Comprehensive analysis of effects of intermittent eating on Human health
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
NEJM: Comprehensive analysis of effects of intermittent eating on Human health, aging and disease
Comprehensive analysis of effects of intermittent eating on Human health. Professor Mark Mattson of Johns Hopkins University in the United States and others published a review research paper on NEJM, pointing out that intermittent fasting is beneficial to human health, and can prevent and improve obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory disease and brain Cognitive impairment.
With the development of society and economy, the quality of life is steadily rising, and human health and lifespan have also increased significantly. At present, health concepts such as exercise, fitness and balanced diet have become a consensus. These scientific health concepts also guide us to actively pursue a healthy lifestyle.
Interestingly, fasting is not a healthy lifestyle, but it has always been sought after. In recent years, more and more scientific studies have shown that short-term fasting can promote the treatment of certain diseases, such as diabetes, cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
Not only that, fasting is also an effective way to treat obesity. Nowadays, obesity has become a global epidemic, and the obesity rate is on the rise all over the world, including China. In order to combat obesity and other metabolic functions, people have tried many dietary interventions, the most popular of which is Intermittent Fasting (IF).
Intermittent fasting is good for health
On December 26, 2019, Professor Mark Mattson of Johns Hopkins University in the United States and others published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) the title: Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease (Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease). A review article on the effects of fasting on health, aging and disease.
This review pointed out that intermittent fasting is indeed beneficial to human health. It can improve blood sugar regulation, reduce the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. It can also improve brain function and may help prevent the Alzheimer’s. Murr’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, etc.

Intermittent fasting promotes fat metabolism and cell health
Fasting strategies can be roughly divided into two categories: one is to limit food intake, that is, to reduce the amount of food per meal or to eat only within a limited time each day; the other is to intermittent fasting, that is, to alternate fasting and ingestion, such as 5: 2 Intermittent fasting, that is, restrict yourself to a medium-sized meal two days a week.
In fact, it is very common for humans to eat less meals during the course of evolution. Therefore, relatively speaking, intermittent fasting is a simpler and easier to implement strategy in clinical trials, which also makes intermittent fasting an attractive option to combat metabolic diseases.
In humans and rodents, fasting has been shown to lower insulin levels, improve glucose tolerance, and lower blood cholesterol levels, even if the fasting person does not lose weight. In addition, studies have shown that adipose tissue plays a central role in regulating the acute fasting response. During fasting, adipose tissue activates corresponding signaling pathways to promote lipolysis by secreting hormones such as leptin.

The human body’s metabolic adaptation to intermittent fasting
Professor Mark Mattson pointed out in the review that a series of animal and some human studies have shown that the alternation of fasting and eating time is beneficial to cell health, which may be through triggering an ancient adaptation to the period of food shortage, that is, metabolic conversion. This conversion occurs when the cell consumes the sugar-based fuel that can be obtained quickly and begins to convert fat into energy in a slower metabolic process.
The cell’s response to intermittent fasting is to participate in a coordinated adaptive stress response, thereby increasing antioxidant defense, DNA repair, protein quality control, mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy, and down-regulation of inflammation. These reactions enable cells to remove oxidatively damaged proteins and mitochondria, and to recover undamaged molecular components. However, for those who eat too much or are sedentary, none of these approaches have been developed.

Cell response to eating and fasting cycles combined with metabolic energy limitation
Professor Mark Mattson said: “This conversion can improve blood sugar regulation, increase resistance to stress, and inhibit inflammation. However, many people’s diet is usually three meals plus snacks. They have not experienced this transition and cannot experience intermittent. The benefits of sexual fasting.”
Intermittent fasting is beneficial for metabolic diseases and cognitive ability of the brain
Not only that, the article pointed out that four studies conducted on animals and humans found that intermittent fasting can also reduce blood pressure, blood lipid levels and resting heart rate. More and more research evidence shows that intermittent fasting can change the risk factors related to obesity and diabetes.
Two studies conducted by South Manchester University Hospital on 100 overweight women showed that women who adopted a 5:2 intermittent fasting diet had the same weight loss as women who adopted calorie restriction, but in terms of insulin sensitivity and abdominal fat loss. The upper fasting group performed better than the calorie restriction group.
In addition, preliminary studies have shown that intermittent fasting is also beneficial to brain health. In April 2019, a multi-center clinical trial conducted by the University of Toronto in Canada found that in a series of cognitive tests, 220 healthy non-obese adults who maintained a calorie-restricted diet for two years showed signs of memory improvement.

Cellular and molecular mechanisms of intermittent fasting to improve organ function and resistance to stress and disease
Although more research is needed to prove the effect of intermittent fasting on learning and memory, Professor Mark Mattson said that if further evidence is found, fasting, or drugs that can produce similar effects, are expected to be used for prevention Prevention and treatment of diseases such as neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease.
How to promote the intermittent fasting lifestyle?
Professor Mark Mattson has studied the health effects of intermittent fasting for more than 25 years, and he himself started intermittent fasting about 20 years ago.
He said that there have been enough studies to prove the potential benefits of intermittent eating for humans, and many doctors are asked by patients whether they should eat intermittently and how they should perform intermittent fasting. This review article aims to help clarify the scientific and clinical applications of intermittent fasting to help doctors guide patients who want to try intermittent fasting.
It takes a while for the patient’s body to adapt to intermittent fasting and to get rid of the initial hunger and subsequent irritability. At the same time, patients should be told that it is common to feel hungry and irritable at first, usually after two weeks to one month, as the body and brain adapt to the new habits, this feeling will disappear.
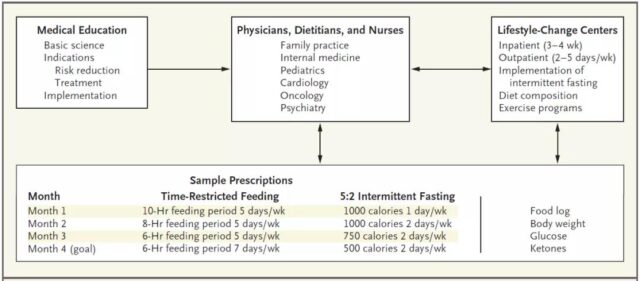
Incorporate intermittent fasting patterns into healthcare practices and lifestyles
In order to overcome this obstacle, Professor Mark Mattson suggested that doctors advise patients to gradually increase the duration and frequency of fasting over a period of several months, instead of “quitting it all at once.” As with all lifestyle changes, it is important for doctors to understand science so that they can communicate with patients about the potential benefits, hazards, and challenges, and provide support.
All in all, this review article confirms that intermittent fasting is beneficial to human health. It can not only prevent and treat obesity, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease and inflammatory diseases, but also improve the cognitive ability of the brain. Prevent stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, etc.
Comprehensive analysis of effects of intermittent eating on Human health
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



