Stem cell knowledge: the difference between immune cells and stem cells
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Stem cell knowledge: the difference between immune cells and stem cells
Stem cell knowledge: the difference between immune cells and stem cells. We know that our body is a kingdom made up of cells, which is extremely sophisticated and highly ordered at the same time. Any great kingdom needs both capable builders and brave defenders, and our body cell kingdom is no exception.
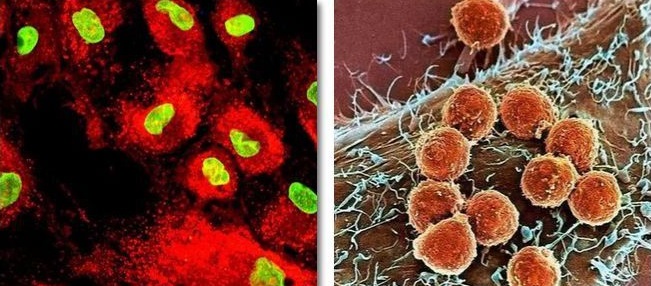
Stem cells (left) and immune cells (right)
What is the difference functions between immune cells and stem cells?
When our human body is still growing, stem cells are the builders of the cell kingdom. They continue to provide new cells through differentiation and increase the number of our body cells. When our bodies no longer grow as adults, stem cells will play the role of the maintainers of the cell kingdom. , Timely replacement and renewal of aging or damaged cells.
Stem cells are the builders
Stem (four tones) cells are the origin cells. Simply put, it is a type of primitive undifferentiated cell with multidirectional differentiation potential and self-replication ability, and it is the primitive cell that forms the tissues and organs of mammals. Stem cells can be divided into embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
Immune cells are the defenders
When foreign enemies invade, such as bacteria and viruses, immune cells will act as the army of the cell kingdom and react quickly to eliminate them. If mutineers appear in the cell kingdom, such as normal cells that mutate into cancer cells, immune cells will act as a security system to identify and eliminate them.
How to classify the two?
Now, let’s take a closer look at stem cells and immune cells, which types are they divided into, and what are the differences in their functions:
(1) According to the classification of differentiation potential, stem cells are divided into totipotent stem cells, pluripotent stem cells and multipotent stem cells.
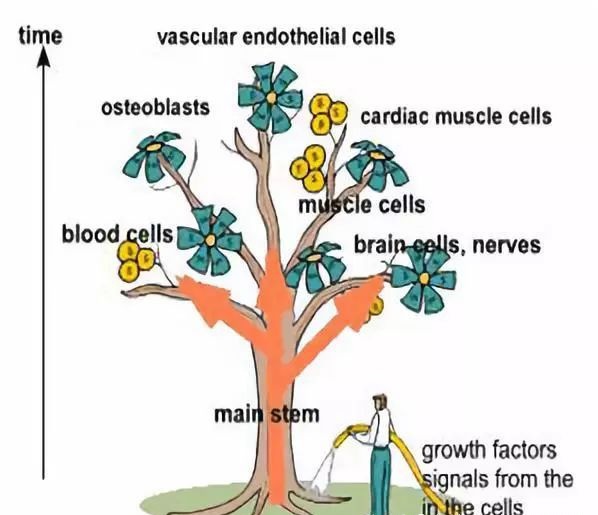
If the human body is likened to a tree, the seeds buried deep in the earth are pluripotent stem cells, just as seeds can grow into a towering tree; the main branches of the tree can be likened to pluripotent stem cells, such as bone marrow pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells , It can differentiate into at least twelve kinds of blood cells; the terminal branches are multipotent stem cells, such as epithelial basal stem cells, muscle myoblasts, etc., just like the terminal branches can grow fruits and leaves.
The mature functional cells of the human body, such as skin cells, cardiomyocytes, kidney cells, etc., are like the leaves and fruits at the ends of large branches. They wither with the change of the seasons. Stem cells need to be continuously differentiated, supplemented and renewed to maintain the operation of life. Next, I will talk about immune cells, mainly to explain the current clinical applications of NK cells (natural killer cells), CIK cells (cytokine-induced killer cells) and CAR-T cells (referring to chimeric antigens) that are particularly popular recently. Recipient T cells).
NK cells are innate immunity and can remove aging and mutated cells in the body at any time, just like police officers, maintaining social order at any time. CIK is to further enhance one’s own immunity and make up for the relative lack of NK cells, just like too many bad people need the armed police to help.
CAR-T is an immune T cell genetically modified by tumor protein. In the process of tumor cells being chased by NK cells and CIK cells, some tumor cells learned to disguise themselves during the war and are no longer recognized by NK and CIK cells. So there is CAR-T, which can target and kill these cunningly disguised tumor cells. Therefore, CAR-T is like an army with a clear mission, capable of completely annihilating the enemy.
How is the extraction method different?
Stem cells can be extracted from a variety of human tissues. Take mesenchymal stem cells, which are currently the most widely used in clinical practice, as an example. They were originally extracted from bone marrow, and later can be extracted from various human tissues such as placenta, umbilical cord, fat, dental pulp, and endometrium.
At present, the main source of immune cells is blood. Adult peripheral blood contains a large number of mature immune cells that circulate in our body constantly to protect our health at all times.
What is the difference in disease treatment?
As mentioned earlier, stem cells are the builders of the cell kingdom. When our body cells are wounded and need to be replaced or repaired, stem cells are required to play a repair role. For example, when the body suffers severe trauma, or when chronic diseases such as diabetes, coronary heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and liver cirrhosis occur, the cells of those organs are essentially damaged. At this time, stem cells can be used to repair damaged tissues and organs. .
Immune cells are the defense forces and mainly play four roles:
(1) Anti-aging can replace the aging cells in the tissue in time and delay the aging process.
(2) Improving chronic diseases In the case of diseases, the stored immune cells can activate the autoimmune system, target and kill diseased cells, and improve chronic diseases.
(3) Sub-health conditioning. When the body’s immunity is weakened or a sub-healthy state occurs, it can effectively regulate and strengthen the immune system to alleviate the sub-health state.
(4) Cancer prevention It can be eliminated at the early stage of cell lesions to prevent cancer cells from expanding.
(sourceinternet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



