Tumor neoantigen vaccine + Chemotherapy + PD-1 to treat lung cancer
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Tumor neoantigen vaccine + Chemotherapy + PD-1 to treat lung cancer
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
New BioNTech paper: Tumor neoantigen vaccine + Chemotherapy + PD-1 to treat lung cancer.
The incidence of cancer is also increasing with the increase in average human lifespan, changes in lifestyle and the increase in pollutants.
Among many types of cancer, lung cancer is undoubtedly one of the most dreaded cancers, and its morbidity and mortality are at the forefront of malignant tumors.
According to the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) , there will be 9.96 million cancer deaths worldwide in 2020, including 1.8 million lung cancer deaths, far exceeding other cancer types and ranking first in cancer deaths.
In some countries, both the incidence and death of lung cancer rank first among malignant tumors.
Among lung cancers, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. Therefore, research on the treatment strategies of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is very important.
On August 25, 2022, BioNTech , in collaboration with researchers from Harvard Medical School, Washington University in St. Louis and other institutions, published in the journal Cancer Cell : Personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01 with chemotherapy and anti-PD-1 as Research paper on first-line treatment for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer .
The study reports a phase 1b clinical trial combining the individualized neoantigen cancer vaccine NEO -PV-01 with chemotherapy and the anti-PD-1 drug pembrolizumab in metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
First-line therapy, demonstrating that this regimen is well tolerated and induces neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses with effector phenotypes.

Tumor cells generate neoantigens (Neoantigen) through gene mutation , and the neoantigens are presented on the cell surface through MHC molecules, which are subsequently recognized by T cells.
Neoantigens are highly immunogenic because they are only present in tumors, not normal tissues.
However, most neoantigens are unique and vary between patients, so neoantigen vaccines need to be produced specifically for each patient as individualized vaccines, which also limits their clinical application.
However, with the rapid development of sequencing and bioinformatics technology, scientists can rapidly identify candidate neoantigens in individual patients through specific algorithms, and design personalized neoantigen vaccines accordingly.
Not only that, studies have shown that such vaccines can synergize with chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors (such as pembrolizumab) to enhance the killing effect of tumor cells.
In this latest study, the research team reports data from a Phase 1b clinical trial combining the personalized vaccine NEO-PV-01 with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab in first-line treatment of metastatic non-squamous NSCLC treat.
NEO-PV-01 is a personalized neoantigen vaccine containing up to 20 unique neoantigens per patient in the form of synthetic long peptides using the TLR3 agonist poly-ICLC as an immune adjuvant.
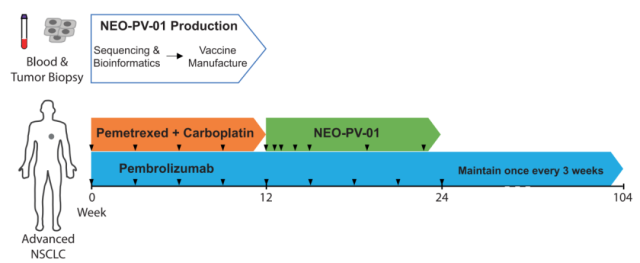
Figure 1: Clinical study design of personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01
The trial is designed to allow patients to receive standard-of-care treatment, which is four cycles of chemotherapy in combination with pembrolizumab, during vaccine production.
This single-arm study enrolled 38 patients who had not received prior systemic therapy and immunotherapy for metastatic disease, enrollment was not limited by tumor PD-L1 status, and who had received at least one dose of pembrolizumab and were treated with Defined as the intention-to-treat group (ITT) .
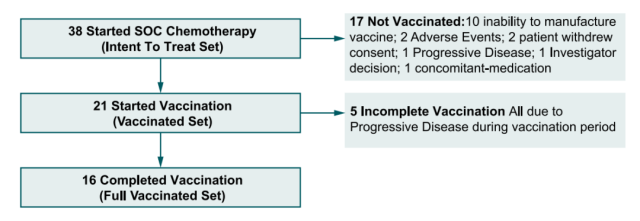 Figure 2: Flow chart of Phase 1b clinical trial of personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01
Figure 2: Flow chart of Phase 1b clinical trial of personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01
In the ITT arm, 16 patients completed vaccination and only minor related adverse events were reported, indicating that the combination of NEO-PV-01 with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab was safe and well tolerated.
As expected, patient responses to neo-epitopes were generally stronger compared with wild-type peptides, with CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses observed in 39% and 31% of vaccine peptides, respectively.
After 40 weeks, long-term persistence of the vaccine-induced immune response was observed for 85% of the 34 epitopes tested.
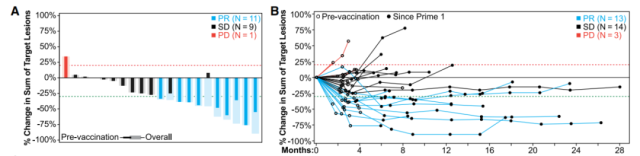 Figure 3: Response rate and durability of NEO-PV-01 combined with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab
Figure 3: Response rate and durability of NEO-PV-01 combined with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab
The research team performed detailed molecular and immune analyses of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and peripheral blood of these patients, and they found that neoantigen vaccination in combination with chemotherapy and anti-PD-1 had a strong synergistic effect.
Surprisingly, these responses were predominantly CD4+ responses (93%) , while 7% involved both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and none involved CD8+ T cells alone.
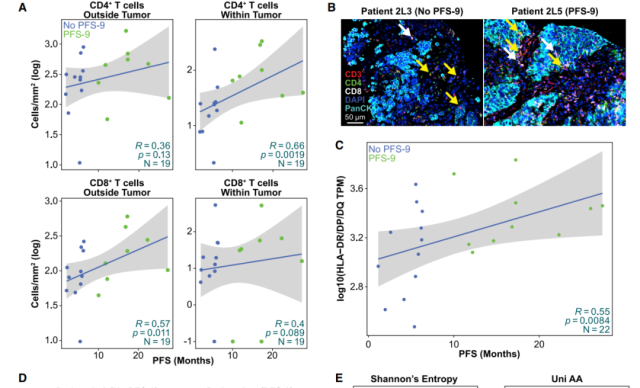 Figure 4: Correlations with clinical response observed in the tumor microenvironment (TME), including T cell infiltration, MHC class II expression, and TCR diversity
Figure 4: Correlations with clinical response observed in the tumor microenvironment (TME), including T cell infiltration, MHC class II expression, and TCR diversity
More interestingly, the research team observed epitope spread responses to common driver mutations KRAS G12C and G12V in multiple patients, with three-quarters of epitope spread to KRAS-mutated patients achieved at least 9 months after treatment initiation. progression-free survival (PFS) . Diffuse epitope responses in a subset of patients (42%) were potentially cytotoxic (CD107a+IFNγ+) , all of which were CD4 responses.
Furthermore, single-cell sequencing of neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells suggested an effector cytotoxic phenotype consistent with a potential role of vaccine-induced CD4+ T cells in mediating tumor cell killing.
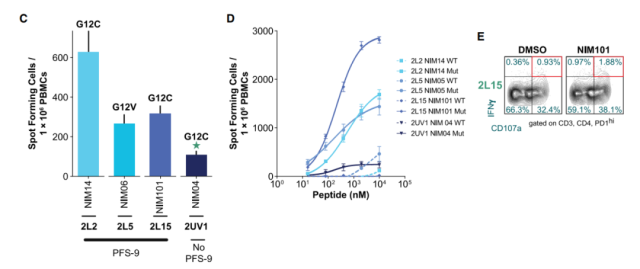 Figure 5: NEO-PV-01 in combination with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab induces epitope spreading responses in the majority of patients analyzed
Figure 5: NEO-PV-01 in combination with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab induces epitope spreading responses in the majority of patients analyzed
Although this study demonstrates the safety and feasibility of NEO-PV-01 in combination with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer, several challenges remain at this stage:
1) Nearly half of the patients were unable to produce vaccines due to low numbers of tumor cells in biopsies or insufficient predicted high-quality neoantigens.
2) Some neoantigens are too hydrophobic to be synthesized as long peptides.
3) Difficulty predicting the processing of candidate epitopes, which may not be processed and presented on the cell surface.
4) The T cell responses induced by neoantigen vaccines tended to be CD4 responses, but were unable to induce strong CD8+ T cell responses.
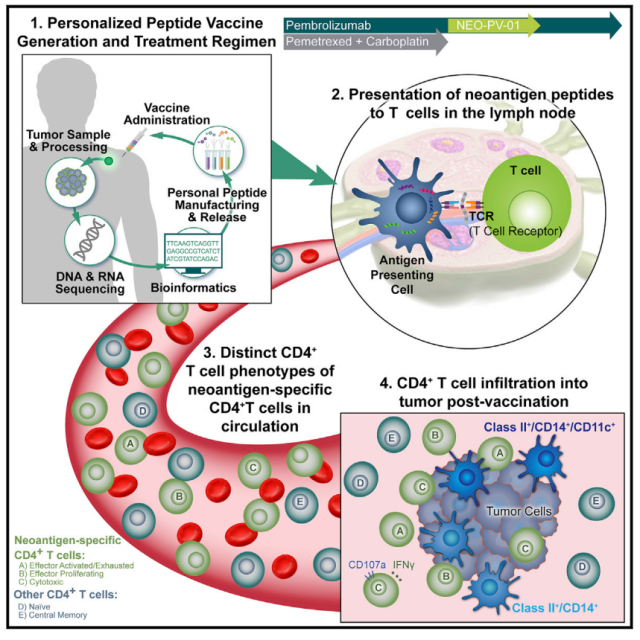 Research Pattern Diagram
Research Pattern Diagram
In conclusion, this latest study demonstrates the safety and immunogenicity of the individualized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01 in combination with chemotherapy and pembrolizumab in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. The anti-tumor efficacy still needs to be further verified.
Paper link :
1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.003
2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.002
Tumor neoantigen vaccine + Chemotherapy + PD-1 to treat lung cancer
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



