Factors Influencing the Efficacy of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Factors Influencing the Efficacy of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Factors Influencing the Efficacy of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors
Children and young patients with recurrent, metastatic, or unresectable osteosarcoma or neuroblastoma face a grim prognosis, with little progress in the treatment of osteosarcoma over the past few decades. Immunotherapy, however, offers a hopeful avenue in these cases by altering the treatment paradigm through targeting tumor-specific antigens.
In fact, the use of monoclonal antibodies targeting GD2 in neuroblastoma treatment has shown progress in the overall survival of high-risk patients and has become a part of first-line therapy. Building on this, clinical trials have explored GD2-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for neuroblastoma, demonstrating safety but unfortunately limited efficacy.
Understanding the basis of this limited effectiveness is crucial for advancing solid tumor CAR-T therapy. Experience with CAR-T therapy in solid tumors and hematological malignancies suggests that the expansion of CAR-T cells is a pivotal first step in achieving therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, progress in solid tumor CAR-T therapy requires an understanding of factors influencing CAR-T expansion.
A recent clinical trial of GD2.CD28.OX40.z CAR-T therapy in neuroblastoma and osteosarcoma patients, reported by researchers from the National Institutes of Health and Stanford University School of Medicine, sheds light on the immune determinants affecting CAR-T cell expansion in patients.
Published on December 21, 2023, in the Cancer Cell journal, the study titled “Immune determinants of CAR-T cell expansion in solid tumor patients receiving GD2 CAR-T cell therapy” analyzes the immune determinants of CAR-T cell expansion in patients with solid tumors (osteosarcoma or neuroblastoma) undergoing GD2-targeted CAR-T cell therapy. The findings provide new insights to enhance the effectiveness of solid tumor CAR-T cell therapy.

The evaluation of CAR-T biomarkers in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and chronic lymphoblastic leukemia establishes a connection between the pre-treatment separation of early memory T cell phenotypes and the success of CAR-T. Conversely, a lower count of early memory T cell groups correlates with a decline in T cell expansion potential. Additionally, exhausted T cells are associated with poor clinical responses. However, comprehensive immune cell analysis is still lacking in the clinical solid tumor field.
So far, central memory cells of GD2.CD3z CAR-T cells in patients correlate with more enduring remission, and pre-clinical models of GD2 CAR-T identify Tonic signals and exhaustion as limitations to CAR-T activity. As CAR-T therapy continues to gain momentum in solid tumor treatment, it is crucial to validate and expand these potential biomarkers for solid tumor CAR-T activity.
Apart from identifying T cell features, the focus has shifted to myeloid cells as their contribution to cancer progression and immune therapy effectiveness becomes more apparent. Patients receiving GD2.CD28.OX40.z CAR-T cell therapy show an expansion of myeloid cells after CAR-T administration. Additionally, in diffuse midline glioma patients treated with GD2.4-1BB.z CAR-T, inhibited myeloid cells may have limited CAR-T activity. Recognizing the role of myeloid cells underscores the importance of in-depth research to unleash the full potential of immune therapy in solid tumor patients.
While CAR-T cell therapy has shown significant efficacy in hematological cancers, its response in solid tumors is limited. In this study, the research team explored the feasibility and safety of providing third-generation GD2.CD28.OX40.z CAR-T cell therapy (containing CD28 and OX40 co-stimulatory molecules) to osteosarcoma and neuroblastoma patients with GD2 positivity.
Due to the necessity for sufficient CAR-T cell expansion for efficacy, patients were categorized into different dose levels of either favorable or unfavorable expansion.
The team evaluated patient samples through multidimensional proteomics, transcriptomics, and epigenetics analysis.
T cell assessment revealed that pre-treated separated initial T cells were associated with good expansion, while depleted T cells in the CAR-T product were linked to poorer expansion.
Myeloid cell assessment found that pre-treated separated CXCR3+ monocytes were associated with good expansion.
Longitudinal analysis of post-treatment samples revealed an increase in CXCR3– classical monocytes across all groups as CAR-T cell numbers decreased.
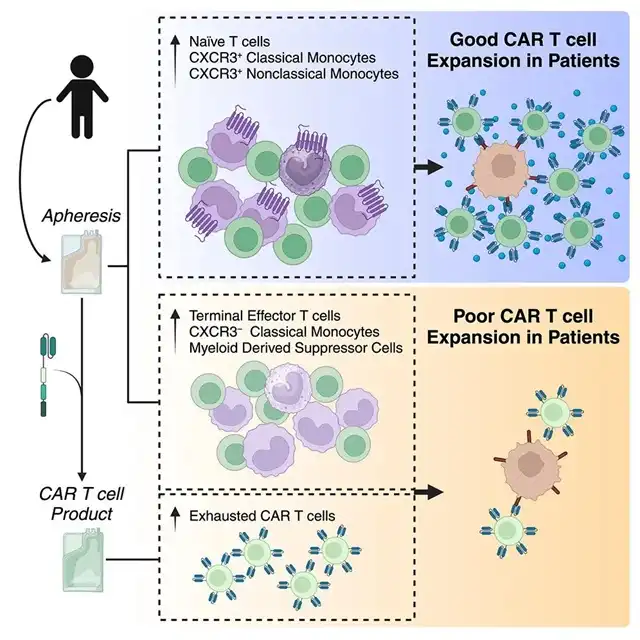
Overall, these experimental data reveal factors influencing CAR-T biology and expansion, contributing to the advancement of CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumor patients.
Factors Influencing the Efficacy of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



