First TIL Therapy for Malignant Melanoma Approved
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
First TIL Therapy for Malignant Melanoma Approved
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
First TIL Therapy for Malignant Melanoma Approved
Recently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated the approval of Amtagvi (lifileucel), a tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy developed by Iovance Biotherapeutics, for the treatment of advanced melanoma.
This is the world’s first approved TIL therapy and also the first approved T-cell therapy for solid tumors, marking a milestone in the field!

Figure 1. FDA approves lifileucel for marketing
TIL Therapy: A Beacon of Hope for Melanoma Patients
Melanoma is a highly malignant tumor derived from melanocytes, commonly known as “malignant melanoma,” which mostly occurs on the skin but can also be found on mucous membranes and internal organs. In China, it is more common on the skin of the extremities (soles, toes, fingertips, and under the nails).
In recent years, the incidence and mortality rates of malignant melanoma have been increasing annually. Compared with other solid tumors, it leads to death at a younger age. It is noteworthy that the prognosis of advanced malignant melanoma is poor, mainly due to its high malignancy and propensity for metastasis. Any stimulation can promote tumor spread, leading to lymphatic and hematogenous metastasis in the late stage.
TILs exist in the interstitial tissue of tumor tissue and consist of heterogeneous cell populations including CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, B cells, NK cells, and γδ T cells, among which the cytotoxic CD8+ T cells are mainly responsible for directly killing tumor cells. TIL therapy involves obtaining tumor tissue from patients, extracting TILs, and then stimulating their expansion in vitro using the cytokine IL-2. This in vitro stimulation not only increases the number of TILs but also activates their anti-tumor capabilities. Subsequently, these TILs are infused back into the patient’s body to more effectively kill tumor cells.
Lifileucel belongs to an autologous TIL therapy, which involves collecting infiltrating lymphocytes from the patient’s own tumor sample, expanding and culturing them in vitro, and then reinfusing them into the patient’s body to utilize the patient’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
The FDA approval of lifileucel this time is applicable to the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who have previously received programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) antibody therapy, with or without BRAF inhibitor therapy in patients with BRAF V600-positive mutations. This marks the first and only time that personalized T-cell therapy has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of solid tumors.
C-144-01 Study Results: Nearly 80% of Melanoma Patients Experience Tumor Remission or Stability!
C-144-01 is a global, multicenter Phase II clinical trial. As of July 15, 2022, a total of 153 advanced melanoma patients received lifileucel treatment in this study, which was divided into 4 cohorts: Cohort 1 patients received non-cryopreserved TIL products; Cohorts 2 and 4 patients received cryopreserved TIL treatment; Cohort 3 consisted of patients who received repeated TIL treatment. The median follow-up time was 36.5 months (over 3 years).

Figure 2. C-144-01 test design
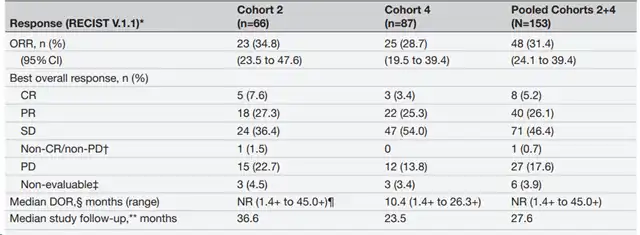
The results showed that the efficacy of lifileucel was relatively long-lasting. As assessed by the independent imaging review committee (IRC), the objective response rate (ORR) was 34.8% in Cohort 2, 28.7% in Cohort 4, and the total ORR in Cohorts 2+4 was 31.4%, including 8 patients achieving complete remission (CR) and 40 patients achieving partial remission (PR).
Table 1.C-144-01 research results
Conclusion:
Since its first clinical attempt in 1988, the development of TIL therapy has spanned decades.
The approval of lifileucel this time has brought hope to patients with advanced melanoma who have deteriorated after standard treatment, marking a significant advancement in the field of immunotherapy using one’s own immune cells to combat cancer.
More and more doctors will have the ability to provide “personalized” and “tailored” treatment plans to suitable individuals.
This one-time cell therapy represents a promising innovation in the field of melanoma treatment, and lifileucel will become a new option for the treatment of advanced melanoma.
First TIL Therapy for Malignant Melanoma Approved
References:
[1]. Iovance’s Amtagvi (lifileucel) receives US FDA accelerated approval for advanced melanoma. News release. Iovance. February 16, 2024. Accessed February 16, 2024. https://ir.iovance.com/news-releases/news-release-details/iovances-amtagvitm-lifileucel-receives-us-fda-accelerated
[2]. Chesney J, Lewis KD, Kluger H, Hamid O, et al. Efficacy and safety of lifileucel, a one-time autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) cell therapy, in patients with advanced melanoma after progression on immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies: pooled analysis of consecutive cohorts of the C-144-01 study. J Immunother Cancer. 2022;10(12):e005755.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



