IL-30: A cytokine that promotes cancer development
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
IL-30: A cytokine that promotes cancer development
IL-30: A cytokine that promotes cancer development. IL-30 was discovered in 2002, with a molecular mass of about 28kDa. IL-30 constitutes a heterodimeric cytokine four alpha helix subunit of IL-27, also known as IL-27p28 (Reference 1).
In humans and mice, IL-30 interacts with IL-27β subunit EBI3 through non-covalent bonds to form biologically active IL-27, which acts through IL-27R activation. IL-27 has the dual effects of promoting tumor and anti-tumor.
Of course, IL-30 and EBI3 are non-covalently bonded, IL-30 can be dissociated, as an independent cytokine, directly bind to gp130, inhibit its signal, and antagonize the anti-tumor effect of IL-27 (Reference 3). The independent IL-30 is mainly to promote the role of tumor.
In addition, IL-35 and IL-27 share β subunit EBI3, and IL-35 is an important cytokine secreted by Breg, and its main role is to promote tumor formation and metastasis.
IL-30/IL-27p28 expression
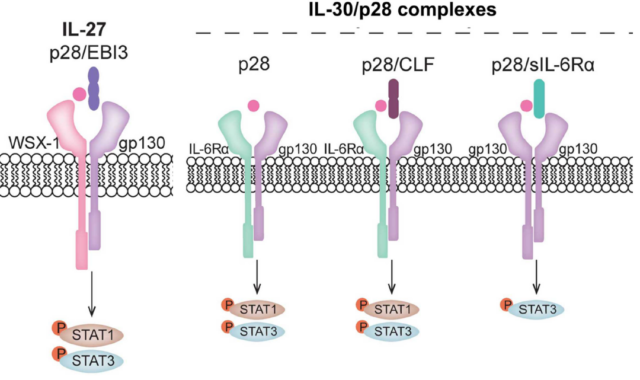
IL-30/IL-27p28 expression
Myeloid cells, including macrophages, monocytes, microglia and giant cells, are activated by various microorganisms and immunostimulants (TNF family members CD40 and CD137, type I and type I and type II IFNs). The main cell source of IL-30/IL-27p28 can also be produced by neutrophils, endothelial and epithelial cells.
IL-27 receptor expression
IL-27R contains the ligand binding chain IL-27Ra (WSX-1, TCCR), (expressed on DC cells, monocytes, macrophages, mast cells, eosinophils, T, B and NK cells, cell activation Later upregulation), and the signal transduction chain gp130 (expressed in almost all cell types).
A variety of cancer cells also express IL-27R and respond to IL-27 stimulation. The latter can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells, and promote the death of apoptosis, which directly exerts an anti-tumor effect. The binding of IL-27 to its receptor can activate the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and immunomodulatory function.
Immunomodulatory function as IL-27 subunit
As the source and target of IL-27, myeloid cells participate in its anti-tumor and tumor-promoting activities, which will depend on the specific type of tumor and the function of myeloid cells.
In a human non-small cell lung cancer xenograft model, IL-27 down-regulates the expression of tumor stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal metastasis (EMT) related genes, and also re-educates the intratumoral myeloid cells to play an anti-tumor effect.
IL-27 promotes the differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages and enhances the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, TNF-a, MIP-1α and MIP-1β.
IL-27 also up-regulates HLA-E, interacts with CD94/NKG2A, inhibits NK cell function and IFN release, which in turn weakens anti-tumor immunity. IL-27 can also up-regulate perforin and promote the cytotoxicity of NK cells. On the contrary, it inhibits the activity of CD56 bright NK cell subsets.
IL-27 can up-regulate the expression of PD-L1/2 and IDO, inhibit T cell function, and induce exhaustion. In addition, it can induce CD4+ T cells to produce IL-10 and IL-17. IL-27 can promote the production of IL-10 by Th1, Th2, Th17, Treg and Tr1 cell subsets, activate the inhibitory activity of myeloid cells, and thereby inhibit Production of macrophages and inflammatory cytokines.
IL-27 has the environment-dependent activation and suppression functions in innate immunity, and emphasizes its role in limiting the activation of macrophages through inflammatory cytokines and maintaining immune homeostasis.
The activity of IL-27 and the results produced are highly dependent on the cell type, activation state and microenvironment.
The role of IL-30/IL-27p28 in tumor microenvironment
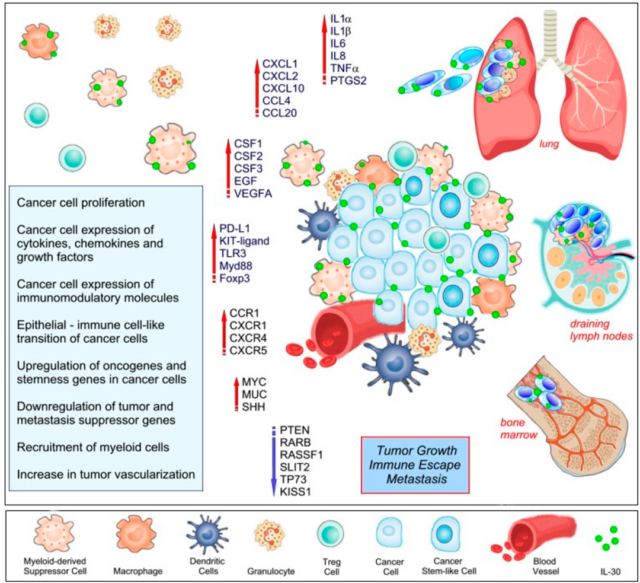
The figure above clearly indicates that IL-30 up-regulates cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, etc.), chemokines (CXCL1/2/10, etc.), immune checkpoint (PD-L1), and down-regulates Tumor suppressor genes (PTEN, etc.).
IL-30/IL-27p28 acts directly or indirectly through the above-mentioned secondary cytokines to achieve crosstalk between cancer cells and myeloid suppressor cells, and IL-30/IL-27p28 promotes cancer stem cell niches, thereby promoting tumor immune escape and tumor progression .
Expert Comments:
Although IL-30/IL-27p28 in the tumor microenvironment mainly promotes tumors, neutralization is one of the targeted treatment strategies. However, because IL-30/IL-27p28 is widely expressed, as the α subunit of IL-27, it has anti-tumor activity. How to avoid the off-target toxicity of its inhibitors needs to be considered in the development strategy, such as the use of antibody prodrug technology, nano-drug delivery systems, etc.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



