type of artificial intelligence that uses a multi-level algorithmic structure or “neural network” to analyze data.
Artificial intelligence deep learning model diagram (picture from the original paper)
The first neural network aligns and crops the CT image to focus on the heart.
The second neural network measures the calcium content in the image extracted from the first neural network.
The deep learning network identified vascular calcification in six different regions of the heart, including the thoracic aorta, aortic valve, mitral valve, and right coronary artery. Using this information, the authors predicted the 5-year cardiovascular mortality rate for each participant. Then they compared the research prediction model with the other three models.
The researchers trained the predictive model with data from 4,451 participants and tested the model with data from 1,113 participants. Approximately 62% of the test group were men, the median age was 61 years, and the smoking history was about 50 pack years.
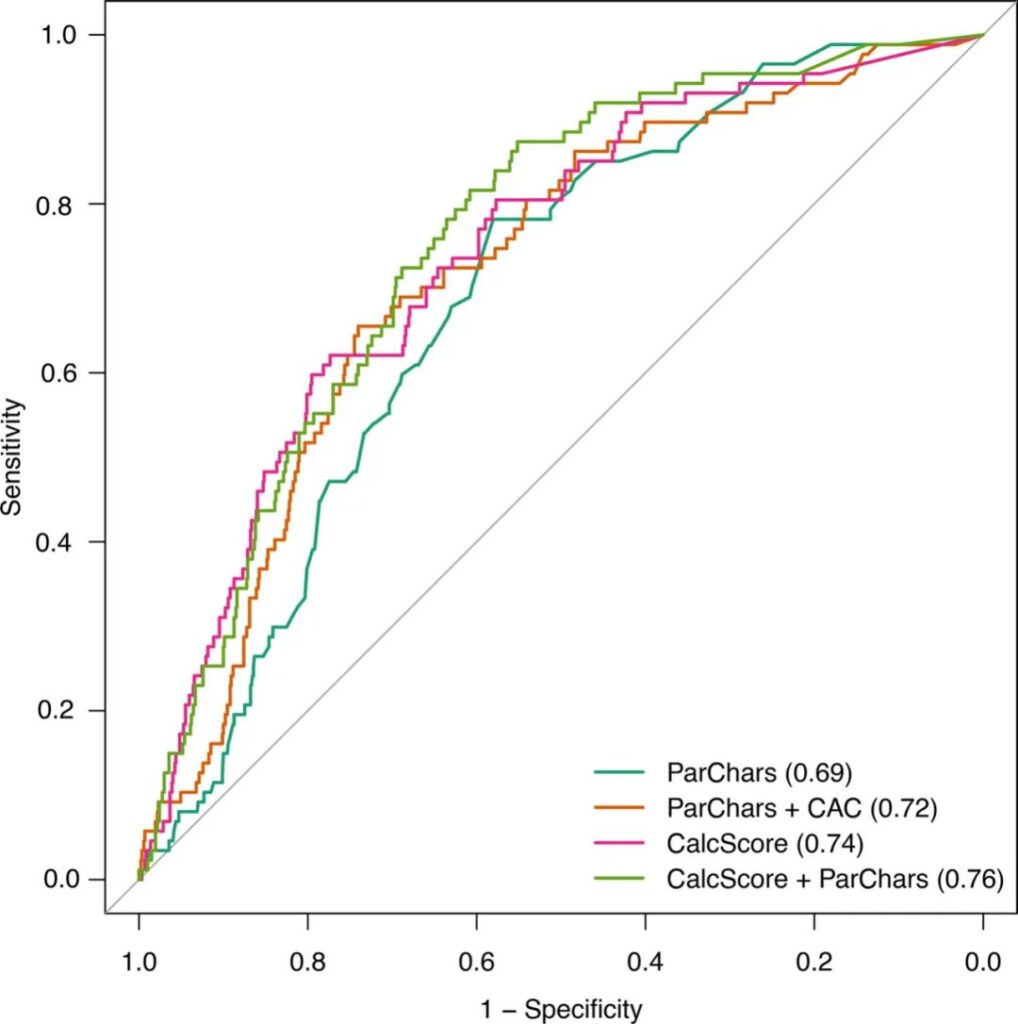
The authors found that their automatic calcium scoring method was as accurate as or even better than other models in predicting the risk of death from CV at 5 years.
The prediction accuracy curves of several models (pictures are from the original paper)
The advantages of this prediction are obvious. The biggest advantage is fast and automatic. As long as you install specific software, you don’t need more labor and cost. The entire analysis is completely automated. The current shortcomings mainly lie in the representativeness of the sampling, because most of the people selected in this study are heavy smokers, mostly men, so the universality of the results needs to be further studied.
Back to the origin of the problem, smoking cessation is still the most appropriate and most important measure to prevent lung cancer and cardiovascular disease.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



