The COVID-19 Omicron strain has undergone evolution in domestic mice
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
The COVID-19 Omicron strain has undergone evolution in domestic mice
The COVID-19 Omicron strain has undergone evolution in domestic mice
November 24, 2021, the COVID-19 a new variant strain of the virus – Austrian McCormick Rong (Omicron) was reported in South Africa.
Just two days later, the strain was judged World Health Organization as ” needs attention of mutants ” (the Variant of Use with Concern as, VOC) .
As of December 16, 2021, 89 countries and regions have confirmed cases of infection found in Austrian McCormick Rong strain and the strain rate of infection was significantly faster than the Delta (Delta) strains.
The other requires a high degree of concern mutant (Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta) different, carry large amounts of rare mutations rarely reported when the Austrian McCormick Rong strains emerge .
Researchers did not find its “close relatives” in the database of the new coronavirus variant strain, so the source of the Omicron strain has attracted widespread attention in the scientific community.
There are currently three mainstream hypotheses regarding the source of the Omicron strain: The first hypothesis is that the Omicron strain has been “secretly” spread for a long time in an area where nucleic acid testing and sequencing has not been adequately performed, leading to its discovery. Many mutations have been accumulated at that time.
The second hypothesis is that the Omicron strain may have undergone long-term evolution in a certain immunodeficiency patient (such as a patient who has received long-term chemotherapy or AIDS) , and therefore has a large number of rare mutations.
The third hypothesis is that the “ancestors” of the Omicron strain may have “overflowed” from humans to other animals, and passed back to humans after a period of evolution in the organism, so it carries a large number of rare mutations in the population.
December 24, 2021, Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology money Wenfeng researcher team in the Journal of Genetics and Genomics , published online entitled: Evidence for A Mouse at The Origin of SARS-CoV of-the Variant 2 Omicron research papers .
The study revealed that the transmission route of the Omicron strain is most likely to be transmitted from humans to domestic mice and back to humans after long-term evolution.

The study first carried out an evolutionary analysis of the Omicron strain’s genome and identified 45 mutations in the ancestral sequence of the Omicron strain.
On this basis, using the mutation spectrum (that is, the relative proportions of 12 different base mutation types) to trace the virus host, it was found that the mutation spectrum of the Omicron strain and the new coronavirus evolved in the human body (including immunodeficiency patients) There are significant differences in the resulting mutation spectrum .
Surprisingly, the mutation spectrum Austrian McCormick Rong strains and murine coronavirus (murine hepatitis viruses) mutation spectrum highly similar, suggesting that the Austrian McCormick Rong strain may have evolved in norvegicus long.
If the Omicron strain did evolve for a long time in domestic mice, then the Omicron strain will have mutations in its genome that can adapt to transmission in domestic mice.
Based on this idea, the study detected the mutation of the Omicron strain on the spike protein that can determine the range of host infection, through the new coronavirus sequence isolated from 18 mammals (such as mink and white-tailed deer) .
By comparison, it was found that these mutations had the highest degree of overlap with the mutations of the new coronavirus isolated from house mice.
The study further molecularly docked the receptor binding domain of the spike protein with 32 kinds of mammalian receptor proteins, and found that the mutation carried by the Omicron strain was the most significant in enhancing the affinity of the mouse receptor protein .
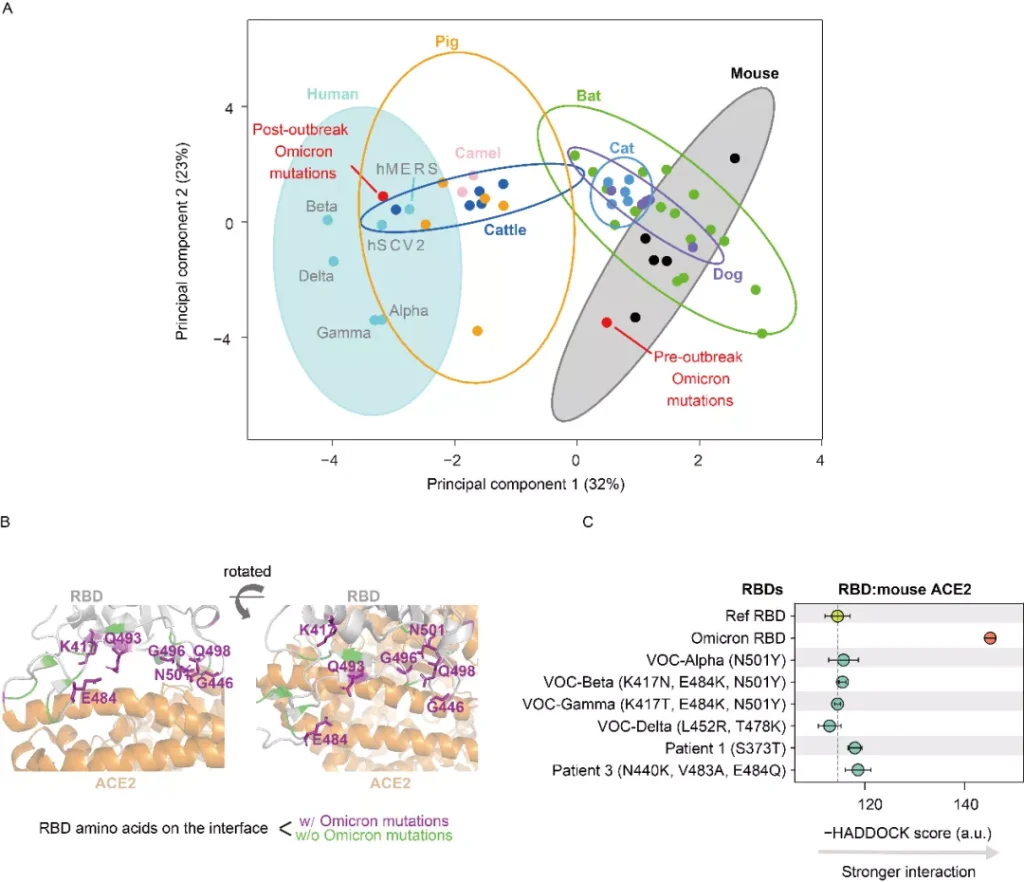
Analysis of the virus genome and protein affinity of Kiron Omi strain ,
A: The mutation spectrum of Kiron Omi strain is similar to that of murine coronavirus, which is significantly different from the evolution of coronavirus in the population (ellipse shows 95% confidence interval) );
B: Mutations on the spike protein of Kiron strain (purple marker) are enriched at the interface between the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein and the cell receptor (ACE2);
C: with the patient Compared with the new coronavirus isolated in, the affinity of the Omicron strain RBD with the ACE2 protein of house mice has increased significantly.
Based on the above results, it is speculated that the ancestor of the Omicron strain was passed from humans to domestic mice roughly in mid-2020, after more than a year of evolution in domestic mice, and returned to humans at the end of 2021 .
The discovery of this transmission route provides inspiration for future COVID-19 epidemic prevention and control strategies.
Graduate students of the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Wei Changshuo , Shan Kejia and Wang Weiguang are the co-first authors of the paper, Zhang Shuya is the co-author, and associate researcher Yun Qing and researcher Qian Wenfeng are the co-corresponding authors.
Related work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Paper link :
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2021.12.003
The COVID-19 Omicron strain has undergone evolution in domestic mice
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



