Ketogenic diet increases anti-cancer effects by reducing abundance of PD-L1
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Cell: The ketogenic diet increases anti-cancer effects by reducing the abundance of PD-L1.
The ketogenic-diet (KD for short) is a formula diet with a high proportion of fat, a low proportion of carbohydrates, and suitable protein and other nutrients.
It has become very popular in recent years. When people are on a ketogenic diet, the body will metabolize to produce more ketone bodies (including acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetone) , which can be used as a source of energy.
Abnormal energy status can lead to a variety of metabolic diseases, including obesity, diabetes, and even cancer, but the underlying mechanism is still elusive.
April 2021, Researchers from Harvard Medical School published a report entitled: Energy Status Dictates PD-L1 Protein abundance and Anti-tumor Immunity to enable checkpoint Blockade at the Molecular Cell journal.
The study showed that the energy status changes induced by the ketogenic diet enhanced the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 immunotherapy by reducing the level of PD-L1 protein and increasing the expression of type I interferon (IFN) and antigen presenting genes.

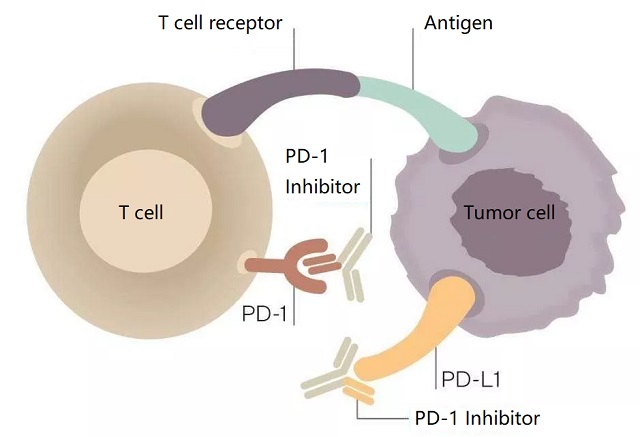
Programmed cell death receptor ( PD-1 ) is an important immunosuppressive molecule, which can down-regulate the response of the immune system to avoid autoimmune diseases.
The PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells binds to the PD-1 on T cells to promote the immune escape of tumor cells.
Therefore, blocking the binding of PD-L1 and PD-1 by inhibitors or reducing PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells can restore the killing effect of T cells on tumor cells.
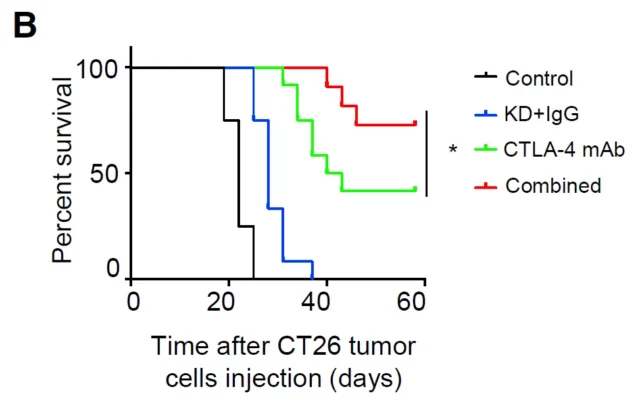
First, the research team found that energy stress or a ketogenic diet can reduce the expression abundance of PD-L1 protein , and the ketogenic diet can enhance the anti-cancer effect of anti-CTLA-4 immune checkpoint blockade.
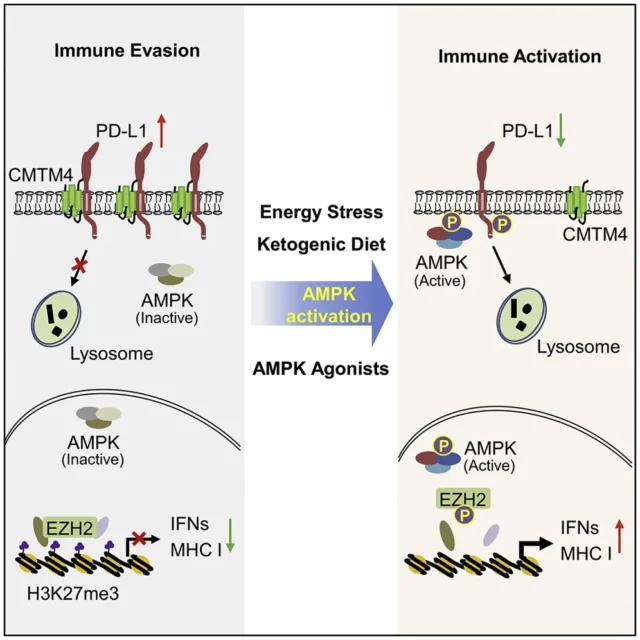
Further studies have shown that energy deprivation activates AMPK kinase, which in turn phosphorylates the serine at position 283 of the PD-L1 protein, thereby disrupting the interaction between PD-L1 and CMTM4, and subsequently triggering PD-L1 degradation .
In addition, AMPK phosphorylates EZH2, thereby disrupting the function of PRC2 and enhancing the expression of type I interferon (IFN) and antigen presenting genes .
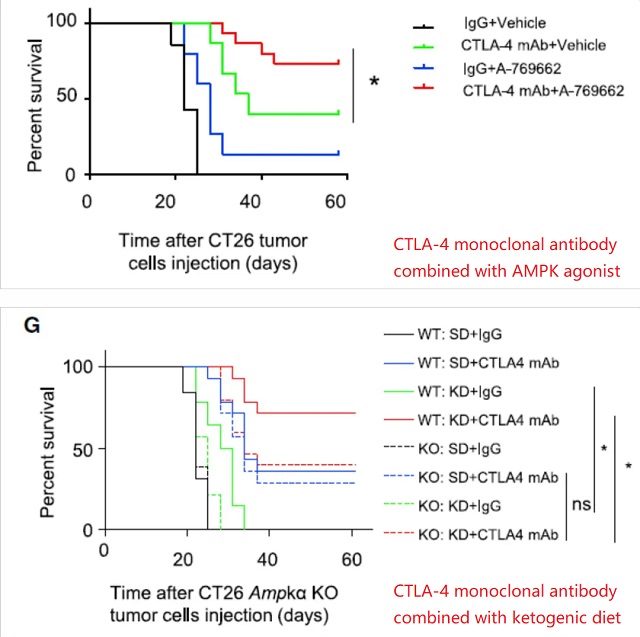
Through these mechanisms, AMPK agonists or ketogenic diets can enhance the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 immunotherapy and increase the overall survival rate of tumor mouse models .
In general, the study shows that energy status determines the abundance of PD-L1 protein and the anti-tumor effect of immune checkpoint therapy, further revealing the key role of AMPK in regulating immune checkpoint therapy against tumors, energy deprivation Activating AMPK, which in turn phosphorylates the serine at position 283 of the PD-L1 protein, disrupts the interaction between PD-L1 and CMTM4, and subsequently triggers PD-L1 degradation .
The study further proved that AMPK agonists or ketogenic diet combined with CTLA4 immune checkpoint therapy can more effectively fight cancer .
Paper link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.037
Ketogenic diet increases anti-cancer effects by reducing abundance of PD-L1
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



