Neonatal stem cells accelerate the recovery of COVID-19 patients
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Neonatal stem cells accelerate the recovery of COVID-19 patients
Neonatal stem cells accelerate the recovery of COVID-19 patients. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from placenta and umbilical cord have broad application prospects in cell transplantation and drug targeted therapy of multi-system diseases.
Recently, the clinical data of neonatal stem cell treatment of new coronavirus pneumonia has attracted attention at home and abroad. According to published literature [1], researchers at the University of Miami’s Miller School of Medicine used umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to treat new coronavirus pneumonia, reducing the patient’s risk of death and speeding up recovery time.
Dr. Camillo Ricordi, the senior author of the study and director of the Diabetes Research Institute and Cell Transplantation Center of the University of Miami, said[2]: “This study clearly shows that these stem cells reduce the incidence of severe cases of new coronavirus pneumonia. High immunity and high inflammatory response. The survival rate of patients (100% survival rate for patients under 80 years of age) and recovery speed are unprecedented, so far there is no other treatment comparable.”

Since the outbreak, mesenchymal stem cells have been used to treat new coronavirus pneumonia, and studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells can reduce immune-mediated lung damage by inhibiting inflammation and stimulating repair. Unlike extensive anti-inflammatory methods that use drugs, mesenchymal stem cells coordinate with tissues in a more precise way.
Advantages of neonatal stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells can be collected directly from the patient’s bone marrow. However, this process is very painful and may cause complications, and only a limited number of mesenchymal stem cells can be produced. Age and disease may affect their ability to replicate themselves. Therefore, researchers have looked for many other tissues as alternative sources of mesenchymal stem cells, including adipose tissue and perinatal tissue. Neonatal perinatal tissue is an important source of mesenchymal stem cells, and compared with other sources, it has many advantages.
Neonatal mesenchymal stem cells are taken from the placenta and umbilical cord tissue after delivery. The collection process does not cause any damage to the mother and newborn. The source is not restricted by ethics and clinical medicine. It is an ideal stem cell storage and utilization resource.
More importantly, perinatal tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells are abundant in number, easy to collect, strong in expansion, and greater homogeneity of related therapeutic products. These advantages make it undoubtedly better than bone marrow in mass production of therapeutic cells. Stem cells from other sources are more attractive.
Neonatal stem cells and other diseases treatment
In recent years, there have been many clinical research cases of neonatal stem cell treatment of diseases. The diseases involved include stroke, osteoarthritis, diabetes and so on.
The placenta is a very important perinatal tissue. It not only provides nutrients for the growth and development of the fetus, but also serves as a storage for various types of stem cells, providing a stable source for stem cell therapy. In recent years, placenta-derived stem cells have been used in more and more disease treatment research.
In April 2019, Monash Medical Center in Melbourne, Australia, injected a 67-year-old stroke patient with placental amniotic stem cells. The treatment time was within 24 hours of the stroke. After the first stage of treatment, there is an obvious therapeutic effect-the symptoms have changed from upper limb weakness and severe speech disorder before treatment to free control of their hands. And the MRI results showed that the patient’s brain tissue was not further damaged.
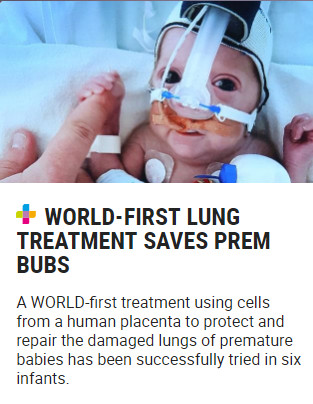
In addition, a research team used placental amniotic epithelial cell transplantation to treat neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The results showed that after treatment, 5 babies were alive at two years old, and there was no occurrence attributable to placental amniotic epithelial cells. Long-term adverse events caused by drugs.
The umbilical cord is also an important organ of neonatal perinatal tissue, which also contains very rich mesenchymal stem cells. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells have the characteristics of wide sources, easy access, high safety, high proliferation and cloning rate, relatively easy in vitro culture, and considerable anti-inflammatory activity. In recent years, they have become a research hotspot in tissue repair and immune regulation. .
According to published literature [3], umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells have good safety in the treatment of osteoarthritis and improve long-term pain. Similarly, domestic scholars conducted a study on 136 patients with active rheumatoid arthritis who did not respond adequately to traditional medications [4]. The results showed that intravenous injection of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can significantly improve clinical symptoms, and the therapeutic effect can be significant. Maintain for 3-6 months.
It can be seen that mesenchymal stem cells derived from placenta and umbilical cord have broad application prospects in cell transplantation and targeted drug therapy of multi-system diseases.
Outlook
Perinatal tissues such as placenta and umbilical cord are very important sources of stem cells, which have attracted more and more attention from scientists. In recent years, with the continuous progress of clinical research on stem cells derived from perinatal tissues such as placenta and umbilical cord, and the increasing understanding of such stem cells, more and more families have begun to cherish this medical resource after delivery. According to the market research report released by Markets and Markets, the world’s second largest market research and consulting company, the placental stem cell market is expected to grow the fastest in the global stem cell storage market. This also reflects that stem cells in perinatal tissues such as placenta have become a new trend and are widely recognized.
Reference:
[1] Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for COVID‐19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: A double‐blind, phase 1/2a, randomized controlled trial
https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/sctm.20-0472
[2] https://www.miamiherald.com/news/coronavirus/article248316345.html
[3] Matas J, Orrego M, Amenabar D, et al. Umbilical Cord-De‑rived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) for Knee Osteoarthri‑tis: Repeated MSC Dosing Is Superior to a Single MSC Dose and to Hyaluronic Acid in a Controlled Randomized Phase I/II Trial[J]. Stem Cell Transl Med, 2019, 8(3): 215-224.
https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/sctm.18-0053
[4] Wang L, Wang L, Cong X, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Safety and Efficacy[J]. Stem Cells and Development, 2013, 22(24):3192- 3202.
http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_PM23941289
(sourcechinanet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



