Research and clinical progress of RNA therapy
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Research and clinical progress of RNA therapy
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Research and clinical progress of RNA therapy.
Many RNA-based therapies involving siRNA, ASO, ribozymes, mRNA, aptamers, and CRISPR/Cas have been developed and are undergoing clinical trials in various diseases.
RNA-based drugs show excellent application potential.
01. SiRNA
siRNA is produced by the ribonuclease Dicer through an endonuclease process, which is an endonuclease belonging to the RNase III family and can produce 21-25 nucleotide double-stranded RNA.
Once produced, Dicer transfers the siRNA to the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which contains Argonaute 2, which degrades the target mRNA molecule.
Because of this ability of siRNA, they are used as a possible treatment. SiRNA therapy is being tested in a variety of cancer treatments.
siG12D-LODER is a biodegradable polymer matrix containing siRNA against KRASG12D. Clinical studies ( NCT01188785 ) have shown that the polymer can target tumors and inhibit tumor progression.
Currently, further research is underway ( NCT01676259 ) to test the efficacy of siG12D-LODER combined with chemotherapy drugs ( such as gemcitabine and nab paclitaxel ) in the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients.
Polo-like kinase ( PLK ) is involved in cell cycle regulation and cell proliferation and is usually overexpressed in cancer cells.
Inhibition of Plk can reduce cancer cell proliferation. TKM-080301 is a lipid nanoparticle ( LNP ) preparation consisting of four lipids and a synthetic double-stranded siRNA targeting human PLK1 mRNA.
Intravenous infusion of TKM-080301 shows good tolerability, but only shows limited anti-tumor effects in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, and has no overall survival effect.
However, TKM-080301 shows a certain tumor suppressor effect in adrenocortical carcinoma ( ACC ).
Protein kinase N3 ( PKN3 ) is a downstream effector of phosphoinositide-3-kinase ( PI3K ) pathway. Blocking PKN3 can inhibit tumor progression and lymph node metastasis.
Atu027 , a liposomal PKN3 siRNA preparation, has good safety in patients with advanced solid tumors.
At the end of treatment, 41% of subjects were in stable condition. In subsequent studies, the combination of Atu027 and gemcitabine in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer showed good safety and tolerability.
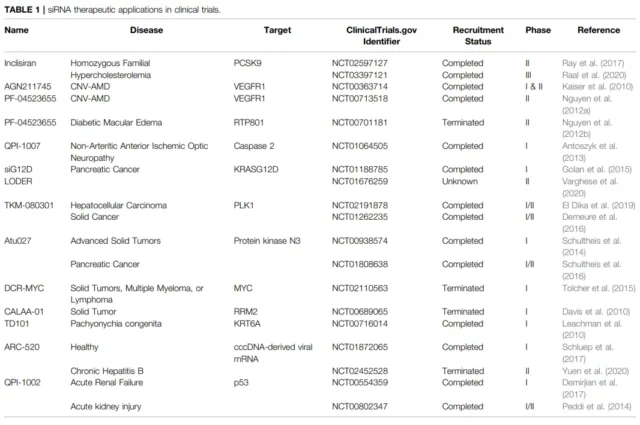
In addition to the cancer field, the application of SiRNA in other disease fields is also being actively developed. Inclisiran , a phosphorothioate, 2′-O-methyl nucleotide and 2′-fluoro nucleotide modified siRNA, targeting PCSK9, subcutaneous injection has been shown to reduce PCSK9 levels in patients with high cardiovascular risk And LDL cholesterol levels.
And it was injected only once every six months, showing excellent patient compliance. On December 11, 2020, Inclisiran was approved by the European Union for listing.
Many siRNA studies are aimed at choroidal neovascularization caused by age-related macular degeneration ( CNV-AMD ), and studies targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 ( VEGFR1 ) or RTP801 have shown that there are The desired result, such as AGN211745 and PF-04523655 .
In addition, QPI-1007 , an siRNA that inhibits the expression of caspase 2, showed good tolerance and improved vision in patients with optic atrophy.
In addition, including autosomal recessive genetic primary hyperoxaluria ( PHs ), hepatitis B virus ( HBV ) and liver and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, SiRNA therapy has shown good application prospects.
02. ASO
Antisense nucleic acid ( ASO ) is a single-stranded RNA/DNA molecule of 18-30 base pairs, designed to specifically inhibit mRNA function.
They are complementary to specific mRNA binding, through RNase H to hinder mRNA translation or degradation of mRNA.
Many preclinical and clinical trials of ASO in the treatment of eye diseases have shown promising results.
Leber congenital amaurosis ( LCA ) causes retinal dystrophy due to intron mutations of various genes including centrosome protein 290 ( CEP290 ), causing blindness or severe visual impairment in adolescents.
QR-110 is a single-stranded, phosphorothioate, 2’O-methyl modified splicing regulatory RNA oligonucleotide for targeting CEP290.
Clinical studies ( NCT03140969 and NCT03913143 ) have shown that intravitreal injection of QR-110 can rebuild CEP290 levels in fibroblasts of LCA patients, and has good tolerability and safety.
03. Aptamer
Aptamers are single-stranded nucleic acid ( DNA or RNA ) molecules that bind and inhibit proteins .
The ability of aptamers to form shapes provides high affinity and excellent specificity to the target. Because their mode of action is similar to that of antibodies, aptamers are also called chemical antibodies.
At present, a variety of aptamers have entered clinical trials for various diseases, such as macular degeneration, diabetic macular edema and chronic inflammatory diseases.
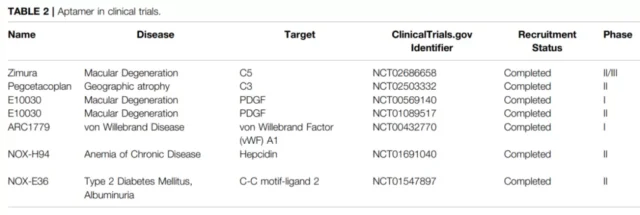
EYE001 is a PEGylated aptamer of VEGF. In an in vitro model, it has shown the ability to completely reduce VEGF-mediated vascular leakage and inhibit retinal neovascularization, thereby improving vision.
The study of EYE001 single or combined photodynamic therapy conducted in CNV-AMD patients showed significant visual stabilization or improvement.
In addition to VEGF, the complement pathway also plays an important role in AMD.
Zimura , a pegylated single-stranded nucleic acid aptamer that targets complement factor C5 and pegcetacoplan targets C3 and C3b.
Their clinical studies have shown that subcutaneous injection can reduce geographic atrophy ( GA ) secondary to AMD . No adverse events will occur.
In addition, ARC1779 is an aptamer that targets the A1 domain of vWF. In clinical trials ( NCT00632242 ), ARC1779 has shown good tolerability and the ability to inhibit vWF-dependent platelet function in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Emapticap-pegol ( NOX-E36 ) is an aptamer that targets CCL2. In type 2 diabetic patients with proteinuria, subcutaneous injection of Emapticap shows good tolerance and inhibits the CCL2/CCL2 receptor axis. ability.
04. Ribozyme
Ribozymes are molecules that catalyze RNA, hybridize with target RNA and cause RNA degradation, thereby inhibiting the production of specific proteins.
Importantly, ribozymes can function without cellular proteins.
RPI.4610 ( Angiozyme ) is a chemically stable anti-VEGFR-1 ribozyme, used in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel for patients with advanced solid tumors, and has proven to have good safety, bioavailability and tumor localization capabilities.
However, it has failed to demonstrate clinical efficacy in patients with metastatic breast cancer.
OZ1 is a tat-vpr specific anti-HIV ribozyme. It is delivered by autologous CD34+ cells. In a clinical trial ( NCT00074997 ), CD4+ lymphocytes have been significantly increased, indicating that gene transfer delivered by cells is equally reliable in maintaining the safety and activity of ribozymes. .
Although it has been successful in many clinical trials, there are also some research reports that show the lack of effectiveness and safety, such as Ad5CRT targeting human telomerase reverse transcriptase ( hTERT ) encoding RNA in patients with gastrointestinal cancer , metastatic breast Vascular enzymes or chimeric ribozymes in cancer patients.
Therefore, ribozymes still need to be improved in terms of stability, in vivo activity, co-localization, delivery to specific cells, and continuous stable and long-term expression.
05. mRNA
MRNA-based treatments represent a relatively novel and highly effective class of drugs.
Several recently published studies have emphasized the potential efficacy of mRNA vaccines in the treatment of different types of malignant tumors and infectious diseases, in which traditional vaccine strategies cannot elicit a protective immune response.
Infectious disease vaccines are currently the leading application of mRNA therapy.
The COVID-19 vaccines of Moderma and Pfizer have proven safety and effectiveness in billions of people, showing a strong application prospect in the future, so I won’t go into details here. (Refer to < Research Progress of mRNA Vaccine in Infectious Disease >)
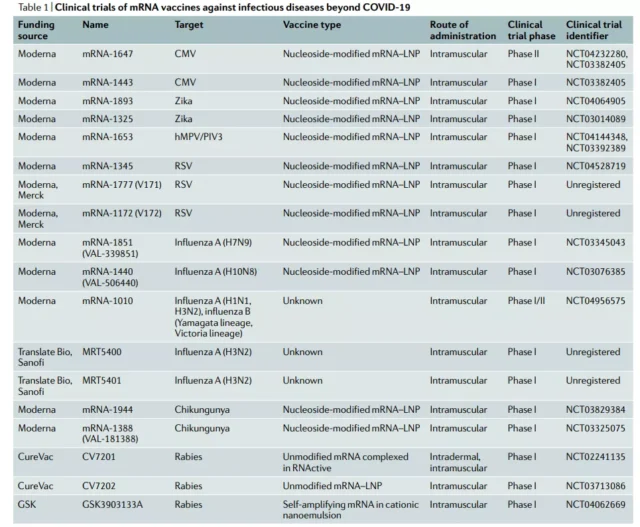
Currently, there are two ways to target tumor mRNA vaccines: i) using in vitro loaded or electroporated DC, and ii) by direct injection of mRNA with or without vector.
Several clinical trials of DC-based mRNA vaccines have been applied in cancer patients.
Combining vaccination with mRNA encoding melanoma-related antigens and TriMix resulted in impressive tumor regression of advanced melanoma.
At present, mRNA vaccines are being developed towards combined treatment methods, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and checkpoint inhibitors. Some of these studies have produced long-lasting tumor growth inhibition.
Although these DC-based methods are effective, they are also limited by cumbersome procedures and high costs.
In contrast, direct injection of naked mRNA or compound mRNA is considered a fast, effective and feasible method.
For example, a phase I/II trial repeatedly applied mRNA vaccines encoding 6 different TAAs ( MUC1, CEA, Her2/neu, telomerase, survivin, MAGE-A1 ) intracutaneously in 30 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma .
Long-term results after 10 years have shown that the mRNA vaccine is safe and effective.
It delays tumor growth and improves survival, which is closely related to the detected immune response against TAAs.
In another study, 7 locally advanced patients and 39 metastatic NSCLC patients received 5 intradermal injections of CV9201 , which encodes 5 NSCLC antigens ( NY-ESO-1, MAGE-C1/2, survivin , 5T4 ) live vaccine. 63% of patients developed an antigen-specific immune response against at least one antigen, and 60% of patients showed an increase in activated IgD+CD38high B cells. 31% of patients had stable disease ( SD ), and the other two-thirds had progressed disease. A similar study aimed at improving anti-tumor immunity tested the use of CV9202 combined with local radiotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC.
CV9202 is an RNA-based live vaccine that encodes 6 types of NSCLC TAA ( NY-ESO-1, MAGE-C1, MAGE-C2, 5T4, survivin and MUC-1 ).
Compared with baseline, most patients have enhanced antigen-specific cellular and humoral immunity. One patient who received vaccines, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy experienced partial remission ( PR ), and 46.2% of patients achieved SD.
The mRNA-4157 vaccine is an mRNA vaccine developed by Moderna in the United States. It is a personalized tumor vaccine tailored for each tumor patient.
The current mRNA-4157 cancer vaccine can contain up to 34 mRNA sequences encoding new antigens.
In the phase I clinical trial of mRNA-4157 combined with Keytruda, 11 of the 13 patients receiving monotherapy maintained stable disease.
In the combination therapy group, 6 out of 20 patients received a response, including 1 complete remission and 5 partial remissions. 6 patients had stable disease, and 8 had worsening conditions.
All adverse events related to mRNA-4157 are reversible and minor. No treatment-related adverse events of grade ≥3 were observed, proving the safety and tolerability of the vaccine.
Currently, a number of tumor mRNA vaccines are in the clinical recruitment stage.
06. CRISPR / Cas9
The CRISPR-Cas9 system is a bacterial defense mechanism that uses guide RNA ( gRNA ) to mediate DNA endonuclease Cas9 to introduce site-specific breaks in target DNA.
This DNA editing capability enables CRISPR-Cas9 to be used as an RNA therapeutic agent in genome modification by synthesizing sgRNA for biological and therapeutic applications.
Many studies have shown that CRISPR/Cas9 can be used to treat genetic diseases, such as cystic fibrosis ( CF ), Duchenne muscular dystrophy ( DMD ), hemoglobinopathy, HIV and β-thalassemia.
In one study, CRISPR/Cas9 was able to increase the number of utrophin in myotubes and remove duplicate DMD exons 18-30, thereby producing full-length dystrophin in DMD.
In β-thalassemia, mutations in the human hemoglobin β ( HBB ) gene can be corrected by CRISPR/Cas9.
Through the piggyBac transposon, the CRISPR/Cas9 in the patient-derived IPSC effectively corrects the HBB mutation without affecting the pluripotency of the IPSC, and restores the expression of HBB when differentiated into red blood cells.
In addition, similar applications of CRISPR-Cas9 have also been confirmed in immune diseases such as AIDS.
Although these studies provide the basis for future CRISPR-Cas9 clinical trials, there are still some challenges to be resolved before CRISPR/Cas9 is further applied to clinical trials and subsequent treatments.
Including possible off-target effects of gene editing tools delivered to target cells.
In addition, before turning CRISPR-Cas9 into therapeutic applications, the ethical issues and germline applications of CRISPR-Cas9 also need to be considered.
Summary
In recent years, RNA-based therapy has gradually become a potential intervention strategy for various diseases.
Generally speaking, RNA therapy is divided into different categories according to its mode of action and the molecules used.
Many RNA therapies have been developed for various diseases, and very promising results have been obtained in many preclinical and clinical studies, especially mRNA vaccines have become one of the hottest research fields at present.
At present, RNA-based therapy still has many obstacles, and many aspects including delivery systems still need to be further researched and developed.
However, it is undeniable that the era of RNA therapy in the next decade will finally come.
references:
1.RNA Therapeutics – Researchand Clinical Advancements. Front Mol Biosci. 2021; 8: 710738.
2. mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: principles, delivery and clinical translation. Nat RevDrugDiscov. 2021 Aug 25 : 1–22.
3. Clinical and immunological effects of mRNA vaccines inmalignant diseases. Mol Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;20(1):52.
Research and clinical progress of RNA therapy
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



