US Faces Surge in COVID-19 Cases as Dominant Strain Shifts
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
US Faces Surge in COVID-19 Cases as Dominant Strain Shifts
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
US Faces Surge in COVID-19 Cases as Dominant Strain Shifts
Significant Shift in Mainstream Strain of COVID-19 in the United States Sparks Concerns.
As the global situation relaxes, the predominant strain of COVID-19 in the United States undergoes a complete upheaval, with a massive predicted increase in infections and 34,000 weekly hospitalizations due to the new strain.
1. BA.2.86 Subvariant JN.1 Emerges as the Dominant Strain
On January 5, 2024, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) updated the data on the mainstream strains of the COVID-19 virus detected in the country. According to the data, from December 24 to January 6, the JN.1 strain accounted for 61.6% of the detected cases, making it the most prevalent strain during that period.
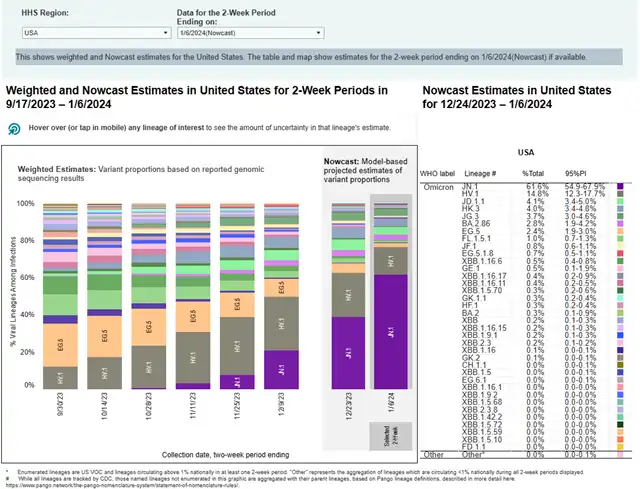
JN.1, a descendant of the concerning BA.2.86 COVID-19 variant, exhibited a significant increase in prevalence, rising from 3.5% eight weeks ago to the current dominance of 61.6%. This shift holds significant implications for the virus’s evolution, challenging previous assumptions about the nature of COVID-19.
This change has prompted a reevaluation of the virus’s characteristics, leading to the initiation of clinical trials for the continued use of paxlovid antiviral treatment for long-term COVID-19 cases.
2. Escalating COVID-19 Infections in the United States
Indicators reflecting the changing pandemic situation, such as the concentration of the virus in wastewater and the positivity rate of COVID-19 tests, demonstrate a worsening scenario in the United States.
2.1 Increased Concentration of COVID-19 in Wastewater
Recent data from the CDC’s wastewater monitoring, updated to December 30, 2023, indicates a continuous rise in the concentration of COVID-19 in U.S. wastewater, reaching 12.85, signifying high viral activity. This level surpasses the 2022 levels, which stood at 10.11.
Experts, including Jay Weiland, suggest that this surge marks the second-largest wave of infections since the onset of the pandemic, with an estimated 1.4 million new infections daily during the JN.1 peak.
2.2 Relatively Stable Positivity Rate in COVID-19 Testing
Recent data from the CDC, up to December 30, shows little variation in the COVID-19 detection rate over the past two weeks, with the latest week’s positivity rate at 12.4%.
2.3 Increase in COVID-19 Proportion of Emergency Room Visits
A crucial indicator of the pandemic’s severity, recent CDC data up to December 16 reveals a 12.8% increase in the proportion of emergency room visits related to COVID-19 over the past two weeks.
3. Marked Increase in COVID-19 Hospitalizations and Deaths
Key indicators of the pandemic’s severity, hospitalizations due to COVID-19 in the past week increased by 20.4%, reaching 34,798 cases, while deaths rose by 12.5%. Despite these spikes, current hospitalization numbers remain below the levels recorded on December 31, 2022.
4. Low COVID-19 Vaccination Rates in the United States
As of December 30, 2023, the vaccination rate for adults against the new COVID-19 variant (XBB.1.5 antigen) in the United States stands at 19.4%, with a higher rate of 38.0% for the elderly. In contrast, the vaccination rates for the flu in adults and the elderly are 44.9% and 69.7%, respectively.
Interestingly, despite COVID-19 deaths accounting for 3.2% of all deaths in the past week, six times higher than the flu death rate of 0.5%, the vaccination rate for COVID-19 is only 43% compared to the flu vaccination rate.
In conclusion, while wastewater analysis indicates a high prevalence of the virus, clinical data reveals a disconnect between the surge in infections and corresponding hospitalizations. Researchers emphasize the importance of understanding the interplay between new strains like JN.1 and existing immunity, while also cautioning against complacency given the unpredictable nature of the virus.
US Faces Surge in COVID-19 Cases as Dominant Strain Shifts
References:
【1】 https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
【2】 https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
【3】 https://erictopol.substack.com/p/sotp-state-of-the-pandemic
【4】 https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#maps_positivity-week
【5】 https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/data-research/dashboard/vaccination-trends-adults.html
【6】 https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/data-research/dashboard/illness-severity.html
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



