BioNTech mRNA neoantigen vaccine shows promising prospects in pancreatic cancer patients
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
BioNTech mRNA neoantigen vaccine shows promising prospects in pancreatic cancer patients
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Nature : BioNTech mRNA neoantigen vaccine shows promising prospects in pancreatic cancer patients.
Pancreatic cancer is a highly malignant tumor of the digestive tract that is difficult to diagnose and treat. Among them, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) accounts for more than 95% of all pancreatic cancers.
In recent years, the incidence of pancreatic cancer has increased significantly.
The early diagnosis rate of pancreatic cancer is not high, and it is often discovered at an advanced stage. Due to its low survival rate and poor prognosis, pancreatic cancer is also known as the “king of cancers” .
Surgery is currently the only effective way to treat PDAC, but nearly 90% of patients still relapse within 7-9 months ( median time ) after surgery, and the 5-year overall survival rate is only 8-10%.
Adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery can delay PDAC recurrence, but nearly 80% of patients will still relapse within 14 months, and the 5-year overall survival rate is <30%.
Radiotherapy, biologics, and targeted therapy were ineffective, and PDAC was almost completely insensitive to immune checkpoint inhibitors (response rate <5%) .
This insensitivity is partly due to the low mutation rate of PDAC, which produces few neoantigens (Neoantigens) , resulting in weak antigenicity of PDAC.
However, some recent studies have shown that most PDAC actually contain more neoantigens than previously predicted.
In addition, studies of long-term survivors of PDAC suggest that neoantigens may stimulate T cells in PDAC.
Therefore, since most PDAC contain neoantigens that may stimulate T cells, strategies to deliver neoantigens may induce neoantigen-specific T cells, thereby improving patient outcomes.
On May 10, 2023, the research team of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, BioNTech, and Genentech (a subsidiary of Roche) published a paper entitled: Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in the top international academic journal Nature Research paper in pancreatic cancer .
The study developed a personalized mRNA vaccine strategy, autogene cevumeran (BNT122) , which expresses 20 neoantigens in PDAC patients through mRNA and is administered intravenously using LNP.
In PADC patients after surgical resection, the mRNA vaccine has the potential to delay recurrence in PDAC patients when combined with chemotherapy and immune checkpoint therapy.

Therapeutic mRNA vaccine technology has facilitated the development of personalized neoantigen vaccines.
Furthermore, mRNA technology can be rapidly developed into personalized vaccines expressing multiple neoantigens, activating antigen-presenting cells (APCs) , and can be delivered using lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) , which have been widely clinically validated.
Long-term survivors of PDAC have been observed to mount spontaneous T-cell responses to tumor-specific neoantigens, but these responses vary between patients.
The research team hopes to develop a personalized mRNA that can provide clinical benefits to PDAC patients after surgical resection by inducing neoantigen-specific T cells, eliminating tumor metastasis and delaying recurrence.
In this phase 1 clinical trial, the research team combined chemotherapy (mFOLFIRINOX regimen) and immune checkpoint therapy (anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody) , injected a personalized mRNA vaccine into 16 PDAC patients after surgical resection—— autogene cevumeran , which expresses up to 20 neoantigens, is delivered using lipid nanoparticles (LNP) and administered intravenously.
The research team observed significant T cell responses in 50% of patients, suggesting that the personalized mRNA vaccine could elicit an enhanced immune response.
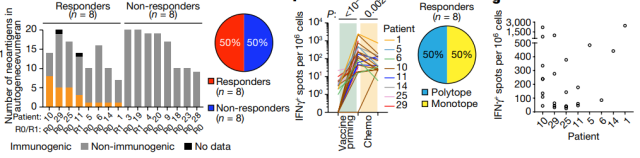
After 18 months of follow-up, enhanced immune responses in patients were associated with delayed time to relapse, whereas patients who did not show a response to the vaccine developed disease a median of 13.4 months after initial assessment.
These results demonstrate the potential of personalized mRNA vaccines in the treatment of PDAC and provide evidence of their general effectiveness as a therapeutic tool.
Despite the low mutation rate of PDAC, mRNA vaccines can still induce T cell activity against neoantigens produced by PDAC. Despite the limited sample size, these early results point to the need for larger clinical studies of this PDAC vaccine, the research team said.
Collectively, the study reports preliminary clinical trial evidence that the personalized mRNA neoantigen vaccine Autogene cevumeran (BNT122) combines with atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody) and mFOLFIRINOX (standard adjuvant chemotherapy regimen after surgical resection of PDAC). ) in combination, induced massive T cell activity in surgically resected PDAC patients associated with delayed recurrence.
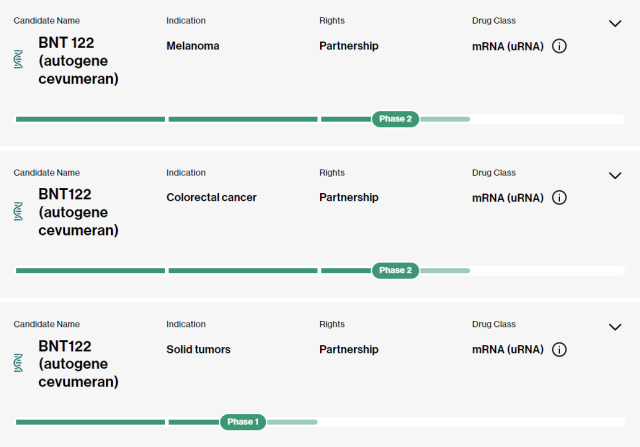
The personalized mRNA neoantigen vaccine Autogene cevumeran (BNT122) , jointly developed by BioNTech and Genentech, a subsidiary of Roche, is currently in phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of melanoma and colorectal cancer .
The study in the thesis) is about to enter phase 2 clinical trials.
Paper link :
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06063-y
BioNTech mRNA neoantigen vaccine shows promising prospects in pancreatic cancer patients
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



