Stem cells successfully saved 138 severely ill patients with COVID-19
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Stem cells successfully saved 138 lives after ICU treatment for severely ill patients with COVID-19 disease failed
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Stem cells successfully saved 138 lives after ICU treatment for severely ill patients with COVID-19 disease failed.
The global COVID-19 pneumonia epidemic is still continuing.
Recently, Pfizer’s COVID-19 oral drug has attracted attention. According to reported data, it can reduce the hospitalization rate or mortality of mild or moderate patients by 89%.
However, in the treatment of the COVID-19, the treatment of critically ill patients still has many challenges. Critically ill patients with COVID-19 disease often have multiple underlying diseases such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular, endocrine, etc.
Therefore, comprehensive systemic treatment with multi-system organ function support is required during treatment, which also increases the difficulty of treatment for critically ill patients with COVID-19 disease.
How difficult is the treatment of critically ill COVID-19? According to the World Health Organization (WHO) report, the mortality rate of critically ill patients with COVID-19 disease exceeds 50%.
At present, many teams at home and abroad have introduced mesenchymal stem cell therapy research programs in the treatment of severely ill patients with COVID-19 disease, and have achieved positive results.
Previously, the results of two clinical trials conducted in Turkey once again confirmed the potential of mesenchymal stem cells to treat patients with severe COVID-19 disease.
01 Conventional ICU treatment is ineffective, and mesenchymal stem cells rescue critically ill patients
In June 2021, a clinical trial from Turkey found that among 210 critically ill patients with COVID-19, mesenchymal stem cell therapy successfully saved the lives of 138 critically ill patients with COVID-19 [1].

The study was approved by the Turkish Ministry of Health Committee.
After the hospital and the patients agreed to sign, 210 patients with critically ill COVID-19 disease who had failed ICU treatment were treated with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation.
The average treatment time was 6.4 days. Of the 138 patients who were successfully discharged from the hospital after mesenchymal stem cell therapy, 86 patients did not receive endotracheal intubation during hospitalization, and 52 patients underwent endotracheal intubation, Figure 1. (Note: Patients undergoing tracheal intubation indicate a more serious condition and a higher risk of death)
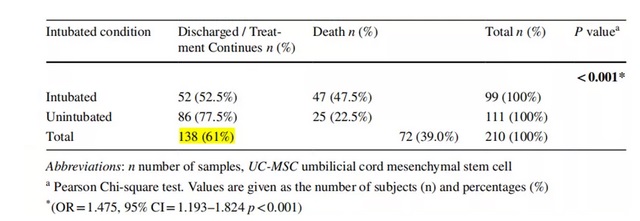
Figure 1 (Picture source reference 1)
In addition, all patients had no adverse reactions such as allergic reactions or secondary infections from the transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells to 2-3 weeks after discharge.
02. Further evidence for mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of critically ill COVID-19s
In May of the same year, another clinical trial in Turkey once again confirmed the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of critically ill Covid-19 from another angle[2]!
The biggest feature of this study is the use of a more scientific and rigorous three-arm randomized controlled trial to get more realistic results, Figure 2.
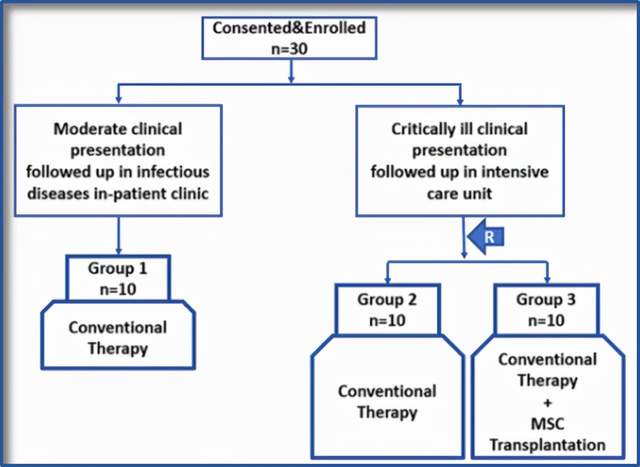
Patients in the mesenchymal stem cell treatment group (group 3) received 1 hour of intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem cells on day 0, day 3, and day 6, respectively; patients in the other 2 groups received conventional treatment (antibiotics, Antiviral, dexamethasone, etc.).
The levels of inflammation markers (Figure 3) and inflammatory cytokines (Figure 4) in the blood of all patients were detected before treatment and one day after each treatment (Day 1, Day 4, Day 7).
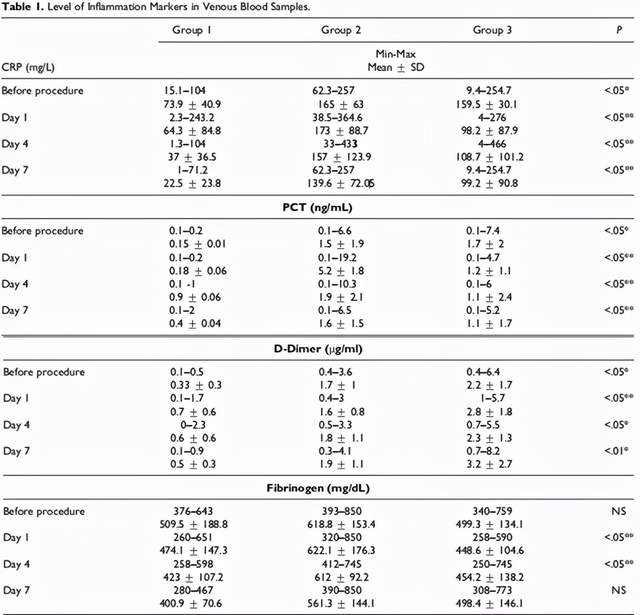
Figure 3 (picture from reference 2)
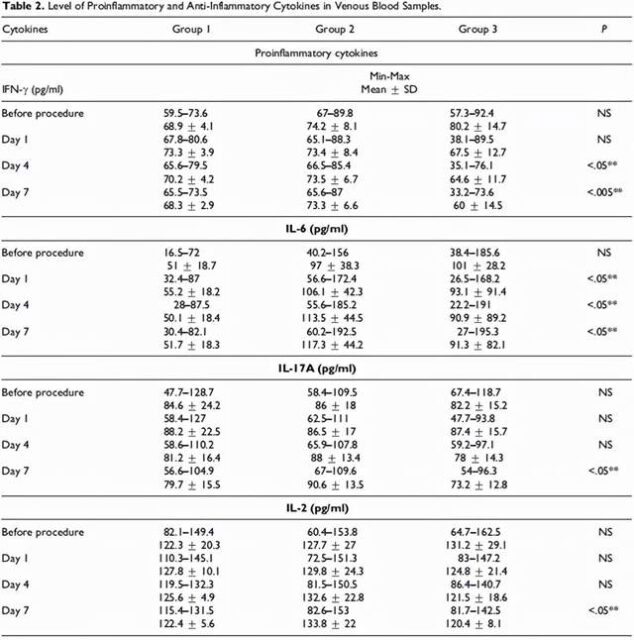
Figure 4 (picture from reference 2)
After treatment, it was found that after treatment with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in critically ill patients with COVID-19 disease, compared with conventional antibiotics and anti-infection treatments, the levels of inflammatory markers and inflammatory cytokines in their bodies were significantly reduced, and they were steadily decreasing, especially in After the third mesenchymal stem cell transplantation treatment.
Further analysis of the study found that the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) levels (immune anti-inflammatory pathways) may be one of the mechanisms for mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19 disease.
In particular, compared with the critically ill COVID-19 group (group 2) undergoing conventional treatment, the levels of MMP-9 and MMP-3 in the mesenchymal stem cell transplantation group (group 3) were significantly lower after treatment, as shown in Figure 5.
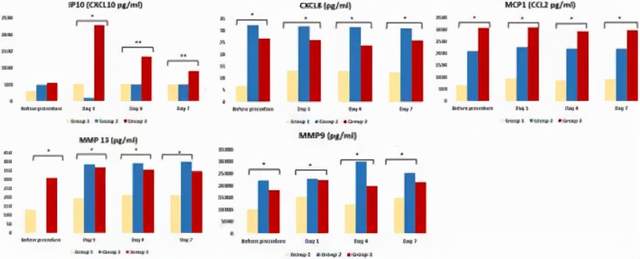
Figure 5 (picture from reference 2)
03. The unstoppable trend of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia
Mesenchymal stem cells have become an unstoppable trend in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia. Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia can go through the following stages:
In the first stage, the transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells can regulate the patient’s immunity and relieve the cytokine storm.
After the body is infected, it causes the rapid and massive production of a large number of cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-12, which can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome.
And important causes of multiple organ failure to reduce the risk of death in patients[3];
In the second stage, mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can increase the oxygenation of most undamaged lung tissues through anti-inflammatory effects, restore oxygen supply to the brain and important organs, and prevent lung fibrosis at the same time [ 4].
Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation has achieved staged success in the treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19s, but it also ushered in new thinking and challenges.
How mesenchymal stem cell treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19s can truly become a standard treatment method needs a deeper level and experience Proof of the final clinical trial results of reasonable design.
References:
[1]Nesrin OE,Kubra CP.Clinical experience on umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell treatment in 210 severe and critical COVID-19 cases in Turkey[J]. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports,2021,17(5):1917-1925.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34319510/
[2]G Adas, Z Cukurova.The Systematic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Critical COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Double Controlled Trial[J].Cell Transplant,2021(30).https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34180719/
[3] Liu J,Li S,Liu J,et al.Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2infected patients.medRxiv,2020.http://lib.cdutcm.edu.cn:7001/rwt/CNKI/https/NNYHGLUDN3WXTLUPMW4A/KXReader/
[4]Basiri, A.Pazhouhnia, Z.& Beheshtizadeh, N. Regenerative medicine in COVID-19 treatment: real opportunities and range of promises[J]. Stem Cell Reviewsand Reports,2021,17(1), 163–175.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32564256/
Stem cells successfully saved 138 lives after ICU treatment for severely ill patients with COVID-19 disease failed
(sourceinternet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



